U1411 Jeep Code: Quick Fixes For Fuel Volume Signal Issues
U1411 Jeep Code: Quick Fixes For Fuel Volume Signal Issues
Welcome to our expert guide on the U1411 Jeep code. If you’ve encountered this code during a diagnostic scan, don’t fret!
As a seasoned mechanic with years of experience working on Jeeps, I’m here to provide valuable insights and help you confidently resolve the issue.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the meaning, severity, symptoms, causes, and diagnosis of the U1411 code. I’ll share my expertise and insider knowledge to empower you to get your Jeep back on the road in no time.
So let’s unlock the secrets behind the U1411 code. Your Jeep’s optimal performance awaits!
U1411 Jeep: A Quick Overview
Below is a summary of the U1411 Jeep Code. Check it out!
- Definition: Implausible Fuel Volume Signal Received
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Advanced
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $100 – $400
Understanding The U1411 Code In Jeeps
The U1411 code in Jeeps is an OBD-II diagnostic trouble code that indicates an “Implausible Fuel Volume Signal Received.” When this code appears during a scan, it means that the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) has detected an inconsistent or unreliable fuel volume signal.
Several systems and components work together in your Jeep to ensure proper fuel volume measurement and delivery. The main players involved are:
- PCM
- Front Control Module (FCM)
- Fuel Pump Control Module (FPCM)
- Fuel Level Sensor
- Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor
- The Controller Area Network (CAN) bus

(Image credit: Jeep Garage – Jeep Forum)
When the FCM in your Jeep fails to receive a fuel volume signal from the Cluster Module over the CAN B bus, it sends a fuel volume signal to the PCM over the CAN C bus. However, if the PCM determines that the signal sent by the FCM over CAN C is implausible or inconsistent, it will result in the U1411 code being triggered.
It’s worth noting that the U1411 code is most commonly found in these Jeep models: Jeep Grand Cherokee (2005, 2006), Jeep Liberty (2006), and Jeep Commander. Additionally, it is commonly associated with other codes such as P0157 (Oxygen Sensor Circuit Low Voltage Bank 2 Sensor 2), U110C (Lost Fuel Volume Message), and U110E (Lost Ambient Temperature Message).
Read more: Dodge, Chrysler, and Jeep OBD1 Codes and OBD2 Codes [Full PDF Free Download]
Assessing The Severity: Is It Safe To Drive With The U1411 Jeep Code?
The severity level of the U1411 code in your Jeep can be considered moderate. While this code typically indicates an issue with the fuel volume signal, it is not a critical or immediate danger to your safety.
It is generally safe to drive with this code. However, it is important not to ignore the U1411 code and address it promptly. Ignoring the code may lead to potential fuel delivery problems, affecting your Jeep’s performance and fuel efficiency. It is advisable to have the issue diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible to prevent further complications.
U1411 Jeep Symptoms: How The Code Manifests In Your Jeep
The U1411 code in your Jeep may manifest itself through various symptoms, indicating an issue with the fuel volume signal. Keep an eye out for the following signs:
- Illumination of the Check Engine Light (MIL)
- Difficulty starting the engine
- No crank condition
- Poor fuel economy
- Stalling or hesitation during acceleration
- Loss of power
- Inaccurate fuel gauge readings
- The instrument cluster remains inactive after remote start until the key is inserted and turned on
Read more: Jeep Dashboard Symbols and Meaning (FULL list, Free Download)
Exploring The Causes Of the U1411 Code
To effectively diagnose and resolve the U1411 code in your Jeep, it is important to understand its potential causes. The following are common culprits associated with this code:
- Ignition switch issues
- Remote starter problems
- Open or shorted CAN C Bus circuit
- Failed instrument cluster module
- Faulty FCM
- Defective PCM
- CAN C module problems
Diagnosis And Repair: Resolving The U1411 Code Like A Pro
In this section, we’ll provide you with the tools, parts, step-by-step guide, and estimated costs to resolve the U1411 code in your Jeep. Let’s begin.
Essential Tools And Parts
To diagnose and repair the U1411 code, you may need the following tools and parts:
- OBD-II scanner
- Di-electric cleaner
- Replacement ignition switch (if needed)
- Replacement parts for wiring, connectors, circuits, PCM, Instrument Cluster, and FCM (as required)
Step-by-step Procedure
The procedure is divided into two parts, Basic and Advanced, to ensure a comprehensive and systematic approach to troubleshooting and resolving issues.
Basic Steps
Trying out the following steps in many situations can often resolve the issue.
You can give them a shot in the comfort of your own home before deciding whether to take your car to a repair shop or dealer.
These steps are accessible to those with beginner to intermediate skill and knowledge levels:
Step 1: First, check the ignition switch for malfunction or damage. Replace it if necessary.
Step 2: If your Jeep has a remote starter, ensure it is installed and functioning properly. Reprogram or replace it if needed.
Advanced Steps
If you have completed the basic steps and the U1411 code persists, doing more advanced troubleshooting that involves working with complex wiring and specific components may be necessary.
Please note that these steps require advanced automotive knowledge and skill. It is recommended to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic or automotive professional with the expertise to perform these tasks accurately and safely.
Step 1: Inspect the wiring and connections related to the CAN bus system, including the CAN C Bus circuit. Repair or replace any damaged or faulty wiring, connectors, or circuits.
Step 2: Perform a thorough check on the PCM using the following steps:
- Disconnect all PCM connectors carefully.
- Use a di-electric cleaner to spray and clean all PCM connections.
- Allow the cleaner to sit and dry.
- Clean the exposed large cable behind the fuse box under the hood on the driver’s side. Let it sit overnight alongside the disconnected PCM cables.
- Reconnect the cables and check if the U1411 code is reset. If not, reprogram or replace the PCM module.
Step 3: Inspect the instrument cluster module for damage or malfunction. Ensure it is properly connected and all wiring is in good condition. Replace or repair as needed.
Step 4: Perform the same inspection with the FCM. Replace or repair if necessary.
Step 5: Clear the U1411 code using an OBD-II scanner and test drive the vehicle.
How Much Does It Cost To Fix The U1411 Jeep Code?
The cost of repairing the U1411 code in a Jeep can vary depending on the specific cause and the parts that need replacement. Below is a table showing estimated costs for some common repair tasks related to the U1411 code based on the troubleshooting steps mentioned earlier.
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Wiring and connector inspection/repair | $100 – $500 |
| Ignition switch replacement | $150 – $300 |
| Remote starter repair/reprogram | $100 – $300 |
| Powertrain Control Module (PCM) inspection/repair/replace | $500 – $1,500 |
| Instrument cluster module inspection/repair | $300 – $800 |
| Front Control Module (FCM) inspection/repair | $300 – $800 |
Remember that these estimated costs are subject to variation depending on factors such as labor rates and the Jeep model. Consulting with a qualified mechanic will provide you with a more accurate estimate tailored to your specific situation.
U1411 Jeep Infographic
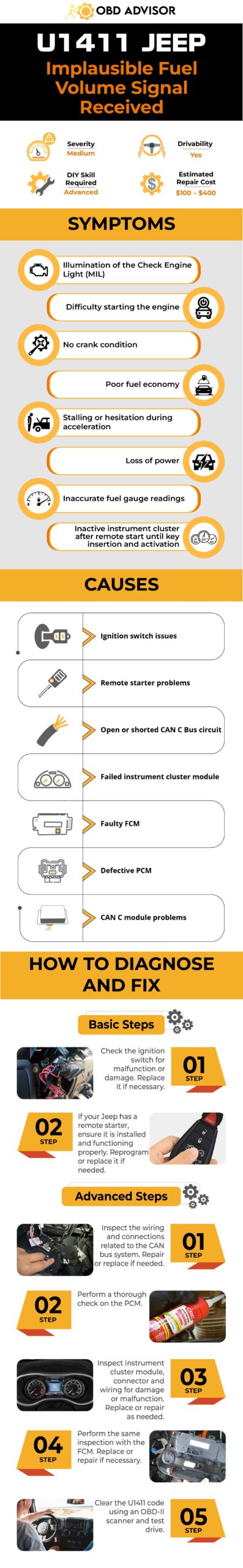
Final Thoughts
Congratulations! You now have a solid understanding of the U1411 Jeep code, from its meaning to symptoms, causes, and possible repair procedures. Armed with this knowledge, you’re better equipped to tackle this issue should it arise in your vehicle.
Remember, if you’re unsure about performing the diagnosis and repair yourself, it’s always wise to seek the expertise of a professional mechanic. They have the experience and specialized tools to accurately diagnose the problem and ensure a proper fix.
We hope this guide has been helpful to you. If you found it informative, don’t hesitate to share it with fellow Jeep owners who may benefit from this knowledge. Feel free to leave any questions or comments below. Happy driving!
Reference Sources
- Zinref.ru, Jeep Grand Cherokee WK. Manual – part 1130.
- RepairPal, DTC Code U1411.
- JustAnswer, Question about U1411 Code in 2006 Jeep Commander Code.
P1345 Chevy: Crankshaft position- camshaft position correlation
P1345 Chevy: Crankshaft position- camshaft position correlation
Vehicle owners who are not mechanics have a major problem in common – the difficulty of getting rid of certain DTCs. The P1345 code is definitely one of these Diagnostic Trouble Codes.
Worry not. This article will dive deep into the P1345 code on GM (Chevrolet) vehicles. We will tackle an older Chevy engine model, specifically the 5.7 Vortec, in which this problem is highly prominent.
However, this knowledge is transferable and will help you fix your Chevy. There will be a few differences depending on the engine design and the types of ignition triggers. At the very end, you will be able to fix the problem yourself, if you are a little bit handy.

P1345 Chevy definition and meaning
Definition
Trouble code P1345 is a manufacturer-specific code defined as Crankshaft position-camshaft position correlation on General Motors vehicles.
Meaning
P1345 is a manufacturer-specific DTC, which means that diagnosing it will be different for different manufacturers. Moreover, the code may only apply to specific vehicles: Audi, Isuzu, Toyota, BMW, GM (Chevrolet and GMC), Lexus, Mazda, and Volkswagen. The P1345 code on a Chevy or GMC truck will defer from the same code in another car model.
Regardless of the definitions, these codes have one thing in common – they indicate an ignition problem. As earlier stated, these codes defer due to the type of engine and ignition triggers used in each specific vehicle. However, they have another thing in common: the application of Camshaft Position Sensors (CMS) and Crankshaft Position Sensors (CKS).
The camshaft position sensor is a sensor in your vehicle. It provides the Engine Control Module (ECM) or Powertrain control module (PCM) as referred to in some vehicles, with the exact position of the camshaft lobes relative to the valve openings on each cylinder. This information will then be used by the Engine control module (ECM) to choose the best fuel injector timing.
On the other hand, there is the crankshaft position sensor (CKS), which is a sensor that provides a signal to the engine control module indicating the position of the crankshaft or crankshaft timing relative to the top dead center on the compression stroke of the cylinder number 1 in the engine.
These two sensors work together with the engine control module to control engine timing. These sensors will be in sync if everything is working properly. When the interrelation between the camshaft position sensor and crankshaft position sensors is out of sync for more than 1 or 2 degrees, the error code P1345 will be recorded.
The P1345 Chevy code may be caused by faulty CKS and CMS sensors, but in most cases, it results from a problem in engine timing. This confusion is done away with in newer vehicles whose engines adjust the timing themselves. In these newer vehicles, you will also receive a p0335 code and p0340, telling you that the CKS and CMS sensors are bad or malfunctioning.
List of OBD2 codes that relate to P1345 on Chevy
1. P0335 – Crankshaft Position Sensor ‘A’ Circuit malfunction
2. P0340 – Camshaft Position Sensor ‘A’ Circuit malfunction
Symptoms of P1345 on Chevy?
1. Check engine light ‘ON’ – like other codes, this code will trigger the ‘check engine’ light and get stored in the vehicle’s memory system.
2. Engine misfires above 1500 rpm – an engine may misfire if there is a problem with the distributor, resulting in the lack of enough current to ignite the spark plugs. The resulting trouble is a misfire. At higher speeds, the ECM usually tries to adjust valve lift. Therefore, engine misfiring may be an indication of your valve timing being off.
3. Rough idling and stalling while driving – most engine problems such as these will deem your engine performance inefficient, resulting in the engine idling and stalling.
4. Difficulty in starting the engine – an engine with poor timing will exhibit difficulties in starting up since the engine timing is crucial for its operation. Newer vehicles improved on this by having the engine time itself.
Causes of P1345 on Chevy?
1. Loose, faulty, or bad camshaft position sensors and crankshaft position sensors (highly unlikely)
The CKS and CMS may be faulty if the p0335 code and/or p0340 codes are recorded too. A quick fix for this would be to replace the sensors or have a mechanic fix them. However, in the absence of these two codes, the problem will be located elsewhere.
2. Stretched, slipped, or improperly installed valve timing chain
There may be an excessive free play on the valve timing chain and gear assembly that may result in the valve timing being off. This may be due to mechanical wear or improper installation.
3. Incorrect distributor positioning or loose distributor rotor on the distributor shaft (most likely)
The distributor transfers current to the ignition coils for firing up the spark plugs. If it fails, it will not deliver current at the right time to the appropriate coil resulting in misfires and engine timing going off.
4. Bad wiring connections causing simple electrical connection failures
Chafing, corroding, rubbing, or burning spots on melted wire insulation may result in connection problems. These types of wiring problems should be checked as a regular maintenance procedure.
How serious is the P1345 Chevy OBD2 code?
As much as you may get by without fixing this trouble code for a while, it is advisable not to. The engine will have trouble starting on multiple occasions, and it may also suddenly stop. These two scenarios are not any driver’s cup of tea. Moreover, the check engine light may end up staying on till you fix the problem.
How to diagnose and fix the code P1345 on Chevy?
Tools needed
- OBD2 scan tool
- Electrical cleaner
- Plastic bristle brush
- Dielectric silicone grease
- Digital Volt Ohm Meter (DVOM)
Method
We are specifically tackling a 5.7 Vortec engine here. You will need to check if there are any technical service bulletins (TBS) for your vehicle. This may save you time and money if the manufacturer has put out a fix for this specific problem.
1. You will first need an OBD scan tool to connect to the OBD port on your car. Use it to scan for all the stored codes to ensure you diagnose those other codes before the P1345.
2. Check for any corroded, burnt, or defective wiring in the connections around the CKS and CMS sensors. Pull the connectors apart and inspect the terminals inside. If they are corroded or burnt, you will have to clean them with an electrical cleaner and the brush listed above.
Let them dry. Apply dielectric silicone grease on the terminals before returning the sensors.
3. Check for any damages and faults on and around the CKS and CMS sensors. If any, you will need to replace them and see if the problem is solved. To see if the sensors are working correctly, you will need to use a Digital Volt Ohm Meter (DVOM). Test the 5V power supply circuit going to each sensor to ensure it is being powered up.
4. Clear the trouble codes from memory and see if the P1345 code returns. If it does, then the problem is elsewhere. Proceed to the next step.
5. Analyze the assembly of the timing chain and gear assembly to make sure there is no excessive free play. Fix the problem by adjusting the installation. You may also need to get spare parts for the affected components. If this does not fix the problem, then the last and final diagnosis will be a problem with the distributor.
A distributor may be loose or missing. It is responsible for current delivery to ignition coils in the correct firing order and correct time period. It contains a rotor, which may be loose in this case. On top of this, the gear inside of the distributor may be bad.
The distributor may need to be replaced, but if it is new and/or in good working condition, its positioning is probably off.
6. Using the scan tool, connect it to the OBD port on your vehicle with ignition OFF. Start the engine. From the scan tool, read the “Cam Retard Offset,” you will need to get your engine to 1000 rpm for accurate results.
7. A reading of +/-2 degrees of Zero is an indication of optimal timing. Otherwise, you will need to adjust the distributor. You can adjust it by loosening the bolt on the distributor while the engine is off. Connect scan tool and monitor the “Cam Retard Offset” reading. Start the engine and make sure it reaches 1000 rpm.
8. Adjust the positioning by turning the distributor clockwise if the reading is positive and anticlockwise if the reading is negative. Do this till the “Cam Retard Offset” reading is within +/- 2 degrees of Zero, finally solving the issue.
Read more: How can I perform CASE relearn without a scan tool?
Tips to avoid P1345 in the Future
1. Perform regular preventive maintenance. Problems related to P1345 will be caught earlier.
2. Avoid driving through deep puddles because water will get into the distributor cap and short out.
FAQs
How do I know the distributor is not the problem for P1345 ?
If other codes such as p0335 and p0340 are saved, there is a high likelihood the problem lies elsewhere but directly or indirectly affects valve timing and its components.
What is the cost of diagnosing the P1345 Chevy code?
The charges vary depending on where you take your vehicle for repair. The charges average at around $75 to $150 an hour. Diagnosing the P1345 Chevy code will take approximately 1 hour.
What if all the solutions listed above do not fix the problem?
If you carefully follow all the steps above, the problem will be fixed. However, if it persists or other issues such as the engine not starting and misfires, you may have another component issue. Scan for the DTCs and see what the codes are indicating. Proceed from there.
Does this solution apply to the P1345 code in other vehicles apart from GM (Chevrolet and GMC truck)?
This solution is specific to GM and Chevrolet vehicles. Search for Technical Service Bulletins by your manufacturer for a detailed solution to different manufacturers.
What if I have the P1345 code, but the engine works fine?
This is a clear indication that symptoms will surely come after some time. Take your car for maintenance to fix it sooner rather than later.
P1281 Dodge Code: Engine Temperature Troubles
P1281 Dodge Code: Engine Temperature Troubles
Today, we’re tackling a common concern for Dodge owners: the P1281 code.
If you’ve noticed your engine temperature acting up and that pesky check engine light popping up, don’t worry! We’re here to help you make sense of it all.
In this article, we’ll take a close look at the P1281 Dodge code and its connection to your engine’s temperature.
Let’s get started! Say goodbye to engine temperature troubles and hello to a reliable Dodge vehicle!
P1281 Dodge: A Quick Overview
Curious about the P1281 Dodge code? Check out our quick summary for essential details!
- Definition: Engine Is Cold Too Long
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $50 – $300
Understanding P1281 Dodge: What Does The Code Mean?
The P1281 code points to a specific issue related to the engine’s operating temperature. Your Dodge vehicle relies on various interconnected systems and components to regulate and maintain the engine’s temperature. Among these key components are the thermostat, engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor, and engine control module (ECM). Together, they work harmoniously to ensure the engine operates within the optimal temperature range.
If the engine fails to reach the required temperature within the specified time frame, the ECM detects this anomaly and triggers the P1281 code. Specifically, this code indicates that the engine has not reached a temperature above 176 degrees Fahrenheit (80 degrees Celsius) for more than 20 minutes of continuous driving since it was first started.
It’s worth noting that the P1281 code is commonly found in Dodge models such as the Ram 1500, Dakota, Durango, and Neon. Additionally, it is often associated with other codes like P0443 (Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Control Valve Circuit) and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold).
P1281 Dodge: To Drive Or Not To Drive?
When it comes to the severity of the P1281 code, it is considered a moderate-level issue. While it may not pose an immediate danger to your vehicle’s operation, it shouldn’t be ignored. It can impact fuel efficiency, emissions, and overall engine performance.
It is generally safe to continue driving with the P1281 code, especially if you haven’t experienced any noticeable symptoms or performance issues. However, we recommend that you diagnose and repair the issue at your earliest convenience to prevent potential long-term complications and ensure the optimal performance of your vehicle.
Common Symptoms Of P1281 Dodge
Typical symptoms associated with this code include:
- Check Engine Light (MIL) illuminated
- Poor fuel efficiency
- Engine running cooler than normal
- Delayed or sluggish engine warm-up
- Reduced heater performance
Read more: Dodge RAM Warning Light Symbols and Meaning (FULL list, FREE Download)
What Triggers P1281 Dodge?
The P1281 code can be triggered by several underlying causes, which may include:
- Stuck open thermostat
- Faulty or wrongly installed thermostat (most common)
- High resistance in the ECT sensor signal circuit
- Damaged or failed ECT sensor
- Low coolant level or incorrect coolant mixture
Diagnosing And Repairing P1281 Dodge: A Step-by-Step Guide
This section will provide you with a step-by-step guide to diagnose and repair the P1281 code. Before we begin, let’s take a look at the essential tools and parts you may need for the procedure:
Essential Tools And Parts
- OBD-II scanner or code reader
- Multimeter
- Coolant tester
- Basic hand tools (wrenches, sockets, etc.)
- Replacement thermostat (if necessary)
- Engine coolant
Your Step-by-Step Guide
- Verify coolant level and mixture
- Using a coolant level gauge or visually inspecting the coolant reservoir, verify the coolant level and ensure it is not low.
- Check the coolant mixture using a coolant tester to ensure it is within the recommended range.
- Inspect and replace thermostat (if necessary)
- With the engine cooled down, locate the thermostat housing.
- Using a suitable wrench or socket, remove the bolts securing the housing and carefully take out the thermostat.
- Inspect the thermostat for any signs of being stuck open, such as a visibly loose valve or debris.
- If the thermostat is bad, replace it with a new one that matches your vehicle’s specifications.
- Test ECT sensor and signal circuit
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to connect the multimeter to the sensor terminals and measure the resistance.
- If the resistance is outside the specified range or there are signs of damage, make necessary repairs or replace the ECT sensor.
- Clear the code and test drive
- After making the necessary repairs or replacements, use an OBD-II scanner or code reader to clear the code and reset the vehicle’s ECM.
- Confirm the resolution of the issue by taking the vehicle for a test drive.
- Keep an eye on the engine temperature and watch for any recurrence of the code or related symptoms.
Notes: It is advisable to consult the specific repair manual for your Dodge model to obtain detailed instructions and specifications tailored to your vehicle.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
Diagnosing and fixing the P1281 code is typically considered an intermediate-level DIY repair. If you have the necessary tools and feel confident in your mechanical abilities, you can try to address the issue yourself. However, if you’re unsure or uncomfortable with the process, it’s best to seek help from a qualified mechanic.
The estimated cost for the main repair tasks associated with the P1281 code can vary depending on factors such as the location, labor rates, and parts prices. Below is a breakdown:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Diagnostic Fee | $50 – $150 (may be waived if repairs are performed at the same facility) |
| Coolant Cost | $20 – $50 (may vary depending on coolant type and quantity) |
| Thermostat Replacement | $50 – $150 (excluding parts and additional labor) |
| ECT Sensor Replacement/Repair | $100 – $200 (including parts and labor) |
| Coolant Cost | $20 – $50 (may vary depending on coolant type and quantity) |
P1281 Dodge Infographic
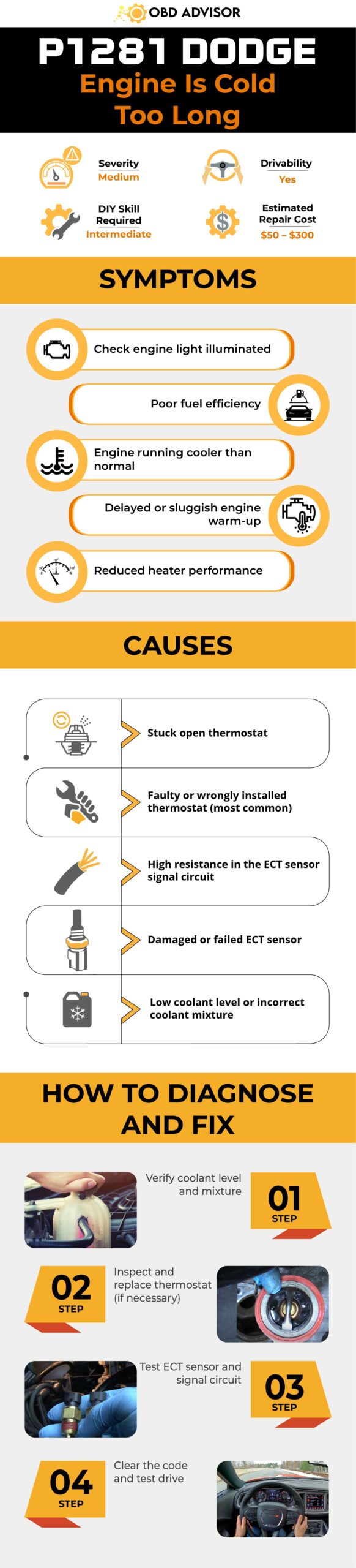
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, addressing the P1281 Dodge code promptly is crucial for maintaining optimal engine temperature.
Whether you choose to handle the repairs yourself or seek professional assistance, taking action is key to ensuring safe and efficient driving.
Share your experiences and spread the knowledge to help others. Wishing you safe travels and a well-regulated engine temperature.
Reference Sources
- RepairPal, Getting Code P1281 w/check engine light.
- CarGurus, Dodge Dakota Questions – P1281.
- JustAnswer, DTC code P1281, what does it mean and how to fix?.
P1516 Chevy Code: Throttle Position Sensor Issues Explained
P1516 Chevy Code: Throttle Position Sensor Issues Explained
The P1516 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is a common issue that arises in the throttle actuator control (TAC) system of Chevrolet vehicles. In this article, we will explore the meaning of the P1516 Chevy code, common symptoms, potential causes, and possible solutions.
By understanding this code and its implications, Chevy owners and technicians will be equipped with the knowledge to diagnose and resolve throttle-related issues effectively.
Let’s get started!
P1516 Chevy: A Quick Overview
Take a look at the summary of the P1516 for Chevy!
- Definition: Throttle Actuator Control Module/ Throttle Actuator Position Performance
- Severity: High
- DIY Skill Level: Advance
- Continue To Drive?: No
- Estimated Repair Cost: $60 – $600
What Does The P1516 Mean In Chevy Vehicles?
The P1516 Chevy DTC indicates a potential issue with the TAC module. This code suggests that there is a malfunction or a communication problem between the TAC module and the Engine Control Module (ECM), which is responsible for managing various engine functions.
When the P1516 DTC is triggered, it typically points to a fault within the TAC system, affecting the electronic throttle body’s operation. The electronic throttle control system plays a crucial role in regulating the engine’s air intake and improving overall performance. The P1516 DTC is commonly encountered in various Chevrolet models, including: the Silverado, Tahoe, Suburban, Trailblazer, etc.
Sometimes, the P1516 DTC may be accompanied by additional diagnostic trouble codes, which can provide further insight into the underlying issue. Some of the common accompanying codes include: P2101, P2119, P2135, and P2176.
How Serious Is The P1516 Chevy Code?
The severity of the P1516 DTC in Chevy vehicles can vary. In general, a P1516 code indicates a potentially serious problem, and it is not advisable to continue driving with this code. The issue can result in reduced engine power and driveability issues. While it may not pose an immediate safety risk, driving with the P1516 code can impact drivability and performance.
It is recommended to seek professional assistance promptly to diagnose and resolve the issue. Ignoring the code may lead to further damage and increased fuel consumption.
What Are The Signs Of The P1516 Chevy Code?
Here are some common signs of P1516 in Chevrolet vehicles:
- Illuminated check engine light (MIL)
- “Reduced engine power” message on the dashboard
- Engine hesitation or stumbling
- Throttle response issues
- Reduced fuel efficiency
- Poor acceleration
What Are The Causes Of The P1516 Code In Chevrolet Vehicles?
The P1516 Chevy code can be caused by various reasons, including:
- Faulty throttle position sensor (TPS)
- Malfunctioning throttle body
- Wiring or connector issues in the TAC system
- Carbon build-up in the throttle body
- ECM software or calibration problems
- Defective TAC system
Read more: P1345 Chevy: Meaning, Symptoms, Causes and Fixes
How To Diagnose And Repair P1516 Chevrolet Code?
Diagnosing and repairing the P1516 Chevy code requires identifying the underlying causes. In this section, we will provide an overview of the essential tools and parts needed, a step-by-step procedure for diagnosis and repair, as well as discuss the level of DIY repair and estimated costs.
Diagnostic Tools And Essential Parts
To diagnose and repair the P1516 Chevy code, you may need the following tools and parts:
- Scan tool or OBD-II code reader
- Multimeter
- Throttle position sensor
- Throttle body cleaner
- Electrical contact cleaner
- Wire connectors and terminals (if required)
- Replacement throttle body (if necessary)
Step-by-Step Guide
- Connect a scan tool or OBD-II code reader to retrieve and record the specific trouble codes, including P1516.
- Inspect the throttle body and wiring connections for any visible damage or loose connections. Repair or replace the throttle body and its wiring if needed.
- Use a multimeter to test the TPS sensor for proper voltage readings. If the sensor is defective, repair or replace it.
- Clean the throttle body and TPS using throttle body cleaner and electrical contact cleaner.
- Clear the trouble codes using the scan tool and test drive the vehicle to ensure that you have resolved the issue.
Note:
- Be cautious when working with electrical components and ensure the battery is disconnected before starting any repairs.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and specifications for testing and replacing components.
- Thoroughly clean the throttle body and TPS to ensure proper functionality.
Read more: P1101 Intake Air Flow System Performance in Chevy Cruze Vehicles
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
Diagnosing and repairing the P1516 Chevy code can range in difficulty depending on the specific cause. DIY enthusiasts with moderate automotive repair experience can perform basic cleaning and inspection. However, for more complex issues or component replacements, it is recommended to consult with an expert or qualified mechanic.
The estimated cost for repairing the P1516 code can vary depending on the cause and the parts required. Here is a general cost breakdown:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Throttle body cleaning | $60 – $120 |
| Repairing wiring/connectors | $60 – $130 |
| Replacement of the TPS | $100 – $250 |
| Throttle body replacement | $300 – $700 |
Please note that the costs provided are estimates and can vary based on factors such as the vehicle model, location, and labor rates. For accurate quotes, we recommend reaching out to local repair shops or mechanics. They can provide precise estimates based on your specific vehicle and the labor rates in your area.
Conclusion
Ready to tackle the P1516 code in your Chevrolet? With the insights you’ve gained, confidently diagnose and resolve this issue. Share this valuable information with fellow Chevy owners who may be facing similar challenges.
If you have any questions or success stories, we’re here to listen in the comments section below. Keep your Chevy running smoothly and stay tuned for more expert automotive guides. Drive with confidence!
Reference Sources
- Wikipedia, Throttle position sensor.
- CarParts.com, What Is a Throttle Actuator? Function and Symptoms of Failure Explained.
P1450 Ford Code: Your Guide To Keeping EVAP System In Check
P1450 Ford Code: Your Guide To Keeping EVAP System In Check
When your vehicle’s check engine light illuminates and you discover the P1450 Ford code, it’s a sign that your car is trying to communicate an issue within the Evaporative Emission (EVAP) system.
In this article, we’ll help you understand what this code means. We’ll talk about the signs your car might show, why it happens, and give you step-by-step instructions to figure out and fix the issue. Whether you’re a car expert or want to know what’s going on under the hood, this article will make dealing with the P1450 code a breeze.
Let’s get started!
P1450 Code On Ford: An Overview
Here is a summary of the P1450 code in Ford vehicles. Check it out!
- Definition: Unable To Bleed Up Fuel Tank Vacuum
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $20 – $400
What Does The P1450 Mean In Ford Vehicles?
The P1450 code indicates an excessive vacuum condition within the EVAP system or fuel tank. This elevated vacuum level prevents the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) from properly bleeding or releasing the vacuum to maintain the required pressure within the system.
When the PCM detects this prolonged high vacuum condition, lasting for more than sixty seconds, it identifies a fault and subsequently triggers the Check Engine Light. Simultaneously, it stores the P1450 code in the vehicle’s diagnostic system, indicating to the vehicle owner or technician that there is a problem within the EVAP system or fuel tank that requires attention and diagnosis.
The purpose of the EVAP system is indeed crucial in preventing the release of gasoline vapors into the atmosphere. When this system fails to maintain the specified vacuum levels, it can increase emissions and environmental pollution.
The P1450 code is commonly encountered in Ford vehicles, including models such as the Ford Focus, Ford Escape, Ford Fusion, Ford Explorer, and Ford F-150, among others. Accompanying codes associated with the P1450 code may include P0442, P0455, P0446, P0456 and P0451.
How Severe Is The P1450 Code In Ford Vehicles?
The severity of the P1450 code can vary depending on the root cause and the vehicle’s overall condition. However, it’s generally considered a moderate-level issue. While this code doesn’t typically represent an immediate safety hazard, it should not be ignored.
So, can you still drive with this code? – Yes, you are able to drive. However, continuing to drive with the P1450 code illuminated for a long time may lead to increased emissions and environmental pollution. Additionally, it can negatively impact your vehicle’s fuel efficiency and overall performance. We advise against extended driving with this code active.
It’s advisable to have your vehicle inspected and repaired as soon as possible by a qualified mechanic to prevent potential long-term damage.
What Are The Signs Of The P1450 Ford Codes?
You may experience the following symptoms when the P1450 code is set:
- Illuminated check engine light
- Reduced fuel efficiency
- Difficulty starting the engine
- Rough idling
- Increased emissions
Note: In some cases, the only noticeable symptom of the P1450 code may be the illumination of the Check Engine Light. Additionally, in rare circumstances, you might experience a delay in engine start-up time after filling the tank.
Read more: B1352 Ford Code: Ignition Troubles Unveiled And Resolved
What Are The Causes Of The P1450 Code On Ford?
The P1450 code can have various causes, with the most common ones being:
- Faulty or stuck EVAP canister vent valve
- Wiring and connector issues
- Damaged EVAP canister
- Issues with the EVAP purge valve
- Defective fuel tank pressure sensor
- Jammed fuel filter cap
P1450 Ford Code Diagnosis And Repair
When dealing with the P1450 code, having the right tools and following a systematic procedure can help diagnose and resolve the issue effectively.
Essential Tools And Parts
- OBD-II scanner
- Multimeter
- Replacement EVAP canister vent valve or EVAP purge valve
- Wiring and connector repair kit
- Fuel tank pressure sensor
- New fuel filter cap
Step-by-Step Guide
- Begin by connecting the OBD-II scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and retrieve the trouble code.
- Inspect the wiring and connectors associated with the EVAP system, repairing any damaged or loose connections.
- If the fuel filter cap is jammed, replace it with a new one.
- Test the EVAP canister vent valve and EVAP purge valve using a multimeter to ensure proper functionality. Replace them if they are faulty.
- Check the condition of the EVAP canister for damage or cracks and replace if necessary.
- Examine the fuel tank pressure sensor and replace it if it’s defective.
- Clear the trouble code with the OBD-II scanner and start the vehicle to confirm that the Check Engine Light remains off.
Note: It’s worth noting that there are Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) related to the P1450 code for specific vehicle models. If you own a 2015-2016 Ford Focus, we recommend consulting TSB 16-0055 for additional guidance. Similarly, if you have a 2013-2017 Ford C-MAX Hybrid or a 2013-2017 Ford Fusion, you should check TSB 19-2207 for relevant information and potential fixes related to the P1450 code. These TSBs may provide specific insights and instructions tailored to your vehicle model, assisting in the diagnosis and resolution of the issue.
Read more: P1151 Ford Code: Decoding And Repair Guide
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
This repair falls within the intermediate DIY level, suitable for those with experience in automotive repair. However, if you are unsure about the diagnosis or lack the necessary tools and experience, it is advisable to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic to avoid any potential complications.
Here’s an estimated cost breakdown for common repair tasks:
| Repair Task | Cost Range |
| Wirings repair | $20 – $150 |
| EVAP canister vent valve replacement | $50 – $150 |
| EVAP purge valve replacement | $150 – $300 |
| Fuel tank pressure sensor replacement | $250 – $290 |
| Fuel filter cap replacement | $30 – $60 |
Remember that labor costs can vary depending on your location and the specific repair shop you choose, so it’s a good idea to obtain quotes from multiple sources if you opt for professional assistance.
Conclusion
Facing the P1450 Ford code can be daunting, but with the insights provided here, you’re better equipped to tackle this challenge. By understanding the symptoms and causes of the P1450 code, you can respond effectively. Whether you decide to roll up your sleeves for a DIY fix or consult a trusted mechanic, the goal is the same: to get your vehicle back on the road running smoothly.
Stay informed, stay proactive, and share your experiences and insights with others in the automotive community. If you found this article helpful, don’t hesitate to share it and leave your comments below. Together, we keep our cars in top shape and our journeys trouble-free.
Reference Sources
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, Technical Service Bulletin – 16-0055.
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, Technical Service Bulletin – 19-2207.
P1299 Ford Code: Resolving Engine Overheating With Confidence
P1299 Ford Code: Resolving Engine Overheating With Confidence
Dealing with the P1299 Ford code in your vehicle? This comprehensive article provides valuable insights, symptoms, and effective repair methods to help you conquer the engine overheating issue. By following our expert guide, you’ll gain the knowledge and confidence to diagnose and resolve the P1299 code, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Read on to address the P1299 Ford code and take control of your vehicle’s cooling system.
P1299 Ford Code: An Overview
Take a look at a summary of the P1299 Ford code below:
- Definition: Cylinder Head Over-temperature Protection Active
- Severity: High
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: No
- Estimated Repair Cost: $20 – $300
What Does The P1299 Mean In Ford Vehicles?
The P1299 code is triggered when the Engine Control System detects engine overheating. It specifically relates to the Cylinder Head Temperature (CHT) sensor and monitoring circuit, which informs the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) about the engine’s temperature status.
The CHT sensor measures the temperature at the cylinder head and converts it into a signal voltage that varies with temperature fluctuations. Once the PCM receives a signal indicating that the engine temperature has exceeded the critical limit set by the manufacturer, it will set the P1299 code.
When the P1299 code is set, it may trigger Ford’s fail-safe cooling system, which is an engine protection feature that activates when the engine begins, to overheat. It reduces the risk of damage by shutting down some cylinders to lower heat production and pumping air through them to aid cooling. During this mode, engine power and performance are significantly reduced.
The P1299 diagnostic trouble code (DTC) commonly occurs in Ford vehicles across several models. Some of the popular models that may encounter this code include: Escape, Fusion, F-150, Edge, Expedition, and Explorer.
This P1299 code is often accompanied by additional codes that provide more specific information about the underlying issue. Some of the codes that might be found along with P1299 include: P0128, P0117, P0118, P0125, P0126, and P2560.
How Severe Is The P1299 Code In Ford Vehicles?
The P1299 Ford DTC indicates a potentially critical issue with the engine’s cooling system, specifically related to overheating. As such, it is considered a severe code that requires immediate attention.
If you encounter the P1299 code, it is strongly recommended not to continue driving the vehicle until the underlying issue is addressed. Continuing to drive with an overheating engine can exacerbate the problem and result in costly repairs. It is advisable to safely pull over, turn off the engine, and allow it to cool down before seeking professional assistance.
What Are The Signs Of The P1299 Ford Codes?
The P1299 Ford DTC is often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Illuminated check engine light
- Engine overheating
- Reduced engine performance
- Engine running rough or misfiring
- Increased fuel consumption
- Possible engine stalling or failure to start
- Failsafe mode activation
Read more: B1352 Ford Code: Ignition Troubles Unveiled And Resolved
What Are The Causes Of The P1299 Code In Ford?
The P1299 Ford DTC can be caused by various factors, including:
- Malfunctioning CHT sensor
- Faulty cooling system components (thermostat or radiator)
- Low coolant level or coolant leaks
- Defective water pump
- Electrical issues in the CHT sensor circuit
- Contaminated engine oil
- Damaged cooling fan
These causes should be properly diagnosed and addressed to resolve the P1299 code.
P1299 Ford Code Diagnosis And Repair
In this section, we will address the repair and diagnosis of the P1299 Ford DTC. To effectively resolve this issue, you will need the following essential tools and parts:
Essential Tools And Parts
- OBD-II Scanner
- Multimeter
- Coolant Pressure Tester
- Replacement CHT Sensor
- Thermostat
- Radiator
- Water Pump
- Coolant
- Engine Oil
Step-by-Step Guide
- Begin by using an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the P1299 code and any additional codes present. Note the freeze frame data.
- Use a multimeter to check the CHT sensor circuit for electrical issues. Look for open circuits or short circuits and repair as necessary.
- Check the CHT sensor for physical damage or loose connections. Replace it if necessary.
- Inspect the cooling system components, including the thermostat, radiator, and water pump, for leaks, wear, or malfunction. Replace any faulty components.
- Ensure the coolant level is adequate. Top up the coolant if needed and inspect for leaks.
- Test the water pump for proper function. If it’s not circulating coolant effectively, replace it.
- Check the engine oil for signs of contamination. If present, replace the oil and address the underlying issue.
- Ensure the cooling fan operates correctly. Repair or replace the fan if needed.
- After making any necessary repairs, clear the diagnostic trouble codes and perform a road test to confirm that the issue has been resolved.
Read more: Ford OBD2 Codes List for FREE Download
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The level of DIY repair for the P1299 code varies from beginner to intermediate. If it’s a simple fix like changing the engine oil or topping up coolant, it can be a DIY task. However, more complex issues like replacing the water pump or radiator may require mechanical expertise.
Here’s an estimated cost breakdown for common repair tasks:
| Repair Task | Cost Range |
| Wirings repair | $20 – $150 |
| CHT Sensor replacement | $20 – $50 |
| Thermostat replacement | $20 – $50 |
| Radiator replacement | $100 – $300 |
| Water pump replacement | $50 – $150 |
| Coolant top up | $10 – $20 |
| Engine oil change | $30 – $50 |
It’s crucial to diagnose the specific cause of the P1299 code accurately to avoid unnecessary expenses. If you’re uncertain about the repair, consult a professional mechanic for assistance.
Conclusion
Resolving the P1299 Ford code and getting your vehicle back on the road is a reachable goal. Armed with the knowledge and steps we’ve provided, you can confidently diagnose and address this issue. Don’t keep this valuable information to yourself – share it with fellow Ford owners who might be facing the same challenge.
Do you have questions or success stories to share? We’re all ears! Feel free to drop your experiences and insights in the comments section below.
Reference Sources
- Professional Automotive Repair, What is Engine Misfiring? Does It Affect Your Car?
- Goodyear Auto Service, Engine Overheating Causes and Actions.
P1457 Honda Code: Diagnosing And Resolving EVAP Problems
P1457 Honda Code: Diagnosing And Resolving EVAP Problems
Dealing with a specific trouble code like P1457 in your Honda vehicle can be frustrating, but with the right knowledge and guidance, you can diagnose and fix the issue. In this article, I will show you the common causes of the P1457 code and provide you with a step-by-step procedure to troubleshoot and repair it.
I’ll give you guidance on essential tools and parts required, as well as the level of DIY repair involved. Whether you’re a seasoned DIY enthusiast or looking to understand the problem before seeking professional help, this article will equip you with the necessary information to tackle the P1457 code in your Honda car.
Let’s dive in!
P1457 Honda Code: A Quick Overview
Take a look at the summary of the Honda P1457 code provided below!
- Definition: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected – B
- Severity: Low
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $20 – $500
What Does The P1457 Honda Code Mean?
P1457 is an OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics) code that refers to an Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) System Leak Detected – B. It indicates that a leak has been detected in the EVAP system. This system is responsible for preventing the release of fuel vapors into the atmosphere, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
While the P1457 code may occur in various Honda models, a few notable ones include the Honda Accord, Civic, CR-V, Odyssey, and Pilot. It is important to note that while P1457 is commonly encountered in Honda vehicles, it is not exclusive to them.
In some cases, P1457 could appear along with some additional DTCs (diagnostic trouble codes)that provide further insight into the issue. Some common accompanying codes include P0440, P0441, P0442, and P0497.
How Severe Is The P1457 Code In Your Honda?
The severity level of the P1457 Honda DTC can be considered relatively low, and you can continue to drive. While this issue may affect the vehicle’s performance and fuel efficiency, it is unlikely to cause immediate or significant safety concerns.
However, it is advisable not to ignore the P1457 code and to address it as soon as possible. It can lead to increased emissions, potential damage to other emission control components, and potential emissions testing failures in the long term.
What Are The Signs Of The P1457 Code On Honda Vehicles?
The P1457 Honda DTC may not present significant noticeable symptoms other than the illumination of the check engine light. However, in the event of a larger leak, you can experience the following signs:
- Fuel odors
- Engine stalls
- Reduced fuel economy
What Are The Causes Of The P1457 Honda Code?
Determining the root cause of the P1457 Honda DTC is crucial for effective diagnosis and repair. The following are some common causes associated with this code:
- Loose, damaged, or missing fuel cap
- Faulty fuel tank pressure sensor
- Corroded or malfunctioning vent valve
- Leaks in the EVAP system hoses or components
- Damaged or deteriorated EVAP canister
- Faulty purge control solenoid (PCS) valve
- Issues with the two-way valve or bypass solenoid (BPS) valve
Read more: P145C Honda Code: Expert Tips for Emission System Repairs
How To Diagnose And Fix The P1457 Code On Honda?
In this section, we will discuss the essential tools and parts required, provide a step-by-step procedure to diagnose and fix the P1457 code, and discuss the level of DIY repair and estimated costs.
Essential Tools And Parts
To diagnose and repair the P1457 code successfully, you may need to have the following tools and parts (if required):
- OBD-II scanner or diagnostic tool
- Fuel tank pressure sensor
- Canister vent shut (CVS) valve
- Fuel tank vapor control valve
- Two-way valve and bypass solenoid (BPS) valve
- EVAP canister
Step-by-Step Procedure
1. Retrieve trouble codes
- Connect the OBD-II scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Retrieve the trouble codes stored in the vehicle’s computer system.
2. Inspect and replace the fuel cap
- Inspect the fuel cap and ensure it is tight and in good condition.
- Replace the fuel cap if it is damaged or missing.
3. Perform the EVAP function test
- Use the Honda diagnostic tool to perform the EVAP Function Test.
- Check for any system malfunctions or abnormalities.
4. Check the fuel tank pressure sensor
- Use the diagnostic tool to check the FTP sensor value.
- If the FTP sensor value is out of the specified range, replace the FTP sensor.
5. Test for leaks in the canister side
- Apply vacuum to the system and monitor the FTP sensor value.
- If a leak is detected, replace the CVS valve.
6. Test the fuel tank vapor control valve
- Apply vacuum to the system and monitor the FTP sensor value.
- If a leak is detected, replace the fuel tank vapor control valve.
7. Test the two-way valve and BPS valve
- Apply vacuum to the system and monitor the FTP sensor value.
- If any leaks are detected, replace the faulty two-way valve and BPS valve.
8. Inspect EVAP canister and hoses
- Inspect the EVAP canister and hoses for any signs of leaks or damage.
- Replace the canister or hoses if leaks are found.
9. Test purge hose
- Apply vacuum to the system and monitor the FTP sensor value.
- If a leak is detected, replace the purge hose.
10. Test purge control solenoid valve
- Use a vacuum gauge to test the PCS valve for leaks.
- Replace the valve if necessary.
11. Clear trouble codes and verify
- Clear the trouble codes from the vehicle’s computer system.
- Drive the vehicle to complete the EVAP system monitor.
- Verify that the P1457 code does not return.
Note:
- It is important to consult the vehicle’s service manual for detailed instructions and specifications specific to your Honda model. There is a Technical Service Bulletin (TSB) from Honda related to the P1457 code for your information.
- In most cases, the main culprits for the P1457 code are indeed the EVAP canister and the CVS valve. Therefore, it is essential to thoroughly inspect the canister and CVS valve for any signs of leaks, damage, or malfunction. If any issues are detected, replace these components.
Read more: Honda OBD2 Codes List [Generic + Manufacturer-specific]
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
This repair procedure involves intermediate-level DIY skills. If you are unsure or uncomfortable performing these tasks, it is recommended to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic or automotive professional.
The estimated costs for the main repair tasks may vary depending on factors such as the specific Honda model and the cost of replacement parts. Here is a general cost breakdown:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Fuel tank pressure sensor replacement | $50 – $100 |
| Canister vent shut valve replacement | $50 – $100 |
| Fuel tank vapor control valve replacement | $50 – $100 |
| Two-way valve and BPS valve replacement | $100 – $200 |
| EVAP canister and hoses replacement | $100 – $300 |
| Purge hose replacement | $20 – $50 |
| Purge control solenoid valve replacement | $50 – $100 |
If you’re uncertain about any aspect of the repair process or lack experience, consulting a certified mechanic is a prudent step to ensure an effective and safe resolution of the issue.
Final Thoughts
Facing the P1457 code in your Honda is a common but manageable challenge. Understanding its triggers and taking swift action can ensure your vehicle remains both efficient and environmentally responsible. By diagnosing and addressing issues within the Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP), you not only restore your vehicle’s performance but also contribute to cleaner air for all.
Have you encountered the P1457 code before, or do you have insights to share? We’d love to hear your experiences and tips. Feel free to comment below and share this valuable information with fellow Honda enthusiasts.
Together, we can keep our vehicles running smoothly and minimize our impact on the environment. Safe driving!
Reference Sources
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. (2013). Technical Service Bulletin: SB-10053545-3978 [PDF document]
- J.D. Power, What Does It Mean When Your Car Stalls?
- Cars.com. Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor
P1157 Honda: Troubleshooting Air/Fuel Sensor Issues
P1157 Honda: Troubleshooting Air/Fuel Sensor Issues
If you’ve come across the P1157 Honda diagnostic trouble code, you’re not alone. This perplexing code has left many Honda owners searching for answers.
In this guide, we’ll explore the meaning, severity, symptoms, causes, and diagnosis of P1157 Honda. With our expertise in Honda vehicles, we’ll help you navigate through this challenge and find effective fixes.
So, let’s get started!
P1157 Honda Code: Quick Summary
Here’s a brief overview of the essential details regarding the P1157 Honda code:
- Definition: Air/Fuel Ratio (A/F) Sensor (Sensor 1) Circuit High Voltage
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes (Short-term)
- Estimated Repair Cost: $50-$200
Understanding The P1157 Code In Your Honda
The P1157 code is a common issue reported by owners of Honda vehicles, particularly the Accord, CRV, Element, and Civic models. This code indicates a potential problem with the A/F (Air/Fuel) sensor, specifically Sensor 1.
The A/F sensor plays a crucial role in measuring the oxygen content in the exhaust gas. It consists of a sensor element with an embedded heater. When activated, the heater warms up the sensor to enhance the detection of oxygen content, allowing for precise measurement. The current flowing through the heater is proportional to the oxygen content, which helps determine the air/fuel ratio.
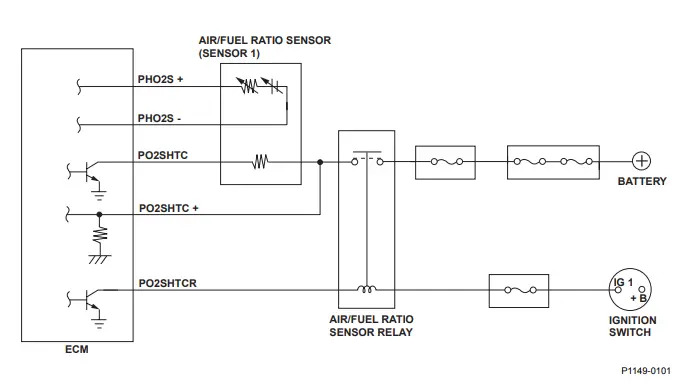
In normal operation, the engine control module (ECM) compares the detected air/fuel ratio with the target air/fuel ratio. Based on this comparison, the ECM adjusts the fuel injection duration to maintain optimal combustion efficiency.
If the A/F sensor (Sensor 1) voltage is low, indicating a lean air/fuel ratio, the ECM issues a Rich command to increase the fuel mixture. Conversely, if the A/F sensor (Sensor 1) voltage is high, indicating a rich air/fuel ratio, the ECM issues a Lean command to reduce the fuel mixture.
The triggering of the P1157 Honda code occurs when the A/F sensor (Sensor 1) fails to activate its heater within a set time period while drawing power. The ECM detects this malfunction and stores the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1157.
Read more: Honda OBD 2 Codes List [Generic + Manufacturer-specific]
How Serious Is The P1157 Honda?
When it comes to the severity of the P1157 Honda code, it is considered a moderate-level issue. While it may not pose an immediate threat to the safety or functionality of your Honda vehicle, it should still be addressed promptly.
In most cases, it is generally safe to continue driving your vehicle when you encounter the P1157 Honda code. However, it is important to address this code as soon as possible to prevent any potential issues with fuel combustion, fuel efficiency, or engine performance.

(Image credit: Drive Accord Forum)
To ensure your vehicle’s longevity and optimal functioning, it is advisable to have the underlying cause of the P1157 Honda code diagnosed and resolved promptly. By doing so, you can restore the proper operation of the A/F sensor system and maintain optimal fuel efficiency and engine performance.
Read more: P1009 Honda Code: VTC System Troubleshooting And Solutions
Common Signs Of P1157 Honda To Watch For
The P1157 Honda code typically presents with the following symptoms:
- Check Engine Light (CEL) illuminated
- Decreased fuel efficiency
- Engine runs rough or misfires
- Poor acceleration or lack of power
- Increased exhaust emissions
P1157 Honda Causes: What’s Behind The Code
Here are some common causes of the P1157 Honda code:
- Wiring damage or break in the A/F sensor (Sensor 1) circuit
- Faulty A/F sensor (Sensor 1)
- Defective ECM (connection issues or internal fault) – rarely
Diagnosis And Repair For P1157 Honda
In this section, we’ll provide you with a comprehensive guide to diagnose and repair the P1157 Honda code. We’ll cover the essential tools and parts required, a step-by-step procedure with helpful tips, as well as the level of DIY repair and estimated costs associated with resolving this code.
However, it’s important to note that if you’re unsure or uncomfortable with the repair process, it’s always advisable to seek assistance from a professional mechanic.
Essential Tools And Parts
To diagnose and repair the P1148 code, you may require the following tools and parts:
- OBD-II scanner
- Multimeter
- A/F sensor (Sensor 1) replacement (California-emission compliant)
- Wiring repair kit (if necessary)
- Socket set and wrenches
Step-by-Step Guide
- Connect the OBD-II scanner to retrieve the P1157 Honda code and any additional codes.
- Inspect the A/F sensor wires, wiring, and connectors for any visible damage, such as frayed wires or loose connections. Repair or replace the damaged wiring using a wiring repair kit.
- Use a multimeter to test the voltage and resistance of the A/F sensor and its heater circuit. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- If the readings are abnormal and the wiring has been addressed, replace the A/F sensor (Sensor 1) with a compatible replacement part. Ensure that it meets the necessary specifications for your vehicle, especially if it requires California-emission compliance.
- Inspect the ECM connections for any loose, corroded, or damaged pins. Ensure that the ECM is properly connected. Address any connection issues detected by cleaning the connections, repairing any damaged pins, or replacing the connector if necessary.
- If the problem still persists, consider the possibility of an ECM internal fault. In this case, perform the following steps:
- Perform an ECM idle learn procedure as the vehicle’s service manual recommends.
- Check if the ECM has the latest software version. If not, update the ECM with the latest software available.
- If updating the ECM software doesn’t resolve the issue, you may need to substitute the ECM with a known-good ECM for testing purposes.
- Clear the codes using the OBD-II scanner and test-drive the vehicle to verify if the issue is resolved.
Notes:
- If your car has California emissions, use the California version of the sensor. The PCM is programmed to read the California-emission sensor specifically. The labor required for sensor replacement should be the same.
- Always use OEM sensors on Honda vehicles, as non-OEM sensors may not work properly with the ECM, even if they are functioning correctly.
- The exact location of the A/F sensor (Sensor 1) in a Honda vehicle can vary depending on the specific model and engine configuration. However, as a general guideline, it is typically located in the exhaust pipe near the bend from the engine to the catalytic converter.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The repair procedure for the P1157 Honda code falls under an intermediate DIY level. While enthusiasts with moderate mechanical skills can tackle it, exercising caution and following the steps precisely is important. For those who prefer professional assistance, don’t hesitate to consult a skilled mechanic.
Let’s review the diagnostic and repair tasks involved in addressing the P1157 Honda code. Here’s a breakdown:
| Repair Tasks | Estimated Costs |
| Wiring repair | $20 – $50 |
| A/F sensor replacement | $100 – $200 (parts and labor) |
| ECM update | $50 – $150 |
| ECM replacement | $500 – 1,000 (parts and labor) |
Remember, these are general estimates, and actual costs may differ. It’s advisable to consult local professionals and parts suppliers for the most accurate pricing information in your specific area.
P1157 Honda Infographic

Wrapping Up
Before we wrap up, let’s ensure your Honda runs smoothly with the P1157 code addressed.
If you have any more questions or need further assistance, feel free to ask.
Remember, you don’t have to tackle it alone – professional mechanics are always there to lend a hand.
Stay safe on the road and enjoy your Honda’s optimal performance!
Reference Sources
- Gershon (uCoz), Service Bulletin 03-020.
- Drive Accord Honda Forum, P1157 – New o2 sensor didn’t fix it.
- CR-V Owners Club Forum, P1157 Cannot resolve.
- Honda Accord Forum, P1157 code 2003 Accord LX.
P1148 Nissan Code: Closed-loop Control Issues & Solutions
P1148 Nissan Code: Closed-loop Control Issues & Solutions
If you own a Nissan and are dealing with the P1148 code, you’ve come to the right place.
This article is your go-to resource for all things P1148 Nissan code. I’m here to guide you through it all, sharing my expertise and experience to help you understand what this code means and how to fix it like a pro.
So, let’s dive in!
P1148 Nissan: A Quick Overview
Let’s take a quick look at the key details of the P1168 Nissan code in the summary box below!
- Definition: Closed Loop Control Function Bank 1
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $50 – $200
Inside The P1148 Nissan Code: What Does It Mean?
The P1148 code in Nissan vehicles indicates a problem with the closed-loop control function of the A/F sensor or the conventional Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) circuit for Bank 1. This code is triggered by the engine control module (ECM) when it detects that the closed-loop control function is not operating properly under certain driving conditions.
Note: Throughout this guide, when we refer to “sensor,” we mean both the A/F sensor and HO2S sensor, as they share similarities and can cause the P1148 code.

(Image credit: Pathfinder Talk forum)
To comprehend the P1148 code, it’s important to clearly understand the systems and components involved. The A/F sensor plays a vital role in measuring the oxygen content within the exhaust gases. This crucial data is then utilized by the ECM to finely adjust the air-fuel mixture, optimizing combustion efficiency for better performance.
This code is commonly found in models such as Altima, Pathfinder, Frontier, Titan, Murano, Sentra, Xterra, Maxima, Rogue, 350z, Armada, Quest, Versa, and Juke. It’s worth noting that this code often accompanies codes P0041 and P0031, both of which relate to O2 sensor concerns.
Read more: P1168 Nissan Code – a similar code to the P1148 code, but P1168 is specific to Bank 2 in Nissan vehicles.
How Serious Is The P1148 Nissan Code?
The severity level of the P1148 Nissan code can be considered moderate. While it does not pose immediate dangers or render the vehicle undrivable, addressing the problem as soon as possible is advisable.
Although you may be able to continue driving with the P1148 code for a limited period, it’s important to address the underlying issue. Prolonged driving without resolving the problem can decrease fuel efficiency and potentially impact engine performance.
To avoid further complications and potential damage, diagnose and repair the problem promptly. Taking proactive measures will help prevent more severe issues from arising down the road.
Warning Signs Of P1148 Nissan
The following are common symptoms associated with the P1148 code:
- Check Engine Light (CEL) and/or Service Engine Soon (SES) light illuminated
- Decreased engine performance
- Reduced fuel efficiency
- Rough idle
- Irregular exhaust emissions
Causes Of The P1148 Nissan Code
The P1148 code can be caused by various factors, including:
- Open or shorted circuit in the A/F sensor or HO2S circuit for Bank 1
- Malfunctioning A/F sensor or HO2S sensor for Bank 1
- Faulty A/F sensor or HO2S sensor heater for Bank 1
Read more: Nissan Trouble Codes: Comprehensive List For OBD1/OBD2 Codes
P1148 Nissan Code: DIY Diagnosis And Repair
If you’ve encountered the P1148 code in your Nissan vehicle, you can attempt a DIY diagnosis and repair before seeking professional assistance. Follow the step-by-step guide below:
Essential Tools And Parts
To diagnose and repair the P1148 code, you may require the following tools and parts:
- OBD-II scanner
- Multimeter
- Socket set
- Oxygen sensor socket (if needed)
- Replacement sensor (A/F or HO2S sensor) (if necessary)
Your Step-by-Step Guide To Tackle P1148
- Inspect the wiring and connectors associated with the sensor for Bank 1. Look for any signs of damage, loose connections, or corrosion. Ensure that the wiring is securely connected and free from any obstructions.
- Test the voltage and resistance of the sensor using a multimeter. This will help determine if the sensor is functioning within the specified range. Consult the vehicle’s service manual for the appropriate voltage and resistance values.
- If needed, remove the sensor using an appropriate oxygen sensor socket and replace it with a new one.
- Clear the code and perform a system test to ensure that you have resolved the issue.
Quick Tips:
- Apply anti-seize compound to the sensor threads before installation to facilitate future removal.
- Common location of A/F sensor for Bank 1 in Nissan vehicles: Typically, it’s bolted onto the exhaust manifold or front section of the exhaust pipe. Check the service manual or consult a Nissan dealership for exact location details.
Notes: It’s important to consult the vehicle’s repair manual for specific instructions and diagrams related to your particular Nissan model.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
Diagnosing the P1148 code and inspecting the wiring and connectors can be performed by DIY enthusiasts with intermediate-level skills. However, replacing the sensor may require more advanced knowledge and tools. If you’re unsure or uncomfortable with the repair process, we recommend consulting a qualified mechanic.
The table below provides estimated costs for common repair tasks associated with the P1148 code in Nissan vehicles.
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Diagnosing the code | $50 – $150 |
| Wiring harness connectors and terminals | $50 – $100 |
| Inspecting wiring/connectors | $50 – $100 |
| Replacing sensors | $100 – $200 |
Please note that these estimated costs are only for reference purposes and can vary based on location, the specific vehicle model, and labor rates. We recommend consulting a qualified mechanic or obtaining a detailed quote to assess the cost accurately.
P1148 Nissan Infographic
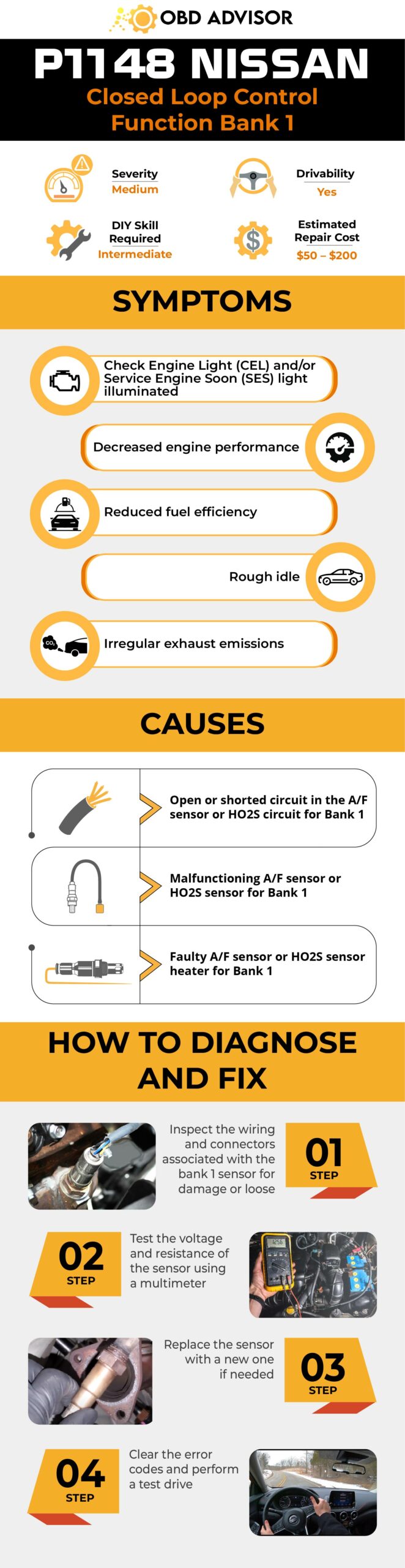
Final Thoughts
To wrap things up, taking on the P1148 code in your Nissan is entirely achievable.
Just make sure you have the right tools and follow the steps provided. By doing so, you’ll be able to address any issues with the A/F sensor and HO2S circuit for Bank 1, ultimately giving your engine a performance boost. You’ve got this!
Remember to stay cautious, consult the repair manual if needed, and consider professional help if unsure.
Share this knowledge with others and enjoy the journey of fixing your vehicle. Safe driving!
Reference Sources
- Tire Review Magazine, 2011 May 6, Fuel System Definitions and Diagnostic Trouble Codes.
- Automotive Manuals, 2007, Nissan Engine Control System Diagnosis Guide – page EC-393.
P1259 Honda Code: Resolving VTEC Issues in Your Vehicle
P1259 Honda Code: Resolving VTEC Issues in Your Vehicle
If you own a Honda vehicle and have encountered the P1259 code, it’s essential to understand its implications and take appropriate action. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll provide you with the knowledge and steps needed to diagnose and resolve the P1259 code, ensuring optimal performance and longevity for your Honda engine.
From symptoms to diagnostic procedures, we’ll walk you through the process, empowering you to tackle this code with confidence.
So, let’s delve into the details of the P1259 code in Honda vehicles.
P1259 Honda Code: A Quick Overview
Take a look at the summary of the Honda P1259 code provided below!
- Definition: VTEC System Malfunction
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $20 – $200
What Does The P1259 Honda Code Mean?
P1259 code is a manufacturer-specific code that is specific to Honda and Acura vehicles. It relates to the VTEC (Variable Valve Timing and Lift Electronic Control) system, a unique technology Honda developed. Some Honda models usually encounter this code, including Accord, Civic, CR-V, Odyssey, Pilot, etc.
The VTEC system is designed to optimize engine performance by adjusting the valve timing and lift according to driving conditions. It operates by using two different camshaft profiles: one for low-speed operation and the other for high-speed performance. This allows the engine to deliver both efficient and powerful performance across a wide range of driving scenarios.
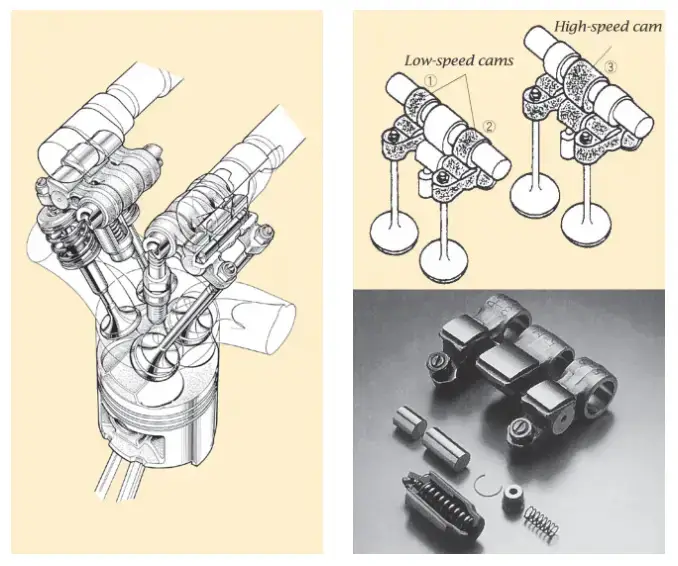
(Credit: global.honda)
The VTEC system in Honda engines engages at higher RPMs or when more power is needed. It uses oil pressure to adjust the camshaft lobes, optimizing valve lift and timing for improved efficiency and performance. This technology is a signature feature of Honda engines, offering benefits such as better fuel economy, increased torque, and overall enhanced performance.
However, when the VTEC system encounters a malfunction, the P1259 code is triggered. This typically indicates an issue with the VTEC oil pressure switch or the solenoid valve. These components play crucial roles in controlling the oil pressure and activating the VTEC mechanism.
Note:
- Honda has issued a Technical Service Bulletin (TSB) to help address the P1259 code in the 2001 Honda Accord models. The TSB suggests that a possible cause of the VTEC system malfunction and stored fault code is a low engine oil level. Before costly troubleshooting of the VTEC system, it is recommended to check the oil level and pressure. Ensuring proper oil supply and pressure may resolve the issue. If the problem persists or the oil level is adequate, consulting a qualified technician or visiting a Honda service center is advised for further diagnosis and repair.
- Typically, if the P1259 code is set below 4000 RPM, it indicates a potential wiring problem or a faulty VTEC pressure switch. However, when the code appears at 4000 RPM or higher, it is usually related to an oil-related issue.
How Severe Is The P1259 Code In Your Honda?
The severity level of the P1259 code in a Honda vehicle is generally considered to be moderate. While the vehicle may still be drivable with the P1259 code present, it is not recommended to ignore it. Therefore, we highly advise addressing the P1259 code promptly by diagnosing and repairing the vehicle.
The common symptoms associated with the P1259 code in Honda vehicles typically include:
- Check Engine Light (MIL) illumination
- Reduced engine performance
- Rough idling or stalling
- Decreased fuel efficiency
- Car shaking at idle
- Knocking or rattling sounds
- Reduced power output in VTEC mode, normal in non-VTEC mode
- Sluggish acceleration and difficulty downshifting in VTEC mode
Causes Of The P1259 Honda Code
The P1259 code in Honda vehicles can be caused by various factors, including:
- Low engine oil level or pressure
- Faulty VTEC oil pressure switch
- Malfunctioning VTEC solenoid valve
- Wiring or connector issues related to the VTEC system
- ECM (Engine Control Module) malfunction
Read more: P145C Honda Code: Expert Tips for Emission System Repairs
P1259 Honda Code: Diagnostic And Repair
In this section, we will provide essential tools and parts required, a step-by-step procedure for diagnosing and fixing the P1259 code, and discuss the level of DIY repair and estimated costs involved.
Essential Tools And Parts
To diagnose and repair the P1259 code in a Honda vehicle, you may need the following tools and parts (if required):
- OBD-II scanner or diagnostic tool
- Digital multimeter
- Engine oil dipstick
- Engine oil
- VTEC oil pressure switch
- VTEC solenoid valve
- Wiring diagram for the vehicle
Step-by-Step Procedure
- Code retrieval: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the P1259 code and record any additional associated codes.
- Check engine oil level: Using the engine oil dipstick, check the oil level and ensure it falls within the recommended range. If it falls out of the range, performing an oil change is a must.
- Inspect wiring and connectors: Examine the wiring and connectors related to the VTEC system for any visible damage or loose connections. Repair or replace if necessary.
- Test VTEC oil pressure switch and VTEC solenoid valve: Utilize a digital multimeter to perform tests on the VTEC oil pressure switch and VTEC solenoid valve, ensuring they function correctly. Replace the parts if needed.
- Verify wiring connections and continuity: Refer to the vehicle’s wiring diagram to confirm the proper wiring connections and continuity for the VTEC system.
- Clear the P1259 code: Clear the trouble code and test drive to make sure the code will not reappear.
Note: It is crucial to adhere to the specific diagnostic procedures provided in the vehicle’s service manual for precise diagnosis and repair of the P1259 code.
Read more: Honda OBD2 Codes List [Generic + Manufacturer-specific]
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The level of DIY repair for the P1259 code will depend on your mechanical experience and access to tools. DIY enthusiasts can perform basic diagnostic steps, such as checking the engine oil level and inspecting wiring connections.
However, dealing with component replacements like the VTEC oil pressure switch or VTEC solenoid valve may require intermediate to advanced mechanical skills. If you’re unsure or uncomfortable with these tasks, we recommend seeking professional assistance.
The estimated costs for repairing the P1259 code can vary depending on the specific vehicle and the need for parts replacement. So, here is a rough breakdown of potential costs:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Oil changing | $20 to $100 |
| VTEC oil pressure switch | $50 to $100 |
| VTEC solenoid valve | $100 to $200 |
Final Thoughts
Are you ready to tackle the P1259 code in your Honda vehicle? Well, with the knowledge you’ve gained, you can confidently diagnose and resolve this issue. Moreover, don’t keep this valuable information to yourself – share it with fellow Honda owners who may be facing similar challenges.
If you have any questions or success stories, we’re here to listen in the comments section below. Additionally, let’s keep our Honda engines running smoothly and efficiently. Drive with confidence and take care of your Honda!
Reference Sources
- Tech Tips Ireland, Honda Accord – Engine Light On Fault Code P1259 [PDF file]
- CarBrain, Unusual Car Noises That Might Ruin Your Budget
- Wikipedia, VTEC
P1449 BMW Code: What To Do When Encountering It
P1449 BMW Code: What To Do When Encountering It
Modern vehicles have advanced diagnostic systems that monitor various components for optimal performance. When a fault is detected, a specific error code is generated to aid technicians in identifying and resolving the issue. In the case of BMW vehicles, one common trouble code is P1449, which is specifically related to the DMTL (Diagnostic Module Tank Leakage) pump.
This article aims to shed light on BMW Code P1449, its symptoms, potential causes, and possible solutions. Moreover, by understanding the underlying factors contributing to this fault code, BMW owners and technicians can effectively diagnose and resolve the issue.
Let’s get started!
P1449 BMW: A Quick Overview
Look over the summary for the BMW P1449 code below!
- Definition: Diagnostic Module Tank Leakage Pump Current Too High
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $50 – $400
What Does The P1449 BMW Code Mean?
The BMW code P1449 indicates a fault within the vehicle’s evaporative emission control system, specifically related to the DMTL (Diagnostic Module Tank Leakage) pump. The evaporative emission control system is designed to prevent the release of harmful fuel vapors into the atmosphere, ensuring environmental compliance.
When the DMTL pump malfunctions or fails to operate as intended, it can trigger the P1449 error code. The DMTL pump is responsible for monitoring the fuel tank for leaks and maintaining the proper pressure within the evaporative emission system. Consequently, if the pump detects a leak or a pressure deviation, it signals the vehicle’s engine control module (ECM) and triggers the P1449 code.

Several BMW models are commonly associated with the P1449 code, including the BMW 3 Series, BMW 5 Series, BMW 7 Series, BMW X3, BMW X5, etc. In some cases, the P1449 code may be accompanied by additional codes, which can provide further insights into the specific issue.
Common accompanying codes related to the DMTL pump and evaporative emission control system, include P1447, P0442, P0455, and P0456. These accompanying codes help technicians narrow down the potential causes and pinpoint the specific area of concern within the evaporative emission control system.
How Severe Is The P1449 Code In BMW?
The severity of BMW Code P1449 can be considered moderate. While this fault code indicates a problem within the evaporative emission control system, it typically does not pose an immediate safety risk or cause drivability issues. However, it is important not to overlook or ignore this code.
It is generally okay to continue driving with this code in the short term. Still, to ensure that the vehicle complies with environmental regulations and the evaporative emission control system functions properly, it is recommended to address the P1449 code promptly.
What Are The Signs Of The P1449 BMW Code?
When a BMW vehicle experiences the P1449 code, the following symptoms may be observed:
- Check Engine Light (CEL) illuminated
- Fuel odor
- Difficulty starting the engine
- Decreased fuel efficiency
What Causes The P1449 Code In BMW Vehicles?
The P1449 code in BMW vehicles can be caused by various factors, including:
- Overfill the fuel tank
- Damaged DMTL wiring harness
- Malfunctioning DMTL pump
- Leaks or cracks in the fuel vapor lines
Repair And Diagnosis Of BMW Code P1449
This section provides a guide to diagnose and repair the P1449 code in BMW vehicles. It includes the necessary tools and parts, a step-by-step procedure, and information on DIY repair level and estimated costs. However, if you are unsure or lack experience, it is recommended to consult a professional mechanic or BMW dealership for accurate diagnosis and resolution.
Essential Tools And Parts
In order to effectively identify and rectify the C1109 code in Nissan vehicle, you will need the subsequent tools and components:
Step-by-Step Procedure
1. Code retrieval
Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the P1449 code and any accompanying codes.
2. Check for blown fuses
- Inspect the fuses related to the evaporative emission control system.
- Replace any blown fuses, as they may indicate a bad DMTL pump or a broken wire shorted to ground.
3. Inspect for vacuum leaks
- Check the fuel vapor lines for vacuum leaks.
- Look for cracked or disconnected hoses, loose fittings, or damaged connectors.
4. Replace OEM gas cap (if applicable)
- If your BMW has the “green” OEM gas cap, replace it with the blue gas cap.
- The blue cap provides a tighter seal and may help resolve the issue.
5. Check the DMTL pump
- Test the DMTL pump’s functionality using a multimeter.
- Assess the pump’s functionality and determine if it needs replacement.
- Ensure the rubber grommet on the old pump is used when reinstalling the pump.
6. Clear the code and test drive
- Once repairs are made, use the OBD-II scanner to clear the BMW C1449 code and any associated trouble codes.
- Take the vehicle for a test drive to verify if the car’s performance is back on track or not.
Note:
- The DMTL pump is usually located at the rear right side of the vehicle, positioned behind the wheel well liner. To find the exact location of the DMTL pump, it is advisable to refer to the manual.
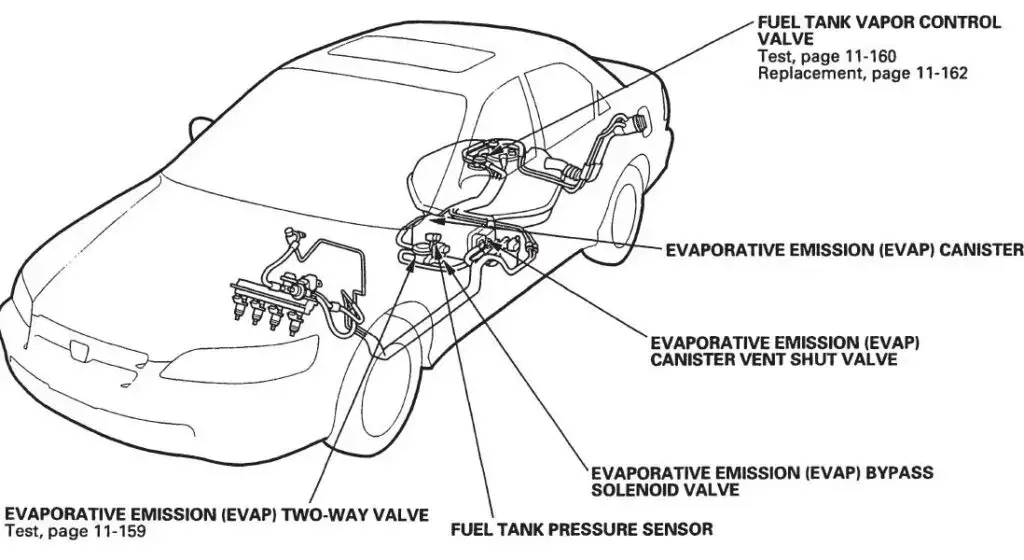
Read more: BMW Fault Codes: FREE Comprehensive OBD1 And OBD2 Codes List
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
Repairing the P1449 code demands intermediate to advanced DIY skills. If you’re confident in your experience with electrical and fuel systems, you can proceed. However, if you’re uncertain or lack relevant experience, it’s recommended to consult an expert mechanic or BMW dealership. They are equipped with specialized knowledge, tools, and resources for proper diagnosis and repair.
Estimated costs for the main repair tasks associated with the P1449 code may vary depending on factors such as the BMW model, location, and source of parts. Here is a table listing approximate costs:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Wiring and connector repair | $50 – $150 |
| Gas cap replacement | $30 – $70 |
| DMTL pump replacement | $200 – $500 |
Please note that these are rough estimates, and actual costs may differ. Consult a trusted mechanic or BMW dealership for accurate pricing and to ensure the use of genuine replacement parts. Remember, prioritizing safety and accuracy is crucial when dealing with complex automotive repairs.
Final Thoughts
Ready to conquer the P1449 code in your BMW? With the insights gained, you’re now equipped to diagnose and resolve the issue confidently. Moreover, don’t keep this knowledge to yourself – share it with fellow BMW enthusiasts who may be facing similar challenges.
If you have questions or success stories, we’re all ears in the comments section below. Furthermore, to keep your BMW running smoothly, stay tuned for more expert automotive guides. Hit the road with confidence!
Reference Sources
- New York State Department of Motor Vehicles, Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP)
- RepairSmith, Why Does My Car Smell Like Gasoline?
U1900 Ford Code: CAN Communication Bus Fault
U1900 Ford Code: CAN Communication Bus Fault
Discover the ins and outs of the U1900 Ford code with our expert guidance.
If you own a Ford vehicle and have encountered this code, understanding its meaning, severity, symptoms, causes, and the necessary steps for diagnosis and repair is crucial.
You’re in good hands! Count on our experience and expertise as we provide you with valuable insights to help you deal with the code.
So, let’s dive in!
U1900 Code on Ford: An Overview
Here’s a brief overview of the U1900 Ford code:
- Definition: CAN Communication Bus Fault (Receive Error)
- Severity: Low
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $0-$200
U1900 Ford Code Meaning: What Does It Signify?
The U1900 code on Ford indicates a failure in the communication bus. When the bus fails to receive a specific error or cannot relay that message to the powertrain control module (PCM), it triggers this error code. This can be caused by a communication failure between various components within the system.
In certain cases, this code is commonly found in models such as the Expedition, Explorer, F150, F250, and Focus. The CAN (Controller Area Network) serial communication system connects all the control modules in a Ford vehicle. However, U1900 primarily refers to communication failures within the circuits connecting the PCM, ABS control module, and instrument cluster. If any of these parts fail to transmit their signals to the PCM, the U1900 code may appear.
Note: The Ford U1900 code can occasionally be a “ghost code,” appearing when connecting a scanner to the data link connector with the ignition on or while the engine is running.
U1900 Ford Code Severity: Assessing Its Impact
The severity level of the U1900 fault code is low to medium. Many experienced mechanics and vehicle owners have reported that this code does not pose a significant concern.
In fact, it is often considered a “ghost code” (as noted above) or a result of the diagnostics process itself rather than an actual fault. However, it is worth mentioning that there might be other Ford-specific stored codes that may not be detected by a generic code reader.
(Image credit: Ford Owners Club)
Considering the widespread occurrence of this code and the general consensus among owners, there is no immediate cause for alarm. If your vehicle displays the U1900 code only without any apparent performance or drivability problems, it is generally safe to continue driving. However, it is advisable to monitor the vehicle’s performance and address any other related codes or symptoms that may arise.
U1900 Ford Code Symptoms: What To Look Out For
The U1900 Ford code typically does not cause specific symptoms or drivability issues on its own. However, in worst cases, it may be accompanied by these signs:
- Illumination of the check engine light and other dashboard lights like the ABS light or AWD light
- 4WD system malfunction (common in 4WD-equipped Ford applications)
- Potential no-start condition (especially on F-series trucks)
Read more: Ford Dashboard Symbols and Meaning (FULL list, Free Download)
Exploring U1900 Ford Code Causes
Common causes of the U1900 code include:
- Loose wiring connections
- Communication failure within the CAN system
- Faulty ABS control module
- Malfunctioning instrument cluster (possible racks in joints, connector pins, or pads on the printed circuit board)
- Issues with the trailer brake controller
Read more: Ford OBD2 Codes List for FREE Download
U1900 Ford Code Diagnosis And Repair
If you’re sure that the U1900 code is not a “ghost code” and it is affecting your driving experience, follow these steps to address the issue effectively.
Essential Tools And Parts
- OBD-II scanner
- Multimeter
- Wiring diagram for the vehicle
- Electrical contact cleaner
- Replacement wiring connectors (if necessary)
- Diagnostic manual for the specific vehicle model
Step-by-Step Guide
- Connect the OBD-II scanner and retrieve any stored codes.
- Inspect the wiring connections related to the U1900 code.
- Use a multimeter to check for continuity and proper voltage levels.
- Check for loose or damaged wiring connectors and repair or replace them as needed.
- Inspect the ABS control module, instrument cluster, and trailer brake controller for any visible signs of damage or malfunction.
- Clean the electrical contacts and ensure proper connections.
- Perform a thorough inspection of the CAN bus system and related components.
- If necessary, consult the vehicle’s diagnostic manual for specific troubleshooting steps.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The DIY repair level for the U1900 Ford fault code is moderate to advanced. You can try basic troubleshooting and inspections, but seeking professional assistance is advisable for complex electrical systems.
The estimated costs for repairing the U1900 code may vary depending on the specific cause and required repairs. Costs can range from minimal expenses for simple wiring repairs to higher expenses if components like the ABS control module or instrument cluster need replacement.
Here is a rough cost estimate for common repair tasks:
| Repair Task | Cost Range |
| Wiring repairs | $50 – $200 |
| ABS control module replacement | $200 – $600 |
| Instrument cluster replacement | $300 – $800 |
| Trailer brake controller replacement | $100 – $400 |
Please keep in mind that these cost ranges are approximate and can vary depending on various factors, such as the specific vehicle model, location, and labor rates. Consult a qualified mechanic or technician to get an accurate diagnosis and cost estimate for your vehicle.
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, the U1900 Ford fault code is generally not a big problem – if you have insights and knowledge about it.
You can fix the code and get everything back to normal by following the steps we’ve provided. If you’re uncomfortable working with electrical systems, it’s best to ask for help from a professional.
We hope this guide has been helpful to you. If you have any questions, feel free to ask in the comments below!
Reference Sources
- JustAnswer, U1900+dtc.pdf.
- Vehicle History, What does the Ford C-Max fault code U1900 mean?
- ACTRONICS LTD, Ford Focus instrument cluster – U1900 fault.
- TroubleCodes.net, U1900 – CAN Communication Bus Fault.
- FORScan forum, U1900 – CAN communication bus fault
- JustAnswer, Fix U1900 code.
- Ford Owners Club, U1900 code, I’ve tried everything.
P1217 Nissan Code: Engine Cooling Insights
P1217 Nissan Code: Engine Cooling Insights
P1217 Code: A Quick Overview
What Does The P1217 Code Mean On Nissan?
Sometimes, code P1217 is accompanied by other codes: DTC UXXXX and DTC P0607. DTC UXXXX points to communication problems in the vehicle’s networks, affecting various systems like the CAN bus. DTC P0607 indicates an issue with the ECM’s memory or processing, often due to electrical or software problems. Fixing these codes is essential for accurate communication between the ECM and other systems.
Before addressing P1217, it’s vital to tackle DTC UXXXX and DTC P0607. These codes highlight underlying issues that can impact temperature readings and engine performance. Addressing them first ensures proper system functioning and sets the stage for resolving the P1217 code effectively.
How Severe Is The Nissan Code P1217?
The severity of this code is moderate to high. Moreover, operating an overheating engine can lead to significant damage, including warped components and potential engine failure. Therefore, continuing to drive with this code activated is not recommended, as it may result in costly repairs and safety hazards.
If the P1217 code appears, it’s advisable to pull over, turn off the engine, and allow it to cool down. Additionally, prompt attention to this issue can prevent extensive damage and ensure the safety and reliability of your vehicle on the road.
What Are The Symptoms Of The P1217 Codes On Nissan Vehicles?
When encountering Nissan Code P1217, drivers and technicians may observe the following symptoms:
- Engine overheating
- Increased engine temperature gauge readings
- Illuminated check engine light
- Reduced engine performance
- Possible engine misfire or hesitation
Read more: P1564 Nissan Code: How to Get Your Cruise Control Back on Track
What Causes The P1217 Nissan Code?
The triggering of Nissan Code P1217 can be attributed to various factors, including:
- Open or shorted cooling fan circuit
- IPDM E/R problems
- Defective cooling fan motor
- Faulty radiator hose or radiator cap
- Bad radiator
- Water pump or thermostat problems
How To Diagnose And Fix The P1217 Nissan Code
Addressing Nissan Code P1217 involves a systematic diagnosis and repair process. Furthermore, here’s a breakdown of the essential tools and parts, followed by a step-by-step guide for the procedure.
Essential Tools And Parts
- Diagnostic scan tool (preferably with active test capability)
- Coolant pressure tester
- Basic hand tools (wrenches, sockets, pliers, etc.)
- Replacement coolant and engine oil
- Cooling system components (cooling fan, radiator, water pump, thermostat, etc.)
Step-by-Step Procedure
Before processing the diagnostic procedure, please top up your coolant to a specified level with a proper mixed ratio. In addition, you need to perform an oil change.
Step 1: Perform an “ACTIVE TEST” using a diagnostic scan tool to assess cooling fan speed.
Step 2: If needed, activate the IPDM E/R auto-active test to check the cooling fan motor operation.
Step 3: Check the cooling system for hoses, radiators, and water pump leaks. Repair or replace malfunctioning parts as necessary.
Step 4: Examine the radiator cap for any issues. Replace if needed.
Step 5: Inspect and test the thermostat’s functionality. Replace if required.
Step 6: Check the water control valve’s operation. Replace if faulty.
Step 7: Inspect the engine coolant temperature sensor. Replace if not functioning properly.
Step 8: If the root cause can’t be determined, refer to the troubleshooting chart for further analysis.
Note: If you’re not confident in completing these steps, consider seeking assistance from a professional mechanic.
Read more: P1701 Nissan Code: Get It Fixed With Ease Like Never Before
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The DIY repair level for P1217 diagnosis and repair can vary based on your experience and comfort level with automotive repairs. While some steps like checking coolant levels and inspecting components are relatively straightforward, tasks like replacing the water pump or thermostat might require more advanced skills.
For professional repair assistance, the estimated costs can vary depending on the specific problem and location. Moreover, here’s a rough estimate of potential costs for main repair tasks:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Coolant Flush and Change | $100 – $200 |
| Oil Change | $35 – $75 |
| Replacing Cooling Fan | $100 – $300 |
| Replacing Radiator | $150 – $400 |
| Replacing Water Pump | $100 – $250 |
| Replacing Thermostat | $50 – $150 |
P1217 Nissan Infographic

Final Thoughts
Facing the P1217 Nissan Code might seem daunting, but armed with the right knowledge, you’re well-equipped to tackle it head-on. Remember, the cooling system is a critical component that keeps your engine running smoothly, and issues like overheating can lead to costly repairs. Whether you’re a seasoned DIY enthusiast or prefer seeking professional assistance, staying proactive is key.
If this article helped shed light on the P1217 code or if you have any insights to share, we’d love to hear from you.
Feel free to drop a comment below and share this information with fellow car enthusiasts who might benefit. Safe driving, and stay cool under the hood!
Reference Sources
- Nissan Sentra. P1217 Engine Over Temperature.
- Nissan Altima. IPDM E/R (Intelligent Power Distribution Module Engine Room).
P1151 Ford Code: Decoding And Repair Guide
P1151 Ford Code: Decoding And Repair Guide
Are you facing the challenging P1151 code in your Ford vehicle? Look no further.
In this article, we provide you with a comprehensive guide to diagnose and resolve the P1151 code, empowering you to take control of the situation. From understanding the underlying causes to providing essential tools and a step-by-step procedure, we’ve got you covered.
Say goodbye to the P1151 code and hello to a smoothly-running Ford.
Let’s dive in!
P1151 Code on Ford: An Overview
Here’s a brief overview of the P1151 Ford code:
- Definition: Lack Of Upstream Heated Oxygen Sensor Switch Sensor Indicates Lean Bank 2
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes (short term)
- Estimated Repair Cost: $20 – $400
What Does The P1511 Mean In Ford Vehicles?
The P1151 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is a common issue encountered by Ford vehicle owners and is defined as “Lack of Upstream Heated Oxygen Sensor Switch Sensor Indicates Lean Bank 2”. This code is indicative of a problem within the upstream oxygen (O2) sensor. Specifically, it signals an issue with the air-fuel mixture, where the system is operating in a lean condition.
In simpler terms, there might be either insufficient fuel or an excess of air in the air-fuel mixture. The engine’s PCM continually adjusts this mixture to maintain optimal performance, but if the oxygen sensor detects a persistently lean environment for an extended period, it triggers the P1151 code.

The P1151 code is predominantly encountered in Ford vehicles. Common Ford models where this code may surface include: the F150, Mustang, Taurus, Ranger, or Expedition. You may also come across related trouble codes set along with P1151, such as P1131, P0171, and P0174.
P1151 Ford Code Severity
The severity level of the P1151 Ford code can be considered as medium. While it may not present an immediate danger to the safety of the vehicle, it should not be ignored.
Driving a vehicle with the P1151 code for short distances is generally acceptable as it may not immediately result in a breakdown or safety hazard. Leaving the issues unresolved for an extended period can potentially lead to severe damage to your vehicle. It is essential to address the underlying issue causing the code as soon as possible to prevent further complications and costly repairs.
P1151 Ford Code Symptoms
An illuminated Check Engine Light is commonly associated with the P1151 code. However, in some cases, there may be no noticeable symptoms or drivability issues at all.
Causes Of The P1151 Ford Code
The P1151 code in Ford vehicles can stem from various underlying causes. Some potential causes of the P1151 code include:
- Failing upstream oxygen sensor on bank 2
- Wiring or connector problems related to the oxygen sensor
- Fuel injector or fuel pressure regulator issue
- Clogged fuel injector
- Vacuum leaks
- PCM software issues or glitches
P1151 Ford Code Diagnosis And Repair
In this section, we will provide a step-by-step guide to diagnose and fix the P1151 code in Ford vehicles. Before proceeding, it is important to have the necessary tools and parts on hand.
Essential Tools And Parts
- OBD-II scanner or code reader
- Multimeter
- Oxygen sensor socket or wrench
- Wire connectors and electrical tape (for wiring repairs)
- Fuel pressure gauge
- Fuel injector cleaning kit (if needed)
- Vacuum hose and clamps (for vacuum leak testing)
- O2 sensor
Step-by-step Guide
- Connect the OBD-II scanner or code reader to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and retrieve the trouble codes. Verify that the P1151 code is present.
- Inspect the wiring and connectors related to the upstream oxygen sensor on bank 2. Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Repair or replace as necessary.
- Test the upstream oxygen sensor using a multimeter. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and compare the readings to the specified values. Replace the sensor if it is faulty.
- Check the fuel injector operation and fuel pressure regulator. Use a fuel pressure gauge to measure the fuel pressure and ensure it is within the specified range. Clean or replace the fuel injectors if necessary.
- Perform a thorough inspection of the intake manifold and vacuum lines for any leaks. Use a vacuum hose and clamps to test for leaks and repair or replace any damaged components.
- If no issues are found with the above components, consider updating the PCM software to the latest version. Consult the vehicle’s service manual or contact a Ford dealership for guidance on updating the software.
Note:
- Follow manufacturer instructions and specifications for sensor installation and torque specifications.
- Vehicles equipped with the 4.2-liter V6 engine are prone to the P1151 code. Ford has provided guidance in the Technical Service Bulletin (TSB) 05-22-6 for addressing the related issues. Give it a check if you have those types of engines.
Read more: Ford OBD2 Codes List for FREE Download
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The diagnosis and repair of the P1151 code can range from moderate to advanced, depending on your experience and access to tools. If you are uncertain or uncomfortable with the procedure, it is recommended to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic. Estimated costs for the main repair tasks include:
| Repair Task | Cost Range |
| Upstream oxygen sensor replacement | $50 – $200 |
| Wiring or connector repair/replacement | $50 – $150 |
| Fuel injector cleaning/replacement | $20 – $200 |
| Fuel pressure regulator replacement | $50 – $150 |
| Vacuum leak repair/component replacement | $150 – $500 |
| PCM software update | $50 – $150 |
Please note that these estimated costs are approximate and can vary depending on various factors such as the vehicle model, location, and labor charges. We always recommend obtaining specific cost estimates from a qualified mechanic or Ford dealership to ensure accurate pricing.
Conclusion
Are you ready to confidently address the P1151 code in your Ford vehicle? Equip yourself with the knowledge and step-by-step guidance to diagnose and resolve the issue. By following the step-by-step procedure outlined earlier, you’ll be able to approach the diagnosis and repair process systematically. With the P1151 code resolved, you can hit the road with renewed confidence.
Comment your questions and success stories in the section below. In addition, share this article with your Ford-owning friends who may be dealing with the P1151 code.
Reference Sources
- Ford Motor Company, MIL ON WITH DTC P1131 AND/OR P1151—4.2L ENGINE (TSB 05-22-6).
- CarParts.com, The Top 5 Symptoms of a Bad Fuel Pressure Regulator.
- Torque, Vacuum Leak: What Causes It and Expensive Fix.
P1077 Honda Code: Insights Into A Common CR-V Issue
P1077 Honda Code: Insights Into A Common CR-V Issue
Encountering the code P1077 in your Honda vehicle? Don’t worry, you’re not alone. This common issue is frequently reported by many Honda owners, particularly CR-V models.
In this guide, we’ll explore the meaning, severity, symptoms, causes, and diagnostic steps for P1077 Honda. Whether you drive a CR-V or another Honda model, we’re here to provide valuable insights and guide you through the diagnostic process.
Let’s get started!!
P1077 Honda Code: Quick Summary
In Honda vehicles, the IMRC system, or the Intake Manifold Tuning (IMT) system, consists of several components working together. These include the intake manifold, IMRC valve, actuator, solenoid, and vacuum hoses.
Let’s take a quick look at the P1077 Honda code and what it entails:
- Definition: IMRC/ IMT System Malfunction (Low RPM)
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes (short-term)
- Estimated Repair Cost: $100-$500
Inside P1077 Honda: What Does It Mean?
The code P1077 is an OBD-II diagnostic trouble code that indicates a malfunction in the intake manifold runner control (IMRC) system. This system is designed to optimize engine performance by varying the intake runners’ length, which helps improve low-end torque and high-end power.
Under normal operating conditions, the ECM commands the IMRC system to adjust the length of the intake runners based on factors like engine speed, load, and temperature. This adjustment is crucial for optimizing airflow and enhancing overall engine performance.

(Image credit: Civic Info forum)
However, when there is a malfunction in the IMRC system, the ECM detects an inconsistency between the desired and actual position of the intake manifold runners. This triggers the P1077 code, indicating that the system is not operating as intended.
It’s important to note that the P1077 code is commonly found in Honda CR-V and Civic models. These vehicles are known for their reliable performance and efficient engines. However, like any complex system, issues can arise over time, triggering diagnostic trouble codes such as P1077.
P1077 Honda Severity: Why Timely Action Is Essential
The P1077 code is classified as a moderate-level issue in terms of severity. While it may not pose an immediate threat to the vehicle’s or its occupants’ safety, it should not be ignored or left unaddressed.
So, should you continue to drive with this code? Yes, but for the short term only. Driving with the P1077 code present for an extended period can affect the engine’s performance and fuel efficiency. The malfunctioning IMRC system can lead to decreased power, reduced fuel economy, and potential drivability issues.
To prevent further damage and ensure optimal engine performance, addressing the P1077 code as soon as possible is advisable. By taking prompt action and resolving the P1077 code, you can ensure that your Honda continues to operate at its best and avoid any potential complications down the road.
Read more: Honda OBD2 Codes List
P1077 Honda Warning Signs
When encountering the P1077 code, several symptoms may manifest, alerting you to a potential issue with the IMRC system:
- Check Engine Light (CEL) illuminated
- Reduced engine power (especially under full throttle)
- Engine takes longer to shift from 2nd to 3rd
- Poor acceleration
- Rough idle
- Decreased fuel efficiency
Read more: Honda Dashboard Lights and Meaning (FULL list, Free Download)
What Triggers The P1077 Honda?
Several factors can contribute to the triggering of this code, including:
- Malfunctioning IMRC valve
- Defective intake manifold
- Vacuum leaks in the IMRC system
- Faulty IMRC actuator
- Wiring or electrical connection issues
- ECM software or programming glitches (rarely)
P1077 Honda Repair and Diagnosis
In this section, we will cover the essential tools and parts needed, provide a step-by-step procedure to diagnose and fix the P1077 code in a Honda CR-V, and discuss the level of DIY repair and estimated costs.
Attention: If you own a 2004 or 2005 CR-V, consult the TSB 05-052. It describes that the internal sticking of the IMT (IMRC) solenoid valve may trigger the P1077 code. Check if the symptoms described in the TSB match the observed problem. If yes, replacing the solenoid valve will solve the problem.
Essential Tools And Parts
To diagnose and repair the P1148 code, you may require the following tools and parts:
- Vacuum pump
- Scan tool
- Wiring harnesses and connectors
- Intake manifold (including runner, diaphragm, and sensor)
- Cleaning supplies for the intake ports
Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Perform Visual Inspection
- Open the hood and locate the engine’s intake manifold.
- Check if the vacuum hose linked to the intake manifold is connected correctly and receiving the vacuum.
Step 2: Check The Intake Manifold And Sensor Functionality
- Connect a vacuum pump to the intake manifold diaphragm while using a scan tool to monitor the sensor voltage.
- Repeat this process several times and observe if the sensor voltage readings are accurate and consistent. If the sensor readings are not correct, it indicates a problem.
Step 3: Test The Sensor
- Remove the intake runner sensor from the intake manifold.
- Manually move the sensor through its full range of motion to check for any glitches or abnormalities. Repair or replace the sensor if you find any faults.
- If the sensor moves smoothly without any issues, proceed to the next step.
Step 4: Check Wiring And Electrical Connections
- Inspect the wiring and connectors for the intake runner sensor, vacuum diaphragm assembly, and intake manifold.
- Look for any damage, loose connections, or corrosion. Test continuity with a multimeter and ensure secure connections.
Note: Working with electrical systems can be hazardous. Be careful!
Step 5: Inspect Vacuum Diaphragm Assembly And Intake Ports
- Remove the vacuum diaphragm assembly from the intake manifold.
- Inspect the assembly for any signs of oil inside it. If oil is present, it indicates an issue.
- With the intake manifold removed, check and clean the intake ports for carbon buildup.
Step 6: Replace The Intake Manifold
- Install the new intake manifold. Replacing the complete manifold (including a runner, diaphragm, and sensor) is recommended to prevent potential issues caused by the manifold warpage, which may lead to the new intake runner binding up.
- Test drive the vehicle.
Please note that the information provided above is a general guide. It’s always recommended to consult a qualified technician or refer to the vehicle’s specific repair manual, such as this DTC Troubleshooting Guide for P1077 on 2006 Honda CR-V, for detailed instructions and safety precautions.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The repair procedure for the P1077 code requires intermediate to advanced mechanical skills. It involves disassembling and reassembling components of the intake manifold. If you are unsure or uncomfortable with these tasks, you should seek assistance from an expert mechanic.
The estimated cost for the main repair tasks may vary depending on labor rates and the parts needed. Here is a general breakdown of potential costs:
| Repair Tasks | Estimated Costs |
| Vacuum Hose Repair/Replacement | $20 – $50 |
| IMRC sensor | $100 – $200 |
| Wiring repair | $20 – $50 |
| New Intake Manifold | $100 – $499 |
Please note that these are approximate costs, and it is advisable to check with local suppliers and mechanics for more accurate pricing information.
Remember, if you are not confident in your abilities or lack the necessary tools, it is always best to consult a professional mechanic to ensure the proper diagnosis and repair of the P1077 code.
P1077 Honda Infographic
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, diagnosing and repairing the P1077 code in a Honda vehicle can be challenging. Still, it is achievable with the right tools, parts, and knowledge. Following the step-by-step procedure outlined in this section, you can effectively address the IMRC malfunction and resolve the illuminated MIL issue.
Remember, if you’re unsure or uncomfortable with the repair tasks involved, it’s always recommended to seek assistance from a professional mechanic.
If you found this information helpful, share it with others who might benefit. Feel free to leave a comment below with your thoughts or questions. Happy repairing!
Reference Sources
- Diagnostic Network, 2004 Honda CR-V Intermittent DTC — P1077 IMRC. Diagnostic Network.
- 2CarPros, Code P1077: I Have a Good Idle and All Hoses Hold Vacuum.
- MotoLogic, DTC Troubleshooting: P1077 • 2006 Honda CR-V.
P1778 Nissan Code: Fix The Step Motor Malfunction!
P1778 Nissan Code: Fix The Step Motor Malfunction!
If you’re driving a Nissan with a CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission), you might be all too familiar with the challenges that can arise. One particular problem that can occur is the triggering of the frustrating P1778 code.
The P1778 Nissan code is directly related to the step motor within the CVT and can signal a range of issues affecting its performance. This article will provide clear explanations about the code and offer effective solutions.
Let’s delve into the details of the P1778 Nissan together.
P1778 Nissan: An Overview
Let’s take a quick look at the essential details of the P1778 Nissan code!
- Definition: Step Motor Function
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $30 – $200
What Does P1778 Mean In Nissan Vehicles?
The P1778 code in Nissan vehicles specifically refers to a problem in the Step Motor Function or its circuit within the CVT system. This code is commonly triggered in Nissan models such as the Altima, Murano, Rogue, Sentra, and Maxima.
The CVT system in Nissan vehicles relies on a step motor, also known as a stepper motor, to control the movement of the ratio control valve, which is responsible for regulating hydraulic pressure and selecting the appropriate gear ratio.
The P1778 code is specifically triggered when the TCM detects that the pulley ratio is not changing properly to match values commanded by TCM, resulting from the mechanical failure of the step motor.

(Image credit: nissanmurano.org)
It is worth mentioning that Nissan has taken steps to address the P1778 code issue through various recall campaigns. For instance, in 2013, there was a recall – the SB-10038184-2435 TSB, specifically for the 2010 Maxima, Murano, and V6 Altima models.
When encountering the P1778 code, the first step is to check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) from Nissan. These TSBs contain valuable information and recommended actions for specific vehicle models. By consulting the relevant TSB for your specific car, you can determine if your vehicle falls under a recall campaign or if there are particular actions you should take to address the P1778 code.
Read more: P1777 Nissan Code: Step Motor Circuit
Special Note Regarding P1778 Nissan Code – Transmission Reverse I/P Circuit Fault
The P1778 Nissan code can have different definitions depending on the car model. The most common definition, which this article focuses on, relates to the Step Motor Function within the CVT system. However, it’s worth noting that this code may be defined as a Transmission Reverse I/P (Input/Output) Circuit fault in certain car models.
This fault occurs when there is a discrepancy between the number of steps for the stepping motor and the actual gear ratio. It is a functional code, rather than a circuit code, for the step motor.
Unfortunately, this issue is often caused by a failing CVT transmission. However, there is some positive news to consider. Nissan has introduced an extended warranty for 10 years and 120,000 miles on the CVT of certain models. Consult with your nearest Nissan dealership or authorized service center for more information if you’re experiencing the Transmission Reverse I/P Circuit fault code.
How Serious Is The Nissan P1778 Code?
The severity level of the P1778 code in Nissan vehicles can be considered medium. It does not pose an immediate safety risk or cause the vehicle to become inoperable. Therefore, it is generally safe to continue driving with this code present.
However, it is essential to address the issue as soon as possible to prevent further damage to the transmission and ensure optimal vehicle performance. Ignoring the code for an extended period may lead to transmission-related problems, such as erratic shifting or reduced fuel efficiency.
Read more: Nissan OBD1/OBD2 Codes List
Common Symptoms Of P1778 In Nissan Vehicles
Common symptoms of the P1778 code in Nissan vehicles include:
- Check Engine Light (CEL) or Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated
- Transmission problems or abnormalities such as:
- Difficulty with light acceleration
- Unresponsive throttle when starting from a stop
- Failure to engage into gear or move
- Transmission stuck in safe mode
Read more: Nissan Dashboard Warning Lights List
Exploring The Causes Behind P1778 Nissan Code
The P1778 code in Nissan vehicles is often caused by:
- Faulty step motor
- Open or shorted step motor harness
- Poor wiring and connection in the step motor circuit
How to Diagnose And Repair P1778 In Your Nissan
Dealing with the P1778 code can be a real headache, especially when service advisors start talking about replacing your entire transmission and the costs pile up.
But here’s the truth: you may not need to break the bank. By taking care of your CVT fluid and addressing the step motor, you can often tackle the issue without draining your wallet.
Dive in and explore the steps to diagnose and repair P1778 in your Nissan, saving you some hard-earned cash.
Essential Tools And Parts
- OBD-II scanner
- Basic hand tools (wrenches, sockets, etc.)
- Multimeter
- Nissan CVT transmission fluid
- Transmission cooler
- Step Motor (if necessary)
Step-by-Step Procedure
Step 1: Retrieve trouble codes
Connect an OBD-II scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and retrieve any trouble codes. Check if there are any associated codes and prioritize addressing them first.
Step 2: Check the CVT fluid
Ensure the CVT fluid level is within the recommended range when the transmission is cold. If it is too high, drain some fluid to bring it to the correct level.
Inspect the CVT fluid. If it appears worn out or there are signs of aeration or contamination, you can either perform a transmission fluid flush yourself or consider having the CVT fluid professionally flushed and replaced.
Step 3: Inspect the trans cooler
Check the transmission cooler for any signs of damage or blockage that could affect fluid flow and cooling. Repair or replace if necessary.
Step 4: Inspect the step motor harness
Check for any damage or loose connections in the step motor harness. Repair if required.
Step 5: Test the step motor
Use a multimeter to test the step motor for proper voltage and continuity. Replace the Step Motor with a new one if necessary.
Step 6: Clear trouble codes and test drive
Use the OBD-II scanner to clear the trouble codes. Take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure that the code does not reappear and that the transmission functions appropriately.
Note: It’s important to refer to the vehicle’s service manual for detailed instructions and specifications during the process.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
Diagnosing the P1778 code can be done by an experienced DIYer, as it involves basic diagnostic procedures using common tools. However, replacing the step motor may require intermediate mechanical skills. It is recommended to consult the vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions.
Below is a breakdown of the main repair tasks and their estimated costs for repairing the P1778 Nissan code:
| Repair Task | Cost Range |
| Diagnostic Fee | $50 – $150 |
| Wiring repair | $50 – $200 |
| CVT fluid replacement | $50 – $200 |
| Step motor replacement | $50 – $150 (part and labor) |
Please note that these are rough estimates, and costs can vary depending on factors such as the vehicle model, location, and quality of parts. If you’re unsure about the diagnosis or repair process, it’s recommended to consult with an automotive professional or mechanic to ensure an accurate diagnosis and proper repairs are performed.
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, if you encounter the P1778 code in your Nissan vehicle, it’s crucial to take action and address it promptly. Ignoring the code can lead to potential transmission issues and increased repair costs. To resolve the problem, seek assistance from a qualified professional or consult your vehicle’s service manual for proper diagnosis and repair guidance.
If you’ve had any experiences or have questions about the P1778 code or any other OBD codes, we’d be thrilled if you could share them in the comments below.
Safe travels and happy fixing!
Reference Sources
- Nissan USA, Xtronic CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission).
- CarParts, Why the Nissan CVT Is Quite Possibly the Worst Transmission Ever Built.
- Pickup Truck Talk, How Reliable Is the Nissan CVT?.
P1132 Ford Code: Ignition Issues Explored
P1132 Ford Code: Ignition Issues Explored
You’re behind the wheel of your dependable Ford, when all of a sudden, a warning light illuminates, signaling a potential problem. Connecting a scanner reveals a puzzling “P1132” code.
Fear not – it’s simply your car’s way of highlighting a hiccup in the engine’s performance. This article takes you on a concise journey to understand the P1132 Ford code, its causes, symptoms, and what steps you can take next.
Let’s dive in and decode the mystery together!
P1132 Ford: A Quick Overview
Check the overview of the P1132 Ford code below!
- Definition: Lack of HO2S11 (Upstream Heated Oxygen Sensor) Switch – Sensor Indicates Rich – Bank 1
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $50 – $300
What Does The P1132 Code Mean On Ford?
The trouble code P1132 is specific to Ford vehicles and indicates an issue with the upstream heated oxygen sensor. This sensor measures the oxygen levels within the exhaust fumes, which helps the car computer (ECM) regulate the air-fuel mixture for efficient combustion. The code is triggered when the ECM detects a lack of variation in the sensor’s voltage signal.

In simpler terms, the oxygen sensor’s job is to tell the ECM about the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. This information helps the computer ensure the engine runs smoothly and produces minimal emissions.
The P1132 code comes up if the sensor’s signal doesn’t change as expected, indicating a problem with the sensor or its communication with the car computer. This behavior might imply that the sensor is persistently reporting one level of oxygen (either rich or lean) or not functioning as intended. This issue can affect how well the engine runs and how efficiently it uses fuel.
Note:
- Please note that the upstream heated oxygen sensor refers to the sensor located before the catalytic converter.
- The P1132 Ford code can sometimes be accompanied by other related codes, like P0171, P0172, P1131 Ford, P1152 Ford, etc., especially if the issue is affecting multiple components of the vehicle’s emissions and fuel system. However, it’s not always guaranteed that additional codes will be present alongside P1132.
How Severe Is The P1132 Ford Code?
The P1132 Ford code can be classified as having a moderate severity level, which means that while immediate catastrophic failure might not be imminent, it’s important not to underestimate the potential impact on your vehicle’s performance, emissions, and safety.
In the short term, you might be able to continue driving with the code present, but it’s strongly recommended to address the issue as soon as possible. Neglecting a malfunctioning oxygen sensor can gradually lead to decreased engine efficiency, reduced fuel economy, and increased emissions. Over time, these effects could compound and potentially cause further complications.
What Are The Symptoms Of The P1132 Code On Ford Vehicles?
The P1132 Ford code is often associated with a range of symptoms that can provide clues to the underlying issue. While not all symptoms might be present in every case, here are some common signs that you might experience when this code is triggered:
- Check engine light
- Reduced fuel efficiency
- Bad engine performance
- Increased emissions
- Rough idling
- Potential for engine overheating
- Lack of power
Read more: P1131 Ford: Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix
What Causes The P1132 Ford Code?
The P1132 Ford code can be caused by the following:
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Wiring issues
- Vacuum leaks
- Fuel system problems
- Exhaust system leaks
- Engine mechanical problems
- Bad ECM (rarely)
How To Diagnose And Fix The P1132 Ford Code
Diagnosing and addressing the P1132 Ford code involves a structured approach to identify the root cause and apply the appropriate fixes. Here’s a step-by-step guide and the needed tools and parts for the fixing process:
Essential Tools And Parts
- Heated oxygen sensor
- Wiring connectors and harnesses
- Vacuum hoses
- Fuel injector(s)
- Fuel filter
- Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve
- OBD-II scanner
- Multimeter
- Vacuum gauge
Step-by-step Procedure
Step 1: Inspect the oxygen sensor
- Visually inspect the wiring, connectors, and harnesses connected to the oxygen sensor.
- Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections that might be affecting the sensor’s operation. Replace the sensor if necessary
Step 2: Check for vacuum leaks
- Inspect the vacuum hoses and connections for leaks, cracks, or disconnections by using a vacuum gauge.
- Fix any vacuum leaks to ensure accurate sensor readings.
Step 3: Test the oxygen sensor
- Test the oxygen sensor’s response using a multimeter or a specialized testing tool.
- Compare the readings to the specifications provided in your vehicle’s repair manual or you can consult this link.
Step 4: Verify exhaust system integrity
- Inspect the exhaust system for leaks before the oxygen sensor.
- Repair any leaks that could introduce oxygen into the exhaust stream.
Step 5: Check fuel system components
- Inspect the fuel system components, including the fuel injector(s) and fuel filter.
- Ensure they are functioning correctly and not affecting the air-fuel mixture.
Step 6: Examine engine mechanical components
- Test the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor and Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve if applicable.
- Address any issues that could impact the air-fuel mixture.
Step 7: Check the ECM (if needed)
Consult with a dealership or qualified mechanic to check if your vehicle’s PCM or ECM requires a software update to resolve issues related to oxygen sensor monitoring.
Step 8: Clear codes and test drive
- After addressing any identified issues, clear the diagnostic trouble codes using the OBD-II scanner.
- Take your vehicle for a test drive to ensure that the code does not reappear and that the symptoms are resolved.
Read more: Complete List Of Ford OBD2 Codes for FREE Download
Estimated Costs For P1132 Code In Ford Vehicles
Estimating the cost to fix the P1132 Ford code can vary significantly based on factors such as the specific issue causing the code, your vehicle’s make and model and labor rates in your area.
Keep in mind that these are just rough estimates and the actual cost can differ. If you’re not confident in your DIY skills or want to ensure the issue is addressed correctly, it’s recommended to have a professional mechanic handle the diagnosis and repair.
While this might come with a higher upfront cost, it provides the peace of mind that the problem will be resolved accurately and that your vehicle’s performance and safety won’t be compromised.
Here’s a general breakdown:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Oxygen Sensor Replacement | $50 – $200 |
| Wiring and Connector Repair | $50 – $200 |
| Vacuum Leak Repair | $50 – $150 |
| Other Component Replacement (fuel injectors, MAF sensors, or EGR valves) | $100 – $300 |
| ECM Replacement/Repair (rarely) | $200- $1000 |
P1132 Ford Infographic

Final Thoughts
Understanding the P1132 Ford code empowers car enthusiasts to navigate potential engine concerns with confidence. From its subtle symptoms to its implications on performance, this code highlights the need for timely attention.
Whether you’re a DIY mechanic or rely on professionals, addressing the code promptly ensures a smoother, more efficient journey.
If this article proved insightful, consider sharing it with fellow drivers and leaving your thoughts in the comments below. Safe travels!
Reference Sources
- FIXD. Oxygen Sensor: How it Works, Symptoms of a Bad One, & Replacement Cost.
- Newparts.com. Bank 1 Sensor 1: Upstream or Downstream?
P1273 Nissan Code: A/F Issues And Lean Condition
P1273 Nissan Code: A/F Issues And Lean Condition
If you’re a Nissan vehicle owner who has encountered the P1273 error code, you’ve come to the right place. This code indicates specific air/fuel (A/F) issues and a lean condition within your vehicle’s system. This comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights into the meaning, severity, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and repair of the P1273 Nissan code.
Whether you’re an experienced car enthusiast or a novice owner, we’ve got you covered. We’ll break down the technical aspects and equip you with practical knowledge to confidently address this issue. Read on!
P1273 Nissan Code: A Quick Summary
Take a quick look at the key information of the P1273 Nissan code!
- Definition: Air Fuel Sensor (Bank 1 Sensor 1) Circuit Lean Shift
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $100 – $400
What Does P1273 Nissan Code Mean
The P1273 error code on Nissan refers to a potential issue in the fuel system. When this code is triggered in your car, it indicates a lean running condition, specifically related to the operation of air-fuel ratio sensor 1 on bank 1.
In other words, the engine control module (ECM) has detected an imbalance in the air-fuel mixture, which can impact engine performance. To understand this code better, let’s explore the components involved and how they interact.
The air-fuel ratio sensor, also known as the A/F sensor, plays a crucial role in measuring the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. It provides feedback to the ECM to ensure the optimal air-fuel mixture (14.7:1 stoichiometric ratio) for combustion. In Bank 1, the ECM monitors the air-fuel ratio for any deviations from the expected values.
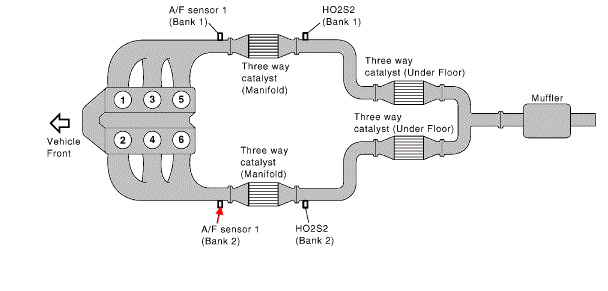
In certain conditions, such as during acceleration or deceleration, the ECM monitors lean-to-rich or rich-to-lean shifts. If the ECM detects a lean shift that persists beyond the specified parameters, it triggers the P1273 code.
It’s important to note that the P1273 code is commonly found in Nissan models such as Altima, Murano, Pathfinder, Sentra, Frontier, Quest, and 350Z. Altima, particularly the 2004 and 2005 models, is notorious for experiencing this code frequently.
Furthermore, there are other associated codes that may accompany P1273, including P1283, P0174, and various A/F sensor codes such as P0036, P0037, P0038, P0042, P0043, P0044, etc.
How Serious Is The P1273 Nissan Code?
The P1273 Nissan code is considered a medium-level severity. While it may not immediately cause a breakdown or severe damage to your vehicle, it should not be ignored. You can continue to drive with the code in the short term, but it is important to address it promptly.
(Image credit: 350Z UK Forum)
Prolonged driving with the P1273 code may result in reduced fuel efficiency, decreased engine performance, and possible damage to the catalytic converter over time. Ignoring the code can also trigger additional related codes, complicating the diagnosis and repair process.
Read more: Nissan Trouble Codes: Comprehensive List For OBD1/OBD2
P1273 Nissan: Spotting the Telltale Signs
When encountering the P1273 Nissan error code, several symptoms may manifest:
- Service engine light illuminated
- Engine hard to start in cold conditions
- Fuel smell
- Mode $06 fault
- Engine starts up but won’t stay on and stalls
However, in some cases, the vehicle may drive well with no noticeable drivability symptoms.
Read more: Nissan Dashboard Warning Lights and Meanings (FULL list, FREE Download)
Root Causes Of P1273 Nissan Code
Some common culprits behind the P1273 code include:
- Poor connection or wiring issues related to the A/F sensor
- Open or short circuit conditions in the A/F sensor circuit
- Failed air-fuel ratio sensor (A/F sensor)
- Vacuum leaks in the intake system
- Issues with the fuel delivery system, such as a clogged fuel filter or weak fuel pump
- Defective MAF sensor
- Malfunctioning ECM (rarely)
Note:
Please remember that the above causes are general and commonly associated with the P1273 code in Nissan vehicles. However, it’s essential to remember that the underlying causes may vary in specific cases.
For instance, based on my experience, I’ve encountered situations where issues with coolant quality and leakage into the engine have been identified as contributing factors. The story from member Stealthm in this forum thread is an example.
Efficient Strategies For Resolving The P1273 Nissan Code
In this section, we will provide step-by-step instructions and a list of essential tools and parts needed to address the issue. By following this guide, you can effectively identify and resolve the C1130 code.
Essential Tools And Parts
To diagnose and repair the P1273 code in a Nissan, you will need the following tools and parts:
- OBD-II scanner or code reader
- Basic hand tools (such as wrenches and sockets)
- Multimeter
- Fuel pressure gauge
- MAF sensor cleaner
- Electrical tape and wire connectors
- A/F sensor
- Intake system components: gaskets, hoses, etc.
- Fuel delivery system components: fuel filter, fuel pump, etc.
- MAF sensor
- ECM
Step-by-Step Procedure
1. Retrieve DTCs
Connect an OBD-II scanner to your Nissan vehicle and retrieve all trouble codes, including P1273. Note any additional codes present. Prioritize addressing the codes directly impacting the air-fuel ratio sensor or related systems.
2. Inspect wiring related to A/F sensor
Inspect the engine bay for damaged or loose wiring related to the air-fuel ratio sensor. Check for disconnected or worn vacuum hoses.
3. Check for circuit issues
Examine the A/F sensor circuit for open or short circuits. Inspect wiring harnesses and connectors. Repair or replace damaged wires or connectors.
4. Test the air-fuel ratio sensor
Measure the sensor’s resistance and voltage output using a multimeter or diagnostic tool. Compare readings to specified values in the service manual. Replace the sensor if it fails the test.
5. Inspect the intake system
Check for vacuum leaks in the intake system. Inspect gaskets, hoses, and components. Repair or replace faulty parts.
6. Check fuel pressure
Measure fuel pressure on the fuel rail (aim for at least 55 psi). If pressure is low, check the fuel pressure regulator, fuel filter, and fuel pump for issues. Repair or replace as needed.
7. Check MAF sensor and intake plumbing
Inspect the MAF sensor for dirt or debris. Clean it if necessary using MAF sensor cleaner. Check clamps and connections between the MAF sensor and throttle body for leaks or looseness.
8. Inspect the ECM
If the previous steps don’t resolve the issue, inspect the engine control module (ECM). Ensure proper connections and check for loose or damaged wires. Consult a professional if ECM malfunction is suspected.
Note:
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and any additional notes or tips in the service manual for your vehicle model.
- The A/F sensor location may vary depending on the specific Nissan model and engine type. To find the precise location of the A/F sensor in Nissan, refer to the vehicle’s manual or visit reliable online sources such as this diagram for A/F sensor location in Nissan Altima.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The DIY repair level for diagnosing and fixing the P1273 code in a Nissan is moderate. It requires basic mechanical knowledge and the ability to use diagnostic tools and perform sensor replacement.
The estimated cost for this repair task may vary depending on factors such as the brand and quality of the A/F sensor, labor rates in your area, and whether you choose to do the repair yourself or seek assistance from a professional mechanic.
Here is a table listing the estimated costs for the main repair tasks:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Diagnostic | $50 – $150 |
| Wiring repair | $50 – $200 |
| A/F sensor repair/replacement | $200 – $400 |
| Intake system components repair/replacement | $100 – $300 |
| Fuel delivery system components repair/replacement | $100 – $300 |
| MAF sensor repair/replacement | $100 – $300 |
| ECM repair/replacement | $200 – $1000 |
P1273 Nissan Infographic
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding and addressing the P1273 code in Nissan vehicles can help ensure optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. By following the general diagnostic and repair steps outlined, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve issues related to the Air/Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor or its circuit.
If you found this information helpful, share it with others who may benefit from it. Additionally, we would love to hear from you if you have any comments, questions, or personal experiences related to the P1273 code.
For information on other OBD2 codes and to troubleshoot specific issues with your vehicle, visit our OBD code lookup tool.
Safe travels and happy diagnosing!
Reference Sources
- Nissan Help Forum, P1273 – Nissan.
- My350z Forum, What does code P1273 mean?.
- YourMechanic, After oxygen sensor replacement I’m getting a P1273 error…
- Reddit, Question about code P1273 and P0174.
P1564 Nissan Code: How To Get Your Cruise Control Back On Track
P1564 Nissan Code: How To Get Your Cruise Control Back On Track
Imagine you’re driving your Nissan when suddenly the “Check Engine” light comes on. You decide to plug an OBD2 scanner in to know where the problem is, and you then discover that the culprit behind the warning is the P1564 Nissan code, linked specifically to the Advanced Speed Control Device (ASCD) steering switch.
In this article, we’ll focus on the P1564 code and explain it in simple terms. By the end, you’ll better understand the issue and what you can do to keep your car running smoothly. So, let’s dive in and unlock the mystery of the P1564 Nissan code!
P1564 Nissan: A Quick Overview
Below is a summary of the P1564 Nissan code. Check it out.
- Definition: ASCD Steering Switch Circuit Malfunction
- How Serious Is It?: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $20 – $1500
What Does The P1564 Nissan Code Mean?
P1564 is a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that pertains to Nissan’s ASCD system. This code is triggered when the Engine Control Module (ECM) detects irregularities in the ASCD steering switch’s electrical signals. This occurs when an excessively high voltage signal is sent from the ASCD steering switch to the ECM, the input signal from the switch is out of the specified range, or the switch is stuck in the ON position.
Let’s learn about the ASCD system. The ASCD steering switch consists of multiple buttons, each associated with specific cruise control functions like setting the desired speed, resuming previous speed, or canceling the system. The switch’s buttons have unique electrical resistance values, and when a button is pressed, the ECM reads the corresponding voltage variations to determine the intended function. So when the voltage is abnormal in the ASCD’s electrical signal, the P1564 is set.

(Credit: usa.nissannews.com)
How Serious Is The P1564 Nissan Code?
The P1564 Nissan code indicates a moderate level of severity. While it may not immediately impact drivability, it should not be ignored. If the ASCD steering switch malfunctions, the cruise control system may become inoperative, affecting driving comfort on long trips. In such cases, you can continue to drive the vehicle with caution. However, it’s essential to have the issue diagnosed and repaired promptly to restore the system’s functionality.
Read more: P1614 Nissan Code: Causes and Solutions of NATS Issues
What Are The Symptoms?
There are some symptoms if P1260 is set on your Ford:
- Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated
- Loss of cruise control capabilities
What Are The Potential Causes?
Causes of the P1564 Nissan code may include:
- Damaged wiring and connectors
- Bad ASCD steering switch
- Faulty ECM
How To Diagnose And Fix the P1564 Nissan Code?
Dealing with the P1564 Nissan code related to the ASCD steering switch can seem daunting, but you can resolve it step by step. Here’s a simple guide to help you fix the issue:
Essential Tools And Parts
- Diagnostic scanner
- ASCD switch assembly
- Multimeter
- Basic tools (screwdrivers, pliers, etc.)
Fixing Nissan P1564: Step-by-step Procedure
Step 1: Visual Inspection
Carefully examine the ASCD steering switch, like cancel sw, cruise lamp sw, or resume/acc sw, etc., and its wiring for any visible damage, loose connections, or signs of wear. Look for frayed wires, corroded connectors, or any other obvious issues that could affect the switch’s functionality.
Step 2: Check Electrical Resistance
Use a multimeter set to the resistance (ohms) setting. Measure the electrical resistance of each button on the ASCD steering switch. Compare the readings you get with the manufacturer’s specifications for each button. Significant deviations from the expected values could indicate a faulty switch.
Step 3: Test Voltage Signals
Set the multimeter to the voltage setting. Here are the expected voltage values you should get when you measure the G/Y wire at the ASCD steering switch with the ignition switch turned ‘ON’:
- When the ASCD steering switch is “OFF”, you should see around 4.0V.
- If the CRUISE switch is “ON”, the voltage should be approximately 0V.
- For the CANCEL switch being “ON”, the voltage should be around 1V.
- When the COAST/SET switch is “ON”, the voltage should be roughly 2V.
- Finally, if the ACCEL/RES switch is “ON”, you should read around 3V.
Step 4: Repair Or Replace
If all the values match the specifications above, then the switch is likely the problem. However, if any of the values are not within the expected ranges, the wiring might have an issue. It’s vital to get the wiring issues addressed in this case.
Step 5: Clear Codes
Using the diagnostic scanner, clear the P1564 code from the ECM. This step is essential after making repairs or replacements. Clearing the code will reset the system and allow you to check if the issue has been resolved.
Step 6: Functional Test
Take your vehicle for a test drive in a safe area. Engage the cruise control functions associated with the ASCD steering switch. Monitor the system’s performance and watch for any warning lights. Make sure the cruise control operates smoothly without any unexpected behavior.
Estimated Cost For Fixing P1564 On Nissan Vehicles
Safety should be a priority when dealing with vehicle repairs. If you find that the necessary skills and expertise required for these repairs are beyond your DIY abilities, it’s strongly recommended to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic. They have the experience and knowledge to ensure the repairs are done correctly and safely.
Below is a rough estimated cost breakdown for the mentioned repairs. Please keep in mind that these are approximate figures and actual costs can vary depending on various factors.
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Wiring and Connectors Repair | $50 to $200 |
| ASCD Steering Switch Replacement | $100 to $200 |
| ECM Replacement | $500 to $1500 |
P1564 Nissan Infographic

Conclusion
In conclusion, comprehending the P1564 Nissan code is crucial. Understanding the code’s implications empowers drivers to make informed decisions about their vehicle’s health. Whether you DIY or get pro help, grasping the code’s meaning means better car care. Decoding and tackling the P1564 code gets your car back on track and shows you’re a driver in the know, taking care of your ride.
If you found this article helpful in demystifying the P1564 Nissan code and grasping the ASCD steering switch, share it with others facing similar challenges. Have questions, insights, or experiences to share? Drop them in the comments below. Let’s start a discussion that enriches our driving journeys!
References Sources
- Nissan_Pathfinder_LE_P1564, PRODEMAND
- Nissan Altima 2007-2012 Service Manual: Automatic speed control device (ASCD), Nissan Altima
B1342 Ford Code: Essential Insights For Ford Owners
B1342 Ford Code: Essential Insights For Ford Owners
Welcome, Ford owners, DIY mechanics, and auto enthusiasts! Today, we’re going to tackle a common code that might have left you scratching your head – the B1342 Ford code.
If you’ve ever seen this code pop up and wondered what it means for your vehicle, you’re in luck. We’re here to break it down for you in simple terms.
Join us as we explore what the B1342 Ford code is, the signs to look out for, what causes it, and how you can diagnose and fix it yourself.
Let’s get started!
B1342 Ford: A Quick Overview
Before we dive into the details, let’s take a quick look at a summary of the B1342 Ford code!
- Definition: ECU Is Defective
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $200 – $500
What Does The B1342 Ford Code Meaning?
The B1342 code on Ford vehicles is commonly associated with a configuration error or fault in the Engine Control Module (ECU). The ECU is a critical component responsible for managing various systems and components in your Ford vehicle, such as the anti-lock braking system (ABS), airbags, climate control, and more. A malfunction within these systems can trigger the B1342 code, alerting you to a potential problem.
(Image credit: Explorer Forum)
The B1342 code commonly appears in several Ford models, including the Ford F150 (especially in the 2009 model year), Explorer, Escape, Expedition, Mountaineer Premier, and Crown Victoria. These models incorporate sophisticated electronic systems interacting with the ECU and BCM (Body Control Module), making them susceptible to triggering the B1342 code.
It’s worth noting that the appearance of the B1342 code doesn’t automatically pinpoint the exact component or system failure. It indicates that further diagnosis is required to identify the specific issue causing the code.
Can You Continue Driving With B1342 Ford?
The severity of the B1342 code is generally considered medium. While it does not indicate an immediate safety concern, it signifies a malfunction within the vehicle’s diagnostic system that can impact the performance of various systems.
Although you can continue to drive with the B1342 code present, it is not recommended to ignore it. Ignoring the code may lead to potential complications and adversely impact the functionality of the affected systems in the long run.
Read more: P1464 Ford Code: A Guide To Handling AC System Issues
Signs Of The B1342 Ford Code
The symptoms associated with the B1342 code in Ford vehicles can vary depending on the specific module that has malfunctioned within the diagnostic system.
Here are some common examples of symptoms observed in relation to this code:
| Malfunctioned Module | B1342 Code Symptoms |
| ABS Module | – ABS warning light turns on – Loss of traction control and stability control features – Braking system behaves unpredictably |
| Audio Control Module | – Issues with the audio system, such as no sound or distorted sound, may occur – Inability to adjust volume or change radio stations |
| Instrument Cluster | – Warning lights flicker or stay illuminated – Incorrect gauge readings (speedometer, fuel gauge, etc.) – Missing or inaccurate vehicle information display |
| Restraints Control Module (RCM) | – Airbag warning light illuminates – Airbags or seatbelt pretensioners may not function – Reduced passenger safety during a collision |
| Smart Junction Box (SJB) | – Multiple warning lights appear – Interior lights, power windows, or door locks malfunction – Unreliable functioning of electrical systems |
Read more: Ford Dashboard Symbols and Meaning (FULL list, Free Download)
Uncovering The Triggers Of B1342 Ford
Several underlying causes can activate the B1342 code in Ford vehicles. Here are some common causes often associated with this code:
- Faulty wiring or loose connections within the ABS module, RCM, SJB, or other related modules
- Power surges, voltage fluctuations, or other electrical system disruptions
- Malfunctioning ABS sensors, RSC sensors, or other relevant sensors
- Software bugs or programming errors within the ABS module, audio control module, instrument cluster, or other involved modules
- Faulty ECU or BCM
Read more: Complete List Of Ford OBD2 Codes for FREE Download
Diagnosing And Repairing B1342 Ford Code
Now that we’ve explored the meaning, severity, symptoms, and causes of the B1342 code in Ford vehicles, let’s delve into the essential steps for diagnosis and repair.
It’s important to note that the specific procedure may vary depending on the module that has a problem. Here’s a general outline:
Diagnostic Tools And Essential Parts
- OBD-II scanner
- Multimeter
- Wiring diagram and service manual specific to your Ford model
- Wiring harness connectors and terminals (if needed)
- Replacement of malfunctioning modules (ABS module, audio control module,..)
Step-by-Step Procedure
- Connect an OBD-II scanner or diagnostic tool to retrieve the B1342 code and any accompanying codes.
- Inspect the wiring connections and harnesses related to the module associated with the B1342 code. Look for loose connections, damaged wires, or corrosion.
- Perform electrical tests using a multimeter to check for voltage irregularities or shorts in the wiring. Refer to your Ford model’s wiring diagram and service manual for guidance.
- Check the sensors associated with the module for malfunctions or failures. Test the sensors using appropriate diagnostic procedures.
- If necessary, reprogram or replace the module following the manufacturer’s instructions. Inspect the module for any visible damage signs, such as burnt components or water intrusion.
- Once the repairs or replacements have been made, clear the codes using the OBD-II scanner.
- Perform a test drive to ensure the issue has been resolved and no codes reappear.
Remember, this is a general approach, and the specific steps may vary depending on the module involved. It’s recommended to consult the appropriate service manual and follow manufacturer guidelines for accurate diagnosis and repair.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The level of DIY repair for the B1342 code diagnosis and repair procedure can range from moderate to advanced, depending on your technical skills and access to tools. If you’re unsure or uncomfortable with the process, it’s advisable to seek the assistance of an expert or professional mechanic.
As for the estimated costs, they can vary depending on the specific cause and required repairs. Here’s a rough breakdown of potential expenses:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Diagnostic scan or professional assistance | $50 – $150 |
| Wiring harness connectors and terminals | $50 – $100 |
| Replacement of malfunctioning sensors | $50 – $200+ (including parts and potentially labor if needed) |
| Replacement of malfunctioning modules (e.g., ABS, audio, etc.) | $200 – $600+ (including parts and potentially labor if needed) |
B1342 Ford Infographic

Final Thoughts
Great job on uncovering the meaning of the B1342 code in Ford vehicles! Now you know more about it and how to tackle the issue.
Remember, maintaining a healthy diagnostic system is crucial for the optimal performance of your Ford vehicle. If you ever see the B1342 code or face any other car problems you’re uncomfortable with, get help from a trusted mechanic or expert.
Have you successfully fixed the B1342 Ford code? Share your experiences in the comments below. Let’s talk and support each other with car diagnostics.
Stay safe on the road, and good luck fixing any issues!
Reference Sources
- Kelley Blue Book, OBD-II Trouble Code: B1342.
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, 2019, Safety Recall 19V-904.
- Ford Motor Company, 2011, TSB 11-3-3.
- Lima-City, Smart Junction Box (SJB).
- Reddit, B1342 Fault Code ABS Module Bad.
- 2CarPros, Code B1342.
P1780 Ford Code: Tackling Transmission Concerns Head-On
P1780 Ford Code: Tackling Transmission Concerns Head-On
Welcome to our guide, where we embark on a journey to decode the P1780 Ford code. As a fellow car enthusiast, I understand the frustration it can spark. But fret not! In this article, we’re stepping into the intricate world of automotive diagnostics, unraveling the puzzle of the P1780 code in your Ford.
With a blend of technical know-how and practical advice, you’ll be equipped to tackle this challenge head-on.
So, let’s dive into the P1780 Ford code and tackle it together, armed with knowledge and determination!
P1780 Ford Code: A Quick Overview
Check the overview of the P1780 Ford code below!
- Definition: Transmission Control Switch Circuit Out of Self Test Range
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $20 – $150
What Does The P1780 Code Mean On Ford?
The P1780 code signifies a Transmission Control Switch Out of Self-Test Range error in Ford vehicles. It points to a potential fault in the transmission control switch (TCS). This code is triggered when the transmission control switch fails to change states as expected.
(Credit: f150forum.com)
The TCS is primarily situated on the shift plate or shift knob, enabling drivers to select different gears while on the move. Commonly denoted as “OD off” or “OD cancel,” or occasionally as “Tow/Haul” in certain trucks, this button serves a specific purpose. Primarily, it prevents the transmission from engaging in overdrive mode. When the P1780 code is set, it means that the TCS is experiencing a malfunction, a situation that can adversely affect the normal functioning of the transmission.
The P1780 code can manifest across various Ford models equipped with automatic transmissions. While not an exhaustive list, some of the Ford models that may encounter this issue include F-150, Explorer, Ranger, Mustang, etc.
Read more: P1464 Ford Code: A Guide To Handling AC System Issues
How Severe Is The Ford Code P1780?
The P1780 code indicating a TCS fault in Ford vehicles carries a moderate severity level. While it doesn’t pose an immediate safety risk, it can lead to transmission-related issues. It’s possible to drive with this code unaddressed. However, it could result in erratic gear changes, reduced fuel efficiency, and potential transmission overheating.
It’s advisable not to ignore this code and to have the TCS inspected and repaired by a qualified technician. Continued driving with a malfunctioning TCS might exacerbate transmission problems, potentially leading to costly repairs. Addressing the issue promptly ensures consistent transmission performance and prevents further complications down the road.
What Are The Symptoms Of The P1780 Codes On Ford Vehicles?
Experiencing the P1780 code in a Ford vehicle may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Check engine light
- Incorrect or erratic shifting
- Inability to shift gears
- Illuminated overdrive light on the dashboard
- Reduced fuel efficiency
- Transmission control indicator lamp
What Causes Of The P1780 Ford Code?
The P1780 code in Ford vehicles can arise from various underlying causes, including:
- Faulty TCS
- Wiring or connector issues related to the TCS
- ECM issues
How To Diagnose And Fix The P1780 Ford Code?
Confronting the P1780 code within your Ford vehicle demands a methodical strategy for effective resolution. So, here’s a breakdown of the essential tools and parts, followed by a step-by-step guide for the procedure.
Essential Tools And Parts
To successfully diagnose and repair the P1780 code, you’ll need the following tools and parts:
- Shift knob or shift plate replacement (if needed)
- Wiring and connector
- OBD-II scanner
- Multimeter
- Wiring diagram
Step-by-Step Procedure
Step 1: Fuse inspection
- Turn off the key
- Measure fuse resistance with a value of less than 5 ohms
- If resistance is below 5 ohms, replace the fuse
Step 2: Short to ground check
- Disconnect the ECM
- Measure resistance between PIN 41 and ground
- Resistance should exceed 10,000 ohms
- If it’s less, repair the circuit
Step 3: Voltage test for TCS circuit
- Disconnect the ECM
- Turn the key to the on position
- Measure the voltage between Pin 41 and the ground while cycling the TCS switch
- If voltage cycles, the ECM requires replacement
Step 4: Open circuit examination
- Turn off the key
- Disconnect the central junction box and transmission control switch
- Measure resistance between CJB fuse 2.13 Pin 10 and power side of TCS Pin 2
- Measure resistance between CJB fuse 2.13 Pin 10 and power side of TCS Pin 1
- Both resistances should match. If not, repair the circuit
Step 5: Short to power check
- Measure resistance between Pin 41 and Pin 1
- Resistance should surpass 10,000 ohms
- If not, repair the circuit
If these steps fail to identify the issue, consider replacing the transmission control switch. In case of uncertainty during testing, follow the steps sequentially and retest accordingly. This thorough approach ensures accurate diagnosis and effective resolution.
The TCS is positioned at various locations on Ford models, commonly integrated into the shift knob or shift plate. Replacing the attached assembly is typically required, as the switch is generally affixed and cannot be individually replaced.
Step 6: Clear code(s) and test drive
Clear the codes with the OBD-II scanner and test drive the vehicle to ensure proper shifting.
Note:
- Double-check the wiring connections before replacing the TCS.
- Be cautious while working around the transmission components.
Read more: P1132 Ford Code: Ignition Issues Explored
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
If you’re confident in your automotive skills, you might consider tackling the issue. Nevertheless, if uncertainties arise, seeking a mechanic’s expertise is advisable.
For those seeking professional repair assistance, costs can vary depending on the specific problem and your location. However, here’s a basic idea of how much you might need to pay for the main repair tasks:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Shift knob or shift plate replacement | $50 – $200 |
| Check and Repair Wiring | $50 – $150 |
| ECM Replacement (rarely) | $200- $1000 |
P1780 Ford Summarize Infographic
Final Thoughts
Armed with insights into the P1780 Ford’s meaning, symptoms, and possible causes, you’re now poised to tackle this challenge head-on. Whether you’re a hands-on enthusiast or prefer professional intervention, addressing the issue is paramount.
Join the conversation – share your experiences or questions in the comments below. Additionally, if this guide proves invaluable, spread the know-how and invite others to explore. Keep the wheels turning smoothly and the road ahead clear. Drive confidently!
Reference Sources
- JustAnswer, P1780 Ford Code Diagnosis
- Yourmechanic, Is It Safe to Drive With the Overdrive Light On?
- Bluespringsfordparts, DTC Decoded: P1780 – Transmission Control Switch Circuit
P1009 Honda Code: VTC System Troubleshooting And Solutions
P1009 Honda Code: VTC System Troubleshooting And Solutions
Discover insights into the P1009 Honda code intricately linked with your Honda’s VTC (Variable Valve Timing Control) system. If you’ve come across this code, there’s no need to worry.
Within this article, we’ll thoroughly explore the P1009 Honda code, its correlation with the VTC system, its implications, severity, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and repair steps.
Leveraging my extensive experience as a seasoned mechanic, I’m here to provide guidance and knowledge to navigate this challenge.
Let’s get started!
P1009 Honda Code: A Quick Overview
Check the summary of the Honda P1009 code provided below!
- Definition: VTC Advance Malfunction
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes (short-term)
- Estimated Repair Cost: $30 – $300
What Does The P1009 Code Mean On Honda?
The diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P1009 in Honda vehicles is an indication of an issue related to the timing control of the variable valve system. More specifically, this code points to problems within the Variable Valve Timing Control (VTC) system.
The VTC system plays a crucial role in determining the opening of the intake camshaft, effectively managing the amount of oil that flows into the camshaft. This control over oil flow is pivotal in optimizing valve timing for the engine’s performance.
The VTC actuator, a central component of this system, is operated through oil pressure. It dynamically adjusts valve timing to maximize power output and ensure efficient operation under varying driving conditions. The valve timing, crucial for proper engine functioning, is directly influenced by the prevailing driving conditions.

A significant player in maintaining precise camshaft timing is the Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor. This sensor collaborates with the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to ensure accurate monitoring of the camshaft’s timing. The PCM provides control commands that are continuously monitored to set the correct direct value for camshaft timing.
When the camshaft phase becomes excessively advanced or deviates abnormally from the direct value, the system detects and stores the P1009 code. This DTC serves as an alert that a malfunction exists within the VTC system. To identify this malfunction, a diagnostic scanner is employed to read the code and highlight the issue.
The P1009 code has been known to appear in various Honda models, indicating potential problems within the VTC system. Some of the Honda models that are commonly associated with the P1009 code include CRV, Accord, Element, Civic, etc.
How Severe Is The Honda Code P1009?
The P1009 code indicates a moderate level of severity. While it may not immediately make your vehicle inoperable, it should not be ignored. Ignoring this code could lead to diminished engine performance, reduced fuel efficiency, burning oil and potential long-term damage to the engine components related to the VTC system.
Is it safe to drive with the Honda P1009 code? – Yes, you can, but short-term only. However, it’s not advisable. Ignoring the issue could result in higher repair costs down the road. To prevent further damage and maintain optimal performance, it’s recommended to have the issue diagnosed and repaired by a qualified mechanic as soon as possible.
What Are The Symptoms Of The P1009 Codes On Honda Vehicles?
When the P1009 code appears in a Honda vehicle, it can manifest through various symptoms, indicating potential issues within the VTC system. These symptoms may include:
- Check engine light
- Reduced power (particularly during acceleration)
- Rough idling
- Poor fuel efficiency
- Car vibration
- Engine misfires
Read more: A Full List Of Honda OBD2 Codes [Generic + Manufacturer-specific] for FREE
What Causes The P1009 Honda Code To Be Set?
The P1009 code can be triggered by various underlying causes, leading to issues in the VTC system. Some common causes include:
- Wiring or connector faults related to the VTC circuit
- Faulty VTC actuator
- CMP sensor issues
- Oil flow restrictions
- Timing chain/belt problems
- PCM malfunction
How To Diagnose And Fix The P1009 Honda Code?
Dealing with the P1009 code in your Honda needs a clear plan. This part explains the important tools and the step-by-step process. We’ll also talk about costs. By following these steps, you can take care of the P1009 code and keep your Honda running well.
Essential Tools And Parts
To successfully diagnose and repair the P1009 code, you’ll need the following tools and parts:
- OBD-II scanner
- Basic hand tools
- New VTC actuator (if needed)
- Camshaft position sensor (if required)
- Engine oil and oil filter
Step-by-Step Procedure
- Visual inspection: Inspect wiring, connectors, and the VTC actuator for visible damage or corrosion.
- Check the VTC strainer for clogging: If it is clogged, clean it.
- Check oil level: Ensure the engine oil level is correct and the oil quality is good. Replace engine oil and oil filter if needed.
- VTC actuator replacement: If the actuator is faulty, replace it following manufacturer guidelines.
- CMP sensor replacement: If needed, replace the sensor according to your vehicle’s specifications.
- Oil flow check: Confirm proper oil flow to the VTC actuator and address any restrictions.
- Clear Codes: Use the scanner to clear the codes and restart the engine to see if the issue persists.
Note:
- Before you start fixing the problem, remember to write down all the freeze data and on-board snapshots. Also, take a good look at the general troubleshooting instructions.
- If you see both DTC P0341 and DTC P1009, work on the P1009 issue first. Then, recheck the P0341 problem.
Read more: P1399 Honda – Random Cylinder Misfire Detected
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
If you are a DIYer and feel comfortable working on engine components, you might consider addressing the P1009 code independently.
When uncertainties arise during the repair process, or you lack experience, seeking an experienced mechanic’s skills is strongly advised.
| Repair TaskEstimated CostVTC Actuator Replacement$150 – $300 (parts and labor)Camshaft Position Sensor Replacement$50 – $100 (parts and labor)Engine Oil Replacement$30 – $50 (oil and filter)Wiring and Connector Repair$50 – $150 |
P1009 Honda Infographic
Final Thoughts
Knowing and fixing codes like P1009 is super important to keep your car running great. The VTC system affects when the engine does stuff, so fixing it quickly really matters.
Whether you’re a seasoned DIY enthusiast or prefer the expertise of a skilled mechanic, tackling the P1009 code ensures a smoother driving experience and prevents potential long-term issues.
Sharing your experiences or questions in the comments. If this guide has been a helpful companion, consider passing it on to fellow Honda owners. Your commitment to your car’s health ensures smoother rides and exciting journeys on the horizon.
Reference Sources
- HCRV, DTC P1009 VTC Advance Malfunction.
- HELLA, Camshaft Position Sensor.
- J.D. Power, What Happens When a Car Misfires.
P1168 Nissan Code: Discover Meaning, Causes & Simple Repair Steps
P1168 Nissan Code: Discover Meaning, Causes & Simple Repair Steps
If you’re a Nissan owner encountering the P1168 code, you’re probably looking for answers. Don’t worry—I’m here to help!
Before you go ahead and replace the O2 sensor right away, let’s take a step back. It’s important to understand the root cause of the issue before jumping to any conclusions.
In this article, my goal is to guide you through the ins and outs of the P1168 code. Together, we’ll explore what’s going on behind the scenes. Plus, I’ll provide you with practical tips to diagnose and fix the problem.
So, let’s dive right in and get to the bottom of the P1168 Nissan code!
P1168 Nissan: A Quick Overview
Check out the handy summary box below for a quick overview of the P1168 Nissan Code!
- Definition: Closed Loop Control Function Bank 2
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $50 – $100
What Does The P1168 Code Mean On Nissan?
The P1168 code found in Nissan vehicles indicates a potential problem within the Air Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor or Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) circuit. When the engine control module (ECM) detects that the closed-loop control function for bank 2 fails to operate, even under the specified conditions while driving, this code is triggered. This code is mostly common in Nissan Titan, Xterra, Murano, Pathfinder, and Nissan Maxima vehicles.
The A/F sensor, or HO2S, is a critical component in the fuel system as it measures the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. This information helps the ECM adjust the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion efficiency. Therefore, encountering the P1168 code suggests a fault with the A/F sensor or its circuitry.

(Image credit: My350z.com forum)
In a closed-loop condition, the ECM continuously monitors sensors to make real-time adjustments to fuel delivery. A closed-loop fault indicates an issue with the A/F sensor or HO2S circuit, disrupting the closed-loop control process.
Additionally, it’s worth noting that the P1168 code may be accompanied by other codes like P0501 (related to the vehicle speed sensor) and P1286 (related to the engine coolant temperature sensor). These additional codes suggest potential issues with the oxygen sensor system and engine coolant temperature regulation, impacting fuel delivery and engine performance.
Is The P1168 Nissan Code Severe?
The severity level of the P1168 Nissan code can be considered moderate. Although it signifies an issue with the A/F sensor or HO2S circuit, it does not imply immediate danger or render the vehicle undrivable.
Some of you might come across several forum discussions suggesting that the P1168 code is not a big deal and you can keep driving without any worries. They even state that the P1168 code only indicates that your Nissan’s catalytic converters might be operating more efficiently than stock, reducing the risk of blowback into the engine. Moreover, there’s an opinion that you shouldn’t worry about this code if you live in a non-emissions county.
However, let me offer you some friendly advice from a mechanic’s perspective. While you’re good to go (for A LITTLE WHILE) with the P1168 code, it’s still a good idea to address the issue sooner rather than later.
While driving with this code won’t pose immediate risks, you may experience decreased fuel efficiency and potential impacts on your vehicle’s performance. To avoid further complications, it’s best to diagnose and repair the issue as soon as possible. Taking proactive measures will prevent more severe issues from arising down the road.
What Are The Warning Signs Of The P1168 Nissan Code?
Beware of these telltale signs that could point to the presence of the P1168 Nissan code:
- Check Engine Light (CEL) illuminated
- Reduced engine performance
- Poor fuel efficiency
- Rough idle
- Abnormal exhaust emissions
- Service Engine Soon (SES) light illuminated (in some cases)
Read more: Nissan Dashboard Warning Lights and Meanings (FULL list, FREE Download)
What Causes The P1168 Nissan Code?
Here are some potential causes of the P1168 Nissan code:
- Open or shorted circuit in the heated oxygen sensor 1 bank 2
- Malfunctioning heated oxygen sensor 1 bank 2
- Faulty heated oxygen sensor 1 heater bank 2
How To Diagnose And Fix The P1168 Nissan Code
In this section, we’ll walk you through the steps to effectively troubleshoot and resolve the P1168 Nissan code. Let’s get started on getting your Nissan back on the road with confidence.
Essential Tools And Parts
- A/F sensor for bank 2
- Sensor gasket or seal
- Electrical connectors
- Wire connectors
- Wrench set
- Wire cutters
- Electrical tape
- Electrical cleaner
- Jack and jack stands
Step-by-step Procedure
Step 1: Get access to the A/F sensor. It is often located before the Catalytic Converter on Bank 2. You can access it conveniently through the driver’s side wheel well.
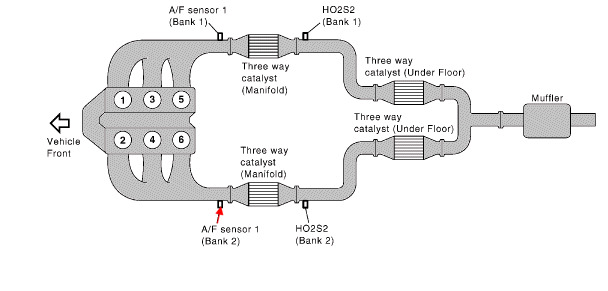
 Check this diagram to locate your Nissan’s A/F sensor 1 bank 2.
Check this diagram to locate your Nissan’s A/F sensor 1 bank 2.(Image credit: justanswer.com)
Step 2: Take a close look at the sensor’s electrical connector and wiring harness. Look for any signs of loose, broken, or damaged wires. Ensure that the connector is securely plugged in.
Step 3: Locate the ground wire, usually black in color, and trace it to its connection point on the vehicle’s chassis or engine. Make sure it is firmly attached without any corrosion or looseness. If needed, clean the connection and reattach the wire securely.
Step 4: Use a multimeter to test the wiring for any issues to ensure there is no discontinuity or abnormal resistance.
Step 5: If the above checks do not reveal any issues and the problem persists, it may be necessary to replace the sensor.
Start by unplugging the electrical connector from the sensor.
Then, carefully unscrew the sensor from the exhaust pipe using an appropriate wrench or socket.
Take note of the sensor’s orientation and the number of wire connectors for the replacement process.
Step 6: Clear the error codes and perform a test drive to verify if the issue has been resolved.
Note: Choose a trusted manufacturer for your replacement O2 sensor to ensure quality and compatibility. Bosch products are known for their quality and compatibility, making them a reliable choice.
Tips: I have a helpful tip for working with A/F sensors! It’s all about using anti-seize, which is a special lubricating compound that helps prevent seizing or sticking of threaded components. Here are some tips for using anti-seize effectively:
- Use a bit of anti-seize on the threads, but keep it off the sensor.
- Choose anti-seize specifically formulated for O2 sensor temperatures.
- Look for included anti-seize tubes in a reputable brand’s packaging (e.g., Bosch, Denso).
- Check if store brand options include anti-seize (e.g., Duralast). If not, purchase a suitable product separately.
Estimated Repair Costs For P1168 Code In Nissan Vehicles
Diagnosing and repairing the P1168 code in Nissan vehicles can be approached as a DIY project, but it does require some automotive knowledge and skills. Accessing the A/F Sensor and inspecting the wiring and grounding are relatively straightforward while replacing the O2 sensor, if necessary, requires more skill and knowledge.
It’s recommended to assess your comfort level and consider seeking professional help if needed. This approach can help ensure that the P1168 code is addressed effectively and avoid unnecessary expenses.
Here’s a general overview of estimated costs for labor and main repair tasks. Please remember that these figures are approximate and can vary based on factors like location and vehicle model.
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Diagnostic Fee | $50 – $150 |
| Wiring and Harness | $50 – $300 |
| A/F Sensor | $70 – $300+ |
| A/F Sensor Replacement (Labor cost) | $75 – $150 per hour |
P1168 Nissan Infographic
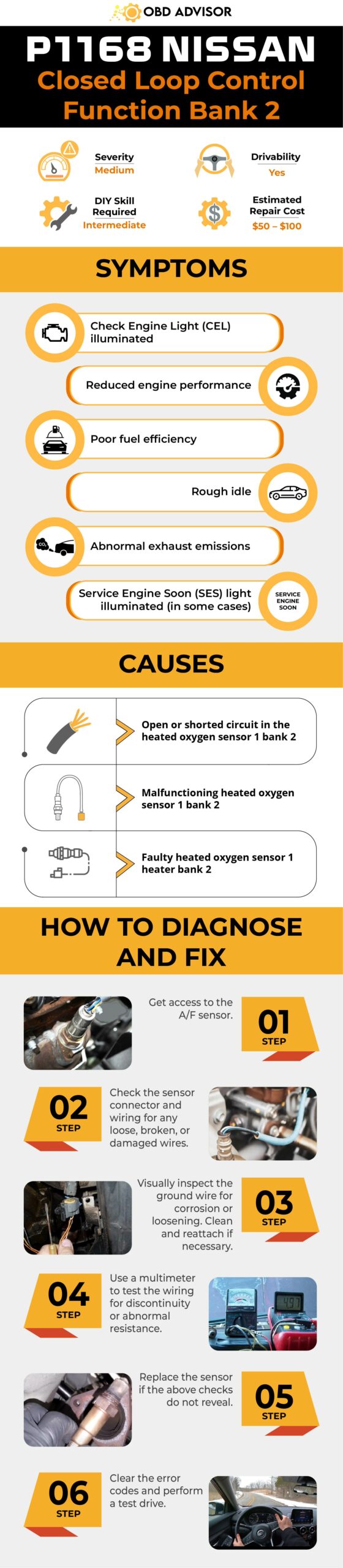
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, diagnosing and fixing the P1168 Nissan code can be a rewarding DIY project. If you have the know-how and confidence, go for it! Remember to prioritize safety and use the right tools.
If you prefer extra support or lack the necessary skills, don’t hesitate to bring in a professional mechanic. They’ll help you get your Nissan running smoothly again.
Whether you choose the DIY route or seek professional assistance, the goal is to resolve the P1168 code and ensure your Nissan is in top shape.
Ready to take on the challenge? Get your hands dirty and enjoy the satisfaction of a job well done!
Feel free to ask if you need more advice or have questions along the way. Best of luck with your P1168 code repair!
References Sources
- JustAnswer, What does a closed loop control fault mean (P1168)? – Answer by Nissan Expert Ron Z.
- Tire Review Magazine, 2011 May 6, Fuel System Definitions and Diagnostic Trouble Codes.
C1201 Toyota Code: How to Tackle Engine Control Problems
C1201 Toyota Code: How to Tackle Engine Control Problems
Prepare to tackle the C1201 Toyota code with our comprehensive guide. If you’ve encountered engine control problems, this article serves as your path to a solution. We’ll explore the likely culprits, provide a detailed diagnostic process, and offer effective remedies for the C1201 code.
Let’s dive in for more details!
C1201 Toyota: A Quick Overview
Here’s an overview of the C1201 for Toyota. Check it out!
- Definition: Engine Control System Malfunction
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: No
- Estimated Repair Cost: $50 – $500
What Does the C1201 Mean in Toyota Vehicles?
C1201 is a common On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD-II) code that relates to the vehicle’s Engine Control Module (ECM/ECU). The C1201 code is predominantly associated with Toyota vehicles, including popular models like the Camry, Corolla, RAV4, Tundra, Sienna, and Highlander, among others. This code points to a problem with the engine control system’s performance. Specifically, it indicates a malfunction in the ECM/ECU’s internal circuitry. This can disrupt the vehicle’s engine management, potentially leading to issues with engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
This code would be triggered when the engine control system malfunction signal lasts for 5 seconds. Simultaneously, a fail-safe function could activate. This function takes precautionary measures to ensure safety and prevent further damage to the vehicle. In the case of the C1201 code, the fail-safe function prohibits the operations of the Vehicle Stability Control (VSC) and Traction Control (TRC) systems.
How Serious is the C1201 Toyota Code?
The severity of the C1201 code in Toyota vehicles is high. Additionally, it’s unwise to continue driving with this code set. This code points to an issue with the engine control system, potentially impacting engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. More importantly, it triggers the fail-safe function, disabling the VSC and TRC systems, which can compromise your vehicle’s stability, especially in adverse road conditions.
Our strong recommendation is not to delay addressing the C1201 code. Continuing to drive with it can lead to further complications, reduced safety, and potentially costly repairs in the future. Having your vehicle inspected and repaired by a qualified technician promptly is the best course of action to ensure your Toyota operates safely and efficiently.
What are the Signs of the C1201 Toyota Code?
When the C1201 code appears in your Toyota vehicle, it may manifest through various symptoms, including:
- Illumination of the check engine light
- Decreased engine performance
- Reduced fuel efficiency
- Unstable or rough engine idling
- Difficulty starting the engine
- Increased exhaust emissions
- Disabled VSC and TRC systems
What are the Causes of the C1201 Code in Toyota Vehicles?
The C1201 code can be triggered by several underlying causes, such as:
- Faulty ECM/ECU
- Wiring or connector issues in the engine control system
- Voltage supply problems to the ECM
Read more: Toyota OBD1/OBD2 Codes List [FREE DOWNLOAD]
How To Diagnose and Repair C1201 Toyota Code?
In this section, we’ll guide you through the necessary steps to diagnose and fix the P0462 code in your vehicle, equipping you with the understanding and tools required to resolve this problem efficiently
Diagnostic Tools and Essential Parts
To diagnose and repair the C1201 code in your Toyota, you’ll need the following tools and parts:
- OBD-II scanner
- Multimeter
- Basic hand tools (screwdrivers, pliers, etc.)
- Wiring diagram for your specific Toyota model
Step-by-Step Guide
- Begin by connecting the OBD-II scanner to your vehicle’s diagnostic port to retrieve the trouble codes and confirm the presence of C1201.
- Inspect the wiring and connectors in the engine control system for any visible damage or corrosion. Repair or replace as needed.
- Check the voltage supply to the ECM. Ensure it is within the specified range by repairing the wiring, fuse, or relay.
- Clear and rescan to know whether the code reappears or not. If all electrical components check out and the code still comes back, the issue may lie with the ECM itself. Replace the ECM following the manufacturer’s guidelines and program it as necessary.
Note:
- You can consult this TSB exclusively for this C1201 Toyota code for more details.
- Consult your vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions and diagrams related to your Toyota model.
- Ensure safety precautions, such as disconnecting the battery, are taken before working on electrical components.
- If you suspect your ECM needs replacement, it’s best to consult a professional. ECM tasks like replacement and reprogramming are complex and not suitable for DIY attempts.
DIY Repair Level and Estimated Costs
Diagnosing the C1201 code can be moderately challenging for DIY enthusiasts with some mechanical and electrical knowledge. However, replacing the ECM may require advanced skills and equipment, so if you have to replace the ECM, have a skilled mechanic perform that to ensure the job is done correctly and to avoid costly mistakes.
Estimated repair costs can vary widely, but here’s a rough breakdown:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Repairing wiring/connectors | $50 – $150 |
| ECM replacement and programming | $500 – $1,500 |
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve shed light on the C1201 code in Toyota vehicles, providing insights into its meaning, severity, symptoms, and possible causes. We’ve also outlined a step-by-step procedure for diagnosis and repair, along with essential tools and parts you’ll need. While some aspects of addressing this code can be tackled by DIY enthusiasts, it’s essential to approach complex tasks, such as ECM replacement, with caution and professional guidance. Remember, timely attention to the C1201 code ensures your Toyota continues to run smoothly and safely on the road
If you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. And if you have any questions or insights to share, don’t hesitate to drop a comment below.
To explore more about other DTCs, simply head over to our OBD2 code lookup for a comprehensive guide to automotive troubleshooting.
Reference Sources
Toyota Gambia, Brake Assist & Traction Control (TRC).
Toyota Motor Corporation, Vehicle Stability Control System. In RAV4 Repair Manual.
Toyota Arlington, What Does the VSC Light on My Toyota Mean?
P1800 Nissan Code: VIAS Control Solenoid Valve Issue
P1800 Nissan Code: VIAS Control Solenoid Valve Issue
If you own a Nissan vehicle and have recently come across the code P1800, you’re in the right place. In this article, we’ll dive into the meaning, symptoms, and possible causes of the P1800 Nissan code.
Simply put, the P1800 code in Nissan vehicles refers to an issue with the Variable Intake Air System control solenoid.
Let’s delve deeper into understanding the P1800 Nissan code and find practical solutions for your Nissan’s issue.
P1800 Nissan: A Quick Overview
Take a quick look at the key information of the P1800 Nissan Code below!
- Definition: VIAS Control Solenoid Valve
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $30 – $200
What Does The P1800 Nissan Code Mean?
In Nissan vehicles, the P1800 code is specifically associated with a malfunction in the Variable Intake Air System (VIAS) control solenoid. This solenoid is a vital component within the VIAS system, which is responsible for optimizing the flow characteristics of the intake manifold.
By regulating the intake vacuum, the VIAS control solenoid plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal engine performance and power delivery. It acts as a valve for controlling the intake vacuum. When the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) detects an excessively low or high voltage signal being sent to the ECM through the valve, it triggers the P1800 code.
(Image credit: Nissan Murano Forum)
The P1800 code is something that many Nissan car owners often come across, especially those who have Maxima, Murano, Quest, and Altima vehicles. These particular models tend to have more frequent reports of experiencing the P1800 code.
How Serious Is The Nissan P1800 Code?
When it comes to the severity of the P1800 code, it is typically considered a moderate issue. While the code itself may not cause immediate breakdown or drivability problems, it should not be ignored.
(Image Credit: Reddit)
It’s generally safe to continue to drive with the code in the short term. However, you should get it addressed as soon as you can. Driving with the P1800 code present for an extended time may lead to decreased engine performance, especially during high-demand situations where additional power is required.
Common Warning Signs Of P1800 Nissan Code
Experiencing the P1800 code in your Nissan vehicle can result in several noticeable symptoms, including:
- Check Engine Light (CEL) or Service Engine Soon (SES) light illuminated
- Unstable motor operation or sluggish engine performance
- Lack of throttle response
- Hesitation, kick, or jerk felt when shifting gears
- Acceleration issues when switching from Drive to Reverse
Read more: Nissan Faults Codes (PDF Free Download)
What Triggers The P1800 Nissan Code?
The P1800 code in Nissan vehicles can have various underlying causes, including:
- Issues with the solenoid valve circuit wiring or connectors (open or shorted)
- Malfunctioning VIAS control solenoid valve
Keep in mind that the above are just main causes. Additionally, some Nissan owners have shared that a faulty Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor can sometimes contribute to triggering the P1800 code. While it’s not very common, it’s good to keep this possibility in mind when diagnosing the issue.
P1800 Nissan Diagnosis & Repair: Step-by-Step Guide For Resolution
The most common approach to address the P1800 code is inspecting and potentially cleaning or replacing the VIAS control solenoid valve. Alternative solutions include replacing the MAF sensor or installing a block-off plate, which is an aftermarket part used to bypass or block the VIAS system.
However, it is essential to note that these solutions may only be applicable or effective for some vehicles or situations. You should consult a professional mechanic or refer to the vehicle’s service manual for guidance specific to your car before proceeding with any alternative solutions.
In this section, we’ll guide you through inspecting and repairing the VIAS valve to solve the P1800 Nissan code. Let’s dive in.
Essential Tools And Parts
- OBD-II scanner or code reader
- Basic hand tools (such as wrenches and sockets)
- Electrical cleaner
- VIAS control solenoid valve
Step-by-Step Procedure
Step 1: Retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
Connect an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the P1800 code and any additional codes stored in the vehicle’s computer system.
Step 2: Locate the VIAS control solenoid valve
The valve in Nissan vehicles is often easy to access. It is typically situated on or near the intake manifold. Refer to the service manual for precise location details.
Step 3: Inspect and clean the valve
Check the valve and its electrical connections. Clean if dirty, repair faulty connections, and secure the wiring harness.
Step 4: Test the resistance
Test the solenoid valve’s resistance using a multimeter. Compare with manufacturer specifications.
Step 5: Replace the solenoid valve
If the solenoid valve is faulty, replace it with a new one following the manufacturer’s instructions. Disconnect electrical connectors, remove mounting bolts, and take note of the valve’s orientation during removal.
Then, install the new valve, ensuring proper alignment, secure fastening, and connection of electrical connectors.
Step 6: Clear codes and test drive
Clear the codes using the OBD-II scanner and test drive the vehicle to verify if the code reappears.
Note: Consult a professional mechanic or refer to the vehicle’s service manual if you have any uncertainties or encounter difficulties during the process.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
Diagnosing and replacing the VIAS control solenoid valve can be a moderately challenging DIY repair. It requires basic automotive knowledge and the ability to use hand tools. Cleaning or replacing the MAF sensor is generally more accessible for DIY enthusiasts.
For estimated costs, here is a breakdown of the main repair tasks:
| Repair Task | Cost Range |
| Diagnostic fee | $50 – $150 |
| Wiring repair | $50 – $200 |
| VIAS control solenoid valve replacement | $50 – $300 (part and labor) |
While DIY repairs can save money, consulting with an expert or mechanic is crucial if you’re uncertain about the diagnosis or repair process. They can provide guidance and ensure proper resolution of the P1800 code in your Nissan vehicle.
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, addressing the P1800 code in your Nissan vehicle is crucial to keep your engine running smoothly. Whether you decide to tackle the repairs yourself or get expert help, following a step-by-step approach is important.
If you have any questions or need further assistance, don’t hesitate to reach out.
Also, check out our user-friendly OBD Code Lookup for diagnosing and understanding other codes.
Share your experiences with the P1800 code in your Nissan vehicle in the comments below!
Best of luck with your Nissan!
Reference Sources
- JustAnswer, DTC P1800 (PDF File).
- Nialtima.com, Nissan Altima 2007-2012 Service Manual: P1800.
C1130 Nissan: Understanding The Engine Signal 1 Fault
C1130 Nissan: Understanding The Engine Signal 1 Fault
Are you puzzled by the C1130 Nissan code appearing on your car scanner? Don’t worry, you’re not alone. Many Nissan owners have encountered this enigmatic code and wondered what it signifies.
The C1130 Nissan code is typically associated with a fault in the engine’s signal. This informative article will reveal the meaning behind this code, its severity, common symptoms, likely causes, and the essential steps for diagnosis and repair.
So, let’s begin!
Nissan C1130 Code: Quick Summary
Let’s take a quick look at the C1130 Nissan code and what it entails!
- Definition: Engine Signal 1
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Advanced
- Continue To Drive?: No
- Estimated Repair Cost: $100-$500
What Does The C1130 Nissan Code Mean?
According to the Nissan TSB BR16-004 and the explanation provided by Andrew Markel at Babcox Media, the C1130 code is commonly found in the ABS module but does not necessarily indicate a problem with the ABS module itself.
When the C1130 code appears, it signifies that the data required by the ABS module from the ECM is missing or incorrect. This missing data prevents the ABS module from performing certain functions. This situation often occurs when P codes are present within the ECM, such as the P0430 and P0335.
It’s important to note that this behavior is not unique to Nissan vehicles but is observed across various vehicle models. Modules on the CAN high-speed bus are designed to communicate with each other, and the information exchanged should be complete.
Read more: Nissan TSB BR16-004
How Serious Is The C1130 Nissan Code?
The severity level of the C1130 code can vary from medium to high, depending on the specific circumstances and associated symptoms. Generally, this code indicates a problem with the engine signal and its recognition by the ABS control unit. While the C1130 code itself may not directly affect the drivability of the vehicle, it can impact essential safety features like Forward Emergency Braking (FEB), Intelligent Cruise Control (ICC), Vehicle Dynamic Control (VDC), Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and Traction Control System (TCS).
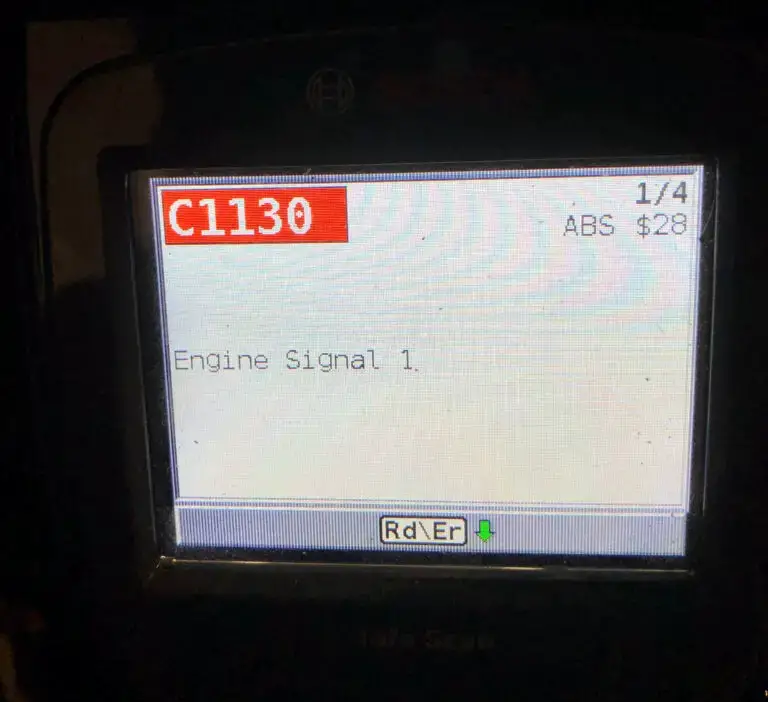
(Image credit: JustAnswer)
So can you drive with the C1130 trouble code present? Yes, you can. However, it is advisable not to ignore the C1130 code and seek proper diagnosis and repair as soon as possible. Continuing to drive with this code unresolved may compromise the functionality of safety systems, potentially increasing the risk of accidents or reduced braking performance.
Signs Of The C1130 Nissan Code
Here are some common symptoms associated with the C1130 code:
- Check engine light and/or slip indicator light illuminated
- Refusal to go into 4WD
Due to the potential impact on safety features, the C1130 code may also result in the following warning signs:
- Malfunctioning or disabled FEB system
- Inoperative or erratic ICC
- Unusual braking behavior
- Traction control issues
Read more: Nissan Dashboard Warning Lights and Meanings (FULL list, FREE Download)
Triggers Behind The C1130 Nissan Code
The C1130 code in Nissan vehicles may have the following causes:
- Connection issues between the ECM and the related system
- ECM internal fault
- Corroded connector (typical of a car that has water damage)
- Other specific causes vary depending on ECM-related DTC (P codes) that arise together with the C1130 code
C1130 Nissan Code: A Guide To Diagnosis And Repair
In this section, we will provide step-by-step instructions, along with a list of essential tools and parts needed to address the issue. By following this guide, you can effectively identify and resolve the C1130 code.
Essential Tools And Parts
- OBD-II scanner
- Basic hand tools (wrenches, sockets, etc.)
- Multimeter
- Wiring harnesses
- Connectors and terminals
- Replacement of ECM, ABS control unit, ABS speed sensor (if necessary)
Step-by-Step Procedure
Step 1: Connect an OBD-II scanner to retrieve all stored codes and freeze frame data.
Step 2: Diagnose, repair, and erase any ECM-related diagnostic trouble codes (P-codes) that are found. It is crucial to address these codes first.
Step 3: If no ECM-related codes are found, the problem may reside in the ECM or the ABS system. Proceed with the following steps:
- Perform an ECM self-diagnosis. If you detect any issues, proceed to repair or replace the identified faulty components.
- Perform another self-diagnosis for the ABS actuator and control unit. If problems are found, make the necessary repairs or replacements as the self-diagnosis indicates.
Step 4: Clear all codes and test the vehicle to ensure the C1130 code does not reappear.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The diagnostic and repair procedure for the C1130 code may require advanced-level automotive knowledge and experience. It involves using specialized diagnostic tools and potentially replacing components like the ECM, ABS control unit or repairing wiring harnesses and connectors. If unsure about your DIY capabilities, you should seek assistance from a qualified mechanic or technician.
The estimated costs for main repair tasks can vary depending on factors such as the specific model, location, and labor rates. Below is a table outlining estimated costs for common repair tasks related to the C1130 code:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Diagnostic fee | $50 – $150 (may vary by location) |
| Electrical circuit repair | $100 – $300 (parts and labor) |
| ECM replacement | $300 – $600 (parts and labor) |
| ABS control unit replacement | $200 – $500 (parts and labor) |
Please note that these are rough estimates, and actual costs may differ. It is recommended to consult with a professional for accurate cost assessments based on your specific vehicle and location.
C1130 Nissan Infographic
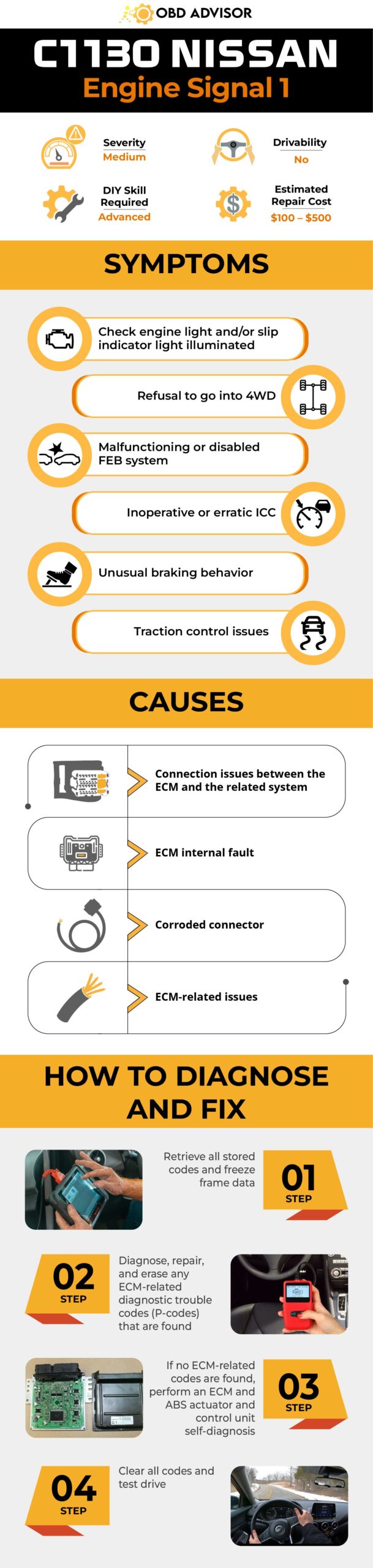
Final Thoughts
In wrapping up, let’s tackle the C1130 code in your Nissan vehicle so you can enjoy a smoother ride and keep your safety features working perfectly.
Whether you’re a DIY superstar or prefer the expertise of a professional, taking action is key. Always remember, safety is the star of the show here.
If you found this information helpful, feel free to comment and share it with others. For further assistance, you can use our convenient OBD code lookup tool and explore our comprehensive Nissan OBD2 code list.
Drive safely and enjoy your Nissan!
Reference Sources
- Babcox Media Youtube Channel, How To Resolve DTC C1130 For Nissan Vehicles | Tech Minute.
- Nissan North America, 2016, TSB BR16-004: DIAGNOSIS INFORMATION FOR ABS DTC C1130.
- CarParts, C1130 Code: Engine Signal 1.
- 2CarPros, Code C1130: My Car Will Move a Little.
- 2CarPros, 2005 Nissan Quest C1130 Engine 1 Fuel Cut System Fault.
- Titan XD Forum, C1130 Code.
P145C Honda Code: Expert Tips for Emission System Repairs
P145C Honda Code: Expert Tips for Emission System Repairs
When the P145C code appears on your Honda’s diagnostics, confusion can set in. This article acts as your guiding light through this issue. We’ll provide a breakdown of the code’s meaning, symptoms, and causes.
A step-by-step guide will be below for you to address the P145C Honda code. Whether you’re a hands-on enthusiast or seeking professional help, the process is made clear, empowering you to tackle the issue effectively.
Let’s explore!
P145C Honda Code: A Quick Overview
Take a look at the summary of the Honda P145C code provided below!
- Definition: EVAP System Purge Flow Malfunction
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes (Short term)
- Estimated Repair Cost: $50 – $500
What Does The P145C Honda Code Mean?
The P145C trouble code is a manufacturer-specific code. It is titled as an “EVAP System Purge Flow Malfunction” or “Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Range/Performance Problem” by the Honda car manufacturer.
This code is triggered when the car’s Powertrain Control Module (PCM) detects a malfunction within the EVAP system of your Honda. In most cases, the culprit is likely the wrong fuel tank pressure sensor readings.

(Credit: crvownersclub.com)
Let’s explore briefly the EVAP system – The purpose of the EVAP system is to capture and manage fuel vapors generated in the fuel system. This system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the environment. It includes components like the fuel tank, charcoal canister to trap vapors, purge valve, vent valve, sealed fuel filler cap, pressure sensors, and various lines.
The P145C code is commonly found in various Honda models, including but not limited to: Civic, Accord, CR-V, HR-V, Pilot, Odyssey, etc.
In some cases, the P145C code might be accompanied by other related codes that provide more information about the specific nature of the problem. These accompanying codes might include the following:
- P1456: Evaporative Emissions Control System Leakage (Fuel Tank System)
- P0443: Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Control Valve Circuit
- P0496: EVAP Flow During A Non-Purge Condition
- P0497: Evaporative Emission System Low Purge Flow
How Severe Is The P145C Code In Your Honda?
The P145C code found in Honda vehicles has a moderate severity level. It’s possible to drive, but short-term driving is allowed (within a range of 30 to 50 miles). Prolonged driving without addressing the issue could lead to increased emissions and reduced fuel efficiency.
It’s still recommended to have the issue addressed as soon as possible. Continuing to drive with a malfunctioning EVAP system can have negative effects on the environment and vehicle performance. After reaching your destination, consider scheduling a diagnostic check with a qualified technician. Timely repairs will prevent further complications and maintain the vehicle’s efficiency and emission control.
What Are The Signs Of The P145C Code On Honda Vehicles?
The presence of the “P145C” code in Honda vehicles is often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Check Engine Light (MIL) illuminated
- Decreased fuel efficiency
- Increased emissions
- Difficulty starting the engine
- Engine stalling
What Are The Causes Of The P145C Honda Code?
There are various factors can trigger the P145C code in Honda vehicles, including:
- Malfunctioning evaporative emission canister vent shut valve
- Wiring or electrical connectivity problems within the EVAP system
- Defective evaporative emission canister purge valve
- Hose leaks or blockages in the EVAP system
- Corrosion or damage to relevant components
- Faulty fuel tank pressure sensor
- PCM issues
Read more: P1009 Honda Code: VTC System Troubleshooting And Solutions
How To Diagnose And Fix The P145C Code On Honda?
When your Honda vehicle displays the “P145C” code, addressing it promptly is crucial. This section outlines the essential tools, a step-by-step procedure, and estimated costs associated with diagnosing and repairing the issue:
Essential Tools And Parts
To diagnose and repair the “P145C” code effectively, ensure you have the following tools and parts at hand:
- OBD-II scanner
- Multimeter
- Wiring and connectors
- Replacement EVAP components (vent shut valve, purge valve) if necessary.
Step-by-Step Procedure
1. Retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Use the OBD-II scanner to retrieve the P145C code, additional codes and associated freeze frame data. This will help you pinpoint the exact issue within the EVAP system.
2. Visual Inspection Of Wiring And Connections
- Thoroughly inspect the wiring and connections related to the EVAP system for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Pay close attention to the wiring harnesses, connectors, and terminals.
- Address any issues found during this inspection.
3. Test Evaporative Emission Canister Vent Shut Valve And Purge Valve
- Using a digital multimeter, perform voltage and resistance tests on both the evaporative emission canister vent shut valve and the purge valve.
- Follow the manufacturer’s specifications for proper voltage and resistance values.
- Replace any valve that does not meet the specified values.
4. Check Hoses For Blockages Or Leaks
- Inspect all hoses within the EVAP system for blockages, kinks, or leaks. Ensure that hoses are properly connected and free from obstructions.
- Replace any damaged hoses to restore proper airflow within the system.
5. Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Inspection
Examine the fuel tank pressure sensor for any signs of damage or malfunction.
6. Update PCM Software
- Check if there are any available software updates for the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) related to the EVAP system.
- If updates are available, follow the manufacturer’s instructions to update the PCM software. This can sometimes address compatibility issues and improve system performance.
- In case the PCM completely fails, find a skilled Honda mechanic nearby for replacement.
7. Clear The Codes And Test Drive
After conducting all procedures, clear the codes by using an OBD scanner. Then, perform a test drive to see if the codes come back or not.
Note:
- Make sure to save all the free data about the issue and any on-board snapshots.
- If any of the codes (P0496, P0497) appear along with P145C, start by fixing those codes, then check for P145C again. If both codes P0497 and P145C are stored together, inspect the line that connects the EVAP canister purge valve and the EVAP canister. Look for poor connections, blockages, or damage. Also, check if the EVAP canister purge valve is stuck closed.
Read more: Honda OBD2 Codes List [Generic + Manufacturer-specific]
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The repair procedure for the “P145C” code involves a moderate to advanced level of automotive expertise. Additionally, it requires diagnostic tools and component testing skills. If you’re confident in your abilities, you may attempt the repairs. However, if you’re unsure or inexperienced, seeking professional assistance is recommended to avoid complications.
Here’s an approximate cost breakdown for key tasks related to resolving the P145C code:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Wiring and connector repair | $50 – $150 |
| EVAP vent shut valve replacement | $50 – $200 |
| EVAP canister purge valve replacement | $50 – $200 |
| EVAP system blockage or leak repair | $50 – $300 |
| Fuel tank pressure sensor | $100 – $250 |
| PCM software update or replacement | $100 – $1,500 |
Keep in mind that these costs can vary based on factors like your vehicle’s make and model, as well as your location. If you’re uncertain about any aspect of the repair process or lack experience, consulting a certified mechanic is a prudent step to ensure an effective and safe resolution of the issue.
P145C Honda Infographic

Final Thoughts
Facing the P145C code in your Honda vehicle might seem daunting, but armed with knowledge and guidance, you’re well-equipped to address the issue.
Remember, proper diagnosis and timely repairs are essential for maintaining optimal vehicle performance and minimizing emissions. Whether you’re a seasoned DIY enthusiast or prefer leaving it to the experts, taking action now ensures a smoother ride ahead.
If you found this guide helpful, share it with fellow Honda owners who might benefit.
Feel free to leave your comments and questions below – we’re here to assist you on your automotive journey. Safe travels and happy troubleshooting!
Reference Sources
- HONDA DTC CODES – page 6
- JustAnswer, 2007 Honda Truck Odyssey V6-3.5L
P1574 Nissan Code: Navigating Transmission Concerns
P1574 Nissan Code: Navigating Transmission Concerns
So, you’ve come across the P1574 code in your Nissan, and it’s left you wondering what’s gone awry. No need to panic – In this article, I’m here to help you decode its meaning.
I will walk you through the basics of the P1574 code, including why it’s popped up and what steps you can take to make it vanish. Buckle up, as I’m gonna clarify the P1574 code and get your Nissan back on track!
Let’s explore!
P1574 Nissan: A Quick Overview
Go through the P1574 Nissan code summary outlined below!
- Definition: ASCD Vehicle Speed Sensor
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: No
- Estimated Repair Cost: $50 – $500
What Does The P1574 Code Mean In Nissan Vehicles?
The P1574 Nissan Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates a problem with the Engine Control Module (ECM) receiving conflicting vehicle speed signals. The ECM receives two speed signals via the Controller Area Network (CAN) communication line. One signal is transmitted from the combination meter, while the other comes from the Transmission Control Module (TCM). These signals are crucial for the operation of the Automatic Speed Control Device (ASCD) system.
When the ECM detects inconsistent or conflicting speed signals, it triggers the P1574 DTC. This code serves as an indicator that there is a communication issue between the combination meter, TCM, and ECM, affecting the ASCD control functionality.
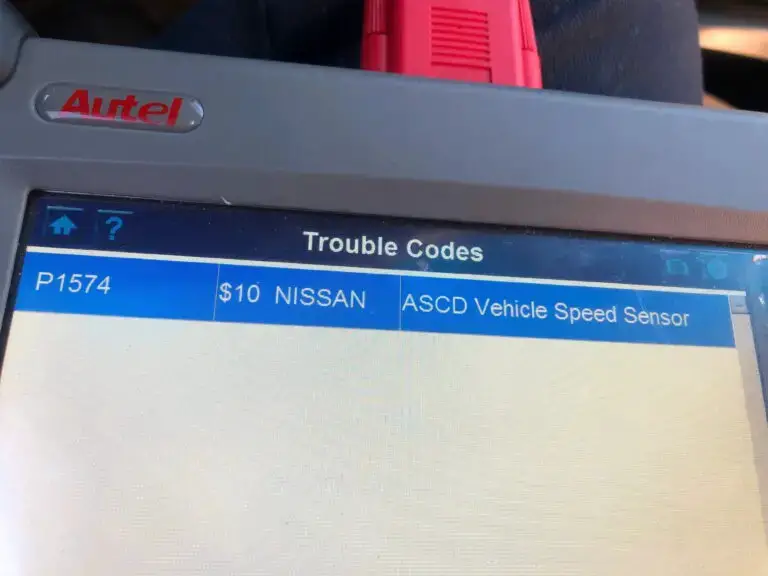
(Credit: maxima.org)
The P1574 trouble code is commonly found in various Nissan models. The following models usually get the P1574 code: Altima, Maxima, Sentra, Rogue, Murano, etc.
In some cases, the P1574 DTC may be accompanied by additional trouble codes. It is essential to address these associated codes before troubleshooting the P1574. The following are some common codes that may appear alongside P1574: Uxxxx (U code), P0500, P0605, P0607
It is important to diagnose and resolve any accompanying codes alongside the P1574 DTC to ensure a comprehensive repair process and restore proper vehicle functionality.
How Severe Is The P1574 Code In Nissan?
The severity level of the P1574 Nissan code can be considered moderate. While it does not present an immediate safety risk or major drivability issues, it is not advisable to continue driving with this code unresolved. Ignoring the P1574 DTC may result in the loss of cruise control functionality.
To ensure optimal vehicle performance and safety, it is recommended to address the code promptly. Therefore, seeking assistance from a qualified mechanic can help identify the cause and facilitate the necessary repairs or component replacements. Resolving the P1574 promptly restores the proper operation of the ASCD system, promoting a safer driving experience.
What Are The Signs Of The P1574 Code?
The P1574 Nissan code can manifest in various symptoms. If you are experiencing this code, you may notice one or more of the following:
- A malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) illuminated
- Loss of cruise control functionality
- Inconsistent or erratic speedometer readings
What Causes The P1574 Code in Nissan Vehicles?
The P1574 Nissan can be caused by various factors. Common causes of this code include:
- Low brake fluid
- Wiring or communication problems in the CAN network
- Faulty combination meter
- Bad wheel sensor(s)
- Malfunctioning ABS actuator and ABS control unit
- Issues with the TCM
- Faulty ECM
It’s important to note that these are potential causes, and a thorough diagnostic procedure is necessary to determine the underlying issue in your specific vehicle accurately.
Read more: P1777 Nissan Code: A Practical Repair Guide
How To Diagnose And Fix The P1574 Code In Your Nissan?
When your Nissan displays the P1574 code, think of it as your car’s way of telling you it’s having a problem. To tackle this, you’ll need certain tools and parts that are necessary. Following a set of steps in order is important, and you should also see if you can manage to fix it yourself. By sticking to these guidelines, you can increase your chances of successfully dealing with the P1574 code problem in your Nissan.
Essential Tools And Parts
To diagnose and repair the P1574 code, the following tools and parts may be required:
- OBD-II scanner
- Digital multimeter
- Brake fluid
- Wiring diagram
- Combination meter
- Wheel sensors
- ABS actuator and control unit
- TCM
- ECM
Step-by-Step Procedure
1. DTCs retrieval
Begin by connecting an OBD-II scanner to the vehicle’s OBD-II port. Then, retrieve and record all present DTCs, including the P1574 code.
2. Brake fluid inspection and refill
- Check the brake fluid level in the vehicle’s brake fluid reservoir.
- If the brake fluid is low, top it up to the recommended level. Use the type of brake fluid specified in the vehicle’s service manual.
3. Wiring and connection testings
- Inspect the wiring connections and harnesses of all the systems above. Look for any visible signs of damage, corrosion, loose connections, or frayed wires.
- Use a digital multimeter to check those connections, and consult the wiring diagram for your specific Nissan model.
- Compare the readings obtained to the specifications provided in the vehicle’s service manual.
- Repair or replace any damaged wiring as necessary.
4. Wheel sensor examination and replacement
- If the problem persists, inspect the wheel sensors.
- Clean the sensors and their mounting surfaces, and check for any damage or excessive debris.
- Replace any wheel sensors that are faulty, damaged, or contaminated.
5. ABS actuator and control unit diagnostic testing
- If the ABS actuator and its control unit are suspected to be the cause of the P1574 code, perform further diagnostic tests.
- This may involve using specialized diagnostic tools to assess the ABS actuator’s functionality and communication with the control unit.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines for testing and diagnosing the ABS system.
6. Comprehensive system diagnostics for combination meter, TCM, and ECM
- If the issue still exists, perform specific tests and procedures outlined in the vehicle’s service manual to diagnose the combination meter, TCM, and ECM.
- Replace any faulty system if necessary.
- It’s advisable to get help from a professional mechanic to execute this step.
7. Clearing DTCs and final road test
Clear all DTCs using the diagnostic tool and conduct a road test to ensure the P1574 code does not reappear.
Read more: C1109 Nissan Code: ABS Voltage Trouble Exposed
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
Diagnosing and repairing the P1574 Nissan code may require intermediate-level automotive diagnostic and repair skills. If you are unfamiliar with the diagnostic procedures or lack the necessary tools, it is advisable to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic or technician.
The cost of repairing the P1574 code can vary depending on the specific cause and the replacement parts required. Now, let’s have a look at an estimated cost breakdown for the primary repair tasks:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Brake fluid change | $50 – $100 |
| Wheel speed sensor replacement | $50 – $200 per sensor |
| Wiring repair | $50 – $150 |
| ABS control module replacement | $200 – $500 |
| Combination meter replacement | $150 – $500 |
| TCM replacement | $200 – $800 |
| ECM replacement | $200 – $1000 |
Please be aware that these cost approximations are not fixed and can differ depending on elements like the type of vehicle, where you are located, and the charges for labor. In order to obtain accurate cost details specific to your vehicle, it is recommended to consult with a mechanic or obtain personalized quotes.
P1574 Nissan Infographic
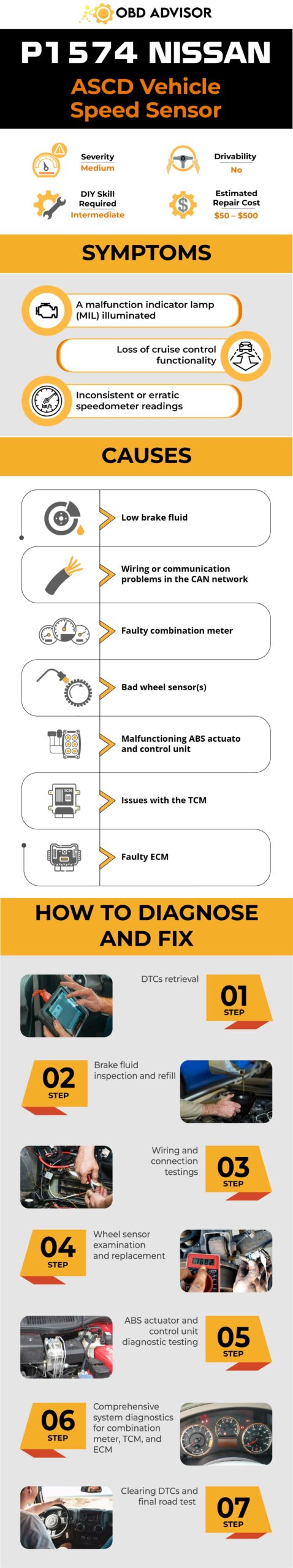
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding the P1574 code and its implications in the ABS system is crucial for maintaining optimal braking performance and vehicle safety. If you encounter challenges or lack expertise, it is advisable to seek assistance from a qualified professional.
Stay proactive in addressing ABS system concerns to ensure a safe and reliable driving experience. Stay informed, drive safely, and don’t hesitate to share this valuable information with others. And, drop a comment below if you have any questions. Safe driving!
Learn more about other codes by using our OBD lookup tool!
Reference Sources
- NiAltima, P1574 ASCD vehicle speed sensor
- AUTONERDZ, Maxima ECM reprogramming data
- J.D. Power, What is a front-wheel speed sensor?
P1777 Nissan Code: A Practical Repair Guide
P1777 Nissan Code: A Practical Repair Guide
Dealing with a P1777 code in your Nissan can be frustrating. Do not fret! – In this guide, we’ll walk you through simple steps to tackle the issue. We’ll cover needed tools, explain the repair process, and discuss DIY feasibility.
This empowers both DIYers and those seeking professional help to make informed decisions and potentially save on repairs.
Let’s find out!
P1777 Nissan Code: A Quick Overview
Check the summary of the P1777 Nissan code below!
- Definition: Step Motor Circuit
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $20 – $200
What Is The Meaning Of The P1777 Nissan Code?
The P1777 Nissan code is a manufacturer-specific trouble code for Nissan vehicles. It indicates a specific concern within the step motor circuit of the automatic transmission. This code is triggered when any of the coils in the step motor fail to energize correctly, often due to an open circuit or a short circuit issue. While the vehicle might remain drivable with this code present, it highlights a potentially significant problem in the transmission system.
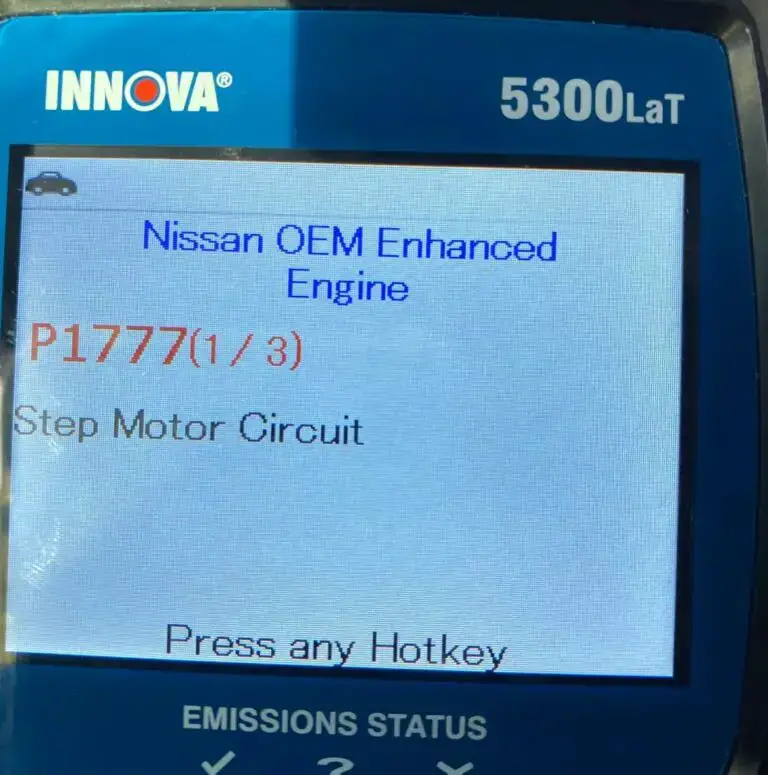
(Credit: nissanclub.com)
The step motor, also called a stepper motor, is crucial for converting pulsing electrical currents into controlled parts rotation. This helps control different mechanical parts within Nissan transmissions effectively.
This part operates through a unique mechanism involving the activation and deactivation of four coils. These coils are turned on and off based on signals received from the Transmission Control Module (TCM). By accurately translating electrical signals into these controlled movements, the step motor ensures the smooth operation and efficiency of the transmission system in Nissan vehicles.
The P1777 code has been reported in various Nissan models, potentially affecting the transmission performance across the following vehicles: Altima, Sentra, Maxima, Rogue (2009), Murano, Pathfinder, Versa (2007), Juke, Cube, etc.
How Severe Is Code P1777 Nissan?
The severity of the P1777 code in Nissan vehicles can be classified as moderate. It may be possible to continue driving the vehicle.
While driving at a safe speed might be viable, it’s important to understand that ignoring the code could result in further damage to the transmission over time. This could lead to issues like harsh shifting and delayed gear engagement, potentially affecting the vehicle’s drivability and overall performance. It’s recommended to address the issue promptly to ensure the vehicle’s safety and longevity by consulting a professional mechanic and seeking necessary repairs.
What Are The Symptoms Of The P1777 Nissan Codes?
The P1777 code in Nissan vehicles can manifest through various noticeable symptoms, indicating potential issues with the step motor circuit. Common symptoms include:
- Harsh or erratic shifting
- Delayed gear engagement
- Poor transmission performance
- Weak acceleration
- Check engine light illuminated
Read more: P1715 Nissan Code: Tips For Dealing With Transmission Issues
What Are The Causes Of The P1777 Nissan Code?
The P1777 code can arise due to several underlying causes. Possible factors include:
- Faulty step motor (stepper motor)
- Wiring or connector issues in the step motor circuit
How To Diagnose And Fix The P1777 Nissan Code?
When you encounter the P1777 code in your Nissan vehicle, it’s important to follow a clear process for diagnosis and repair. Here’s a simple breakdown of the tools and a step-by-step guide you need, along with a discussion of whether it’s a DIY job and how much it might cost:
Essential Tools And Parts
To diagnose and repair the P1777 code, you will likely need the following tools and parts:
- OBD-II scanner
- Multimeter
- Screwdrivers and wrenches
- Replacement step motor (if needed)
- Wiring repair kit (if addressing circuit issues)
Step-by-Step Procedure
- Inspect the wiring: Check the wiring and connectors around the step motor for damage or corrosion. Address any wiring or connector issues as needed
- Test the step motor: Use a multimeter to test the step motor’s resistance and functionality.
- Test the circuit: Check the circuit for continuity and voltage using the multimeter. And then fix it if necessary
- Replace step motor: If the step motor is found faulty, replace it with a new or tested working one.
- Clear codes: After repairs, clear the codes using the OBD-II scanner and test-drive the vehicle to ensure the issue is resolved.
Note:
- Tips: Consult the vehicle’s repair manual for specific testing procedures and values.
- Caution: Ensure safety precautions when working with electrical components.
Read more: Nissan Trouble Codes: Comprehensive List For OBD1/OBD2
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The diagnosis and repair of the P1777 code involve moderate complexity and require a good understanding of automotive systems. If you possess technical skills, you can attempt this repair. However, if uncertain, it’s advisable to consult a professional mechanic.
Here’s a general cost overview for potential repair tasks that may arise during the process:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Replacement step motor (if needed) | $50 – $200+ |
| Wiring repair kit (if needed) | $20 – $50 |
| Mechanic labor (if seeking professional help) | $100 – $200+ |
Keep in mind that these costs can vary based on factors such as location, vehicle model, and the source of parts. If unsure about the repair process or the issue at hand, it’s recommended to consult a qualified mechanic for a proper diagnosis and resolution.
P1777 Nissan Infographic

Final Thoughts
It is essential to equip yourself with good knowledge before popping the hood. This article has provided you, as a professional or even DIY enthusiast, with a good insight into P1777 on Nissan vehicles. Remember to address this issue to ensure the optimal performance of your Nissan.
Share your journey, questions, and insights in the comments below. If this information proves valuable, share it with fellow enthusiasts. Keep the road ahead smooth and the repairs purposeful!
Reference Sources
- Nissan Altima Service Manual, P1777 Step Motor – Nissan Altima – Automatic Transmission (Section TM)
- JustAnswer, P1777 Step Motor PDF – JustAnswer – Questions
P1212 Nissan Code: Meaning, Causes & Simple Steps For A Fix
P1212 Nissan Code: Meaning, Causes & Simple Steps For A Fix
Welcome to our guide, where we’ll shed light on the P1212 Nissan code. As an experienced mechanic, I understand the frustration it can bring. But fear not! In this article, we’ll navigate the intricacies of your vehicle’s electrical system and uncover the mysteries behind the P1212 code on your Nissan.
With our step-by-step approach, you’ll gain the knowledge and confidence to tackle this challenge head-on.
So, let’s dig into the P1212 Nissan code and solve it together!
P1212 Nissan: A Quick Overview
Below is a summary of the P1212 Nissan Code. Check it out.
- Definition: ABS/TCS Communication Line
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $100 – $500
What Does The P1212 Code Mean On Nissan?
The P1212 code on a Nissan vehicle indicates a communication error between the ABS/TCS control module and the engine control module (ECM). This error occurs when there’s an issue with the communication line, which controls smooth engine operation during Traction Control System (TCS) operation. As a result, the Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) and ECM modules fail to exchange important information properly. This condition can also trigger the U1001 and P0607 codes.

(Image credit: Nissan Frontier Forum)
Let’s learn how these modules collaborate to ensure seamless vehicle operation.
The ABS control module is responsible for ensuring that the wheels do not lock up during braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. It constantly monitors the wheel speed sensors and sends signals to the ECM to adjust engine power or apply the brakes as needed to prevent wheel lock-up.
Meanwhile, the ECM serves as the central control unit for the engine. It receives information from various sensors in the vehicle to optimize engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. Additionally, the ECM communicates with other control modules, including the ABS control module, to coordinate their functions and ensure that the vehicle operates smoothly.
Is The P1212 Nissan Code Severe?
The severity of the P1212 Nissan code can be classified as moderate to high. Although it may not require immediate attention, addressing the underlying issue promptly is crucial. This ensures the proper functioning of your ABS system and helps maintain the overall performance of your vehicle.
While you can continue driving with the P1212 code in the short term, it is unsafe, and you should drive with caution. Insufficient communication between the ABS control module and the ECM can result in the ABS system not operating as intended. This can affect your vehicle’s braking performance and lead to ABS system malfunctions and traction control issues. Therefore, to ensure optimal safety and functionality, promptly diagnosing and repairing the issue is strongly recommended.
What Are The Warning Signs of the P1212 Nissan Code?
The warning signs of the P1212 Nissan code may include the following:
- Illuminated ABS, TCS, and/or SLIP warning lights
- Decreased braking performance
- Unusual noises during braking
- Traction control issues

(Image credit: titantalk.com)
Read more: Nissan Dashboard Warning Lights and Meanings (FULL list, FREE Download)
What Causes The P1212 Nissan Code?
The P1212 Nissan code can be caused by the following:
- Corroded harness connector on the ABS unit
- Harness or connectors with open or shorted CAN communication lines
- Faulty ABS actuator and electric unit (control unit)
- Damaged ABS fuse
- Dead or weak battery
How To Diagnose And Fix The P1212 Nissan Code?
Get ready to tackle the P1212 Nissan code like a pro! In this section, we’ll guide you through the process of diagnosing and fixing the issue.
Note: If the retrieved trouble codes include DTC UXXX or P0607, prioritize repairing them before proceeding with the following procedure.
Essential Tools And Parts
- WD-40 Specialist® Contact Cleaner
- Battery terminal cleaner
- Automotive wrenches
- Screwdrivers
- Multimeter
- ABS fuse
- Nissan battery
Step-by-step Procedure
Step 1: Inspect the ABS control module, wiring, and connectors
Thoroughly examine the ABS control module, wiring harness, and connectors for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Clean the affected components using an electrical contact cleaner if you find any issues. Repair or replace any damaged parts as necessary.
Pro Tip: Pay attention to the ABS connector, as it’s one of the most common causes. Clean corroded connectors using a suitable electrical contact cleaner. WD-40 Specialist® Contact Cleaner is a good choice.
Step 2: Check the ABS fuse
Locate the ABS fuse in the fuse box. It is typically a red 10-amp fuse located on the passenger side by the overflow tank in the engine bay. Inspect the fuse visually to determine if it is blown or damaged. If you find a blown fuse, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating.
Step 3: Examine the battery
Ensure that the vehicle’s battery has sufficient charge. If needed, recharge the battery. Inspect the battery cable for signs of corrosion or loose connections. Clean the battery cable and terminals using a battery terminal cleaner or a mixture of baking soda and water. If the battery is old or faulty, consider replacing it with a new one.
Step 4: Reset the ABS system and test drive
Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery and wait for at least 10 minutes. Reconnect the negative terminal and start the vehicle. Take the vehicle for a test drive to verify if the P1212 error code has been cleared. During the test drive, ensure that the ABS system functions properly and that no warning lights or error codes appear.
If the error code persists after following these steps, it is recommended to consult a qualified mechanic or Nissan dealership for further diagnosis and assistance.
Estimated Costs For P1212 Code In Nissan Vehicles
The procedure provided above for addressing the P1212 code in Nissan vehicles is suitable for DIY enthusiasts with intermediate automotive repair skills. However, it is essential to note that diagnosing and repairing electrical issues can be complex. If you lack confidence in your abilities or do not have the necessary tools, it is highly advisable to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic or Nissan dealership.
When it comes to the cost of repairing the P1212 code, it can vary depending on several factors, including the specific model of your vehicle, the extent of the issue, and prevailing labor rates in your area. As the code is related to communication issues within the ABS system, the cost may involve various elements, as outlined in the table below:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Diagnostic Fee | $50 – $150 |
| ABS Fuse Replacement | $5 – $20 |
| Battery Replacement | $100 – $300 |
| Wiring Repair | $100 – $500 |
| Connector Replacement/Repair | $50 – $200 (per connector) |
| ABS Control Module Replacement/Repair | $300 – $800 (excluding programming) |
| Labor Costs (per hour) | $80 – $150 |
P1212 Nissan Infographic
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, tackling the P1212 code in Nissan vehicles requires careful consideration. If you’re a DIY enthusiast with intermediate to advanced automotive repair skills, you can give it a shot. Just remember, electrical issues can be tricky, so don’t hesitate to seek professional help if needed.
The cost of repairs can vary based on factors like your vehicle model and the extent of the issue. It’s crucial to weigh your skills and resources before diving in.
Got more questions or insights? Comment below!
And if you found this information helpful, share it with others who might benefit. Let’s hit the road with confidence and keep those wheels turning!
References Sources
- P1212 TCS communication line, Nissan Rogue Owners & Service Manual Website
- What is an Anti-lock Brake System, Nissan of Mobile
P1610 Nissan – Lock Mode: Causes, Symptoms & Solutions
P1610 Nissan – Lock Mode: Causes, Symptoms & Solutions
Is your Nissan refusing to start, and you find the annoying P1610 code on the scanner? I know how frustrating it can be! That’s why I’m here to help!
Simply put, the P1610 Nissan code suggests potential issues with the NATS system or the use of an incorrect key. Don’t wait any longer; gain valuable insights and learn how to fix it in this article!
P1610 Nissan: An Overview
Let’s take a quick look at the essential details of the P1610 Nissan code!
- Definition: Immobilizer Lock Mode
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: No
- Estimated Repair Cost: $30 – $200
P1610 Nissan Code: Immobilizer Lock Mode Explained
The P1610 code, defined as “Immobilizer Lock Mode,” is specifically associated with the Nissan Anti-Theft System (NATS), also known as the Vehicle Immobilizer System. When this code appears, it signifies that the immobilizer system has entered lock mode, preventing the vehicle from starting even with the correct key. It is commonly triggered in various Nissan and Infiniti models, including the Altima, Almera, Frontier, Murano, Pathfinder, Sentra, and Maxima.
The NATS is designed to prevent the unauthorized starting of the vehicle by immobilizing the engine unless the correct key is detected. It works by immobilizing the engine unless the correct key is detected. When you insert the key into the ignition, the NATS antenna amplifier reads the unique binary code transmitted by the key. If the Engine Control Module (ECM) determines that the coded key is valid and matches the registered keys, it activates the fuel-injection sequence, allowing the engine to start.
However, if the ECM detects an issue with the key or the NATS system during the starting process, it will trigger the P1610 code, indicating a problem with the immobilizer system.
More specifically, this code becomes active when engine start is attempted 5 or more times using an unprogrammed or faulty key. Other associated codes may include P1614, P1612, P1611, and P1615, each indicating specific issues related to the NATS system, such as antenna amplifier malfunction, key problems, or communication failures.
Is your Nissan refusing to start, and you find the annoying P1610 code on the scanner? I know how frustrating it can be! That’s why I’m here to help!
Simply put, the P1610 Nissan code suggests potential issues with the NATS system or the use of an incorrect key. Don’t wait any longer; gain valuable insights and learn how to fix it in this article!
P1610 Nissan: An Overview
Let’s take a quick look at the essential details of the P1610 Nissan code!
- Definition: Immobilizer Lock Mode
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: No
- Estimated Repair Cost: $30 – $200
P1610 Nissan Code: Immobilizer Lock Mode Explained
The P1610 code, defined as “Immobilizer Lock Mode,” is specifically associated with the Nissan Anti-Theft System (NATS), also known as the Vehicle Immobilizer System. When this code appears, it signifies that the immobilizer system has entered lock mode, preventing the vehicle from starting even with the correct key. It is commonly triggered in various Nissan and Infiniti models, including the Altima, Almera, Frontier, Murano, Pathfinder, Sentra, and Maxima.
The NATS is designed to prevent the unauthorized starting of the vehicle by immobilizing the engine unless the correct key is detected. It works by immobilizing the engine unless the correct key is detected. When you insert the key into the ignition, the NATS antenna amplifier reads the unique binary code transmitted by the key. If the Engine Control Module (ECM) determines that the coded key is valid and matches the registered keys, it activates the fuel-injection sequence, allowing the engine to start.
However, if the ECM detects an issue with the key or the NATS system during the starting process, it will trigger the P1610 code, indicating a problem with the immobilizer system.
More specifically, this code becomes active when engine start is attempted 5 or more times using an unprogrammed or faulty key. Other associated codes may include P1614, P1612, P1611, and P1615, each indicating specific issues related to the NATS system, such as antenna amplifier malfunction, key problems, or communication failures.
P1610 Nissan – Technical Service Bulletins
Nissan knows that many people experience the P1610 code issue, and they have released Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) to help. For example, if you own a 2005-2008 Nissan car with the NATS/Immobilizer system, there is a TSB called “MY 2005 – 2008; ENGINE NO-START WITH NATS DTC P1610” that provides guidance on how to diagnose and fix the problem. So, if you come across the P1610 Nissan code or any NATS-related issues, it’s a good idea to check if your vehicle is covered under any TSB.
How Serious is the Nissan P1610 Code?
The P1610 code is classified as a medium-severity issue. It relates to the immobilizer system and may prevent your vehicle from starting. While it doesn’t typically pose an immediate safety concern, it’s important to take it seriously.
(Image credit: obrazki.elektroda.pl)
If you encounter the P1610 code, you won’t be able to continue driving because the car enters lock mode. Trying to escape lock mode without fixing the underlying problem is not recommended.
Address the issue promptly to avoid future inconvenience or starting problems. Ignoring the code could result in occasional difficulty starting your car or complete immobilization.
Symptoms Of The P1610 Nissan Code
When your Nissan is affected by the P1610 code, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Engine cranks but does not start
- Intermittent starting issues
- Security indicator light stays on or flashes
- Malfunction indicator lamp (MIL)/ check engine light illuminates
Important Note: Check the security indicator light. If it remains off during or after engine cranking, the issue may not be related to NATS.
Causes Of The P1610 Nissan Code
The P1610 code can be triggered by various factors and underlying issues, including:
- Faulty NATS ignition key (most possibly the transponder)
- NATS antenna amplifier malfunction
- Issues with the Body Control Module (BCM) or Immobilizer Control Unit (IMMU)
- Problems with the ECM
- Wiring or connection problems within the NATS system
Read more: Nissan OBD1/OBD2 Codes List [Free PDF Download]
P1610 Nissan Code: Diagnosis And Repair Guide
In this section, we’ll walk you through diagnosing and resolving the P1610 error code in your Nissan, providing valuable repair insights along the way.
Essential Tools And Parts
- Test light or multimeter
- NATS ignition key(s)
- Replacement NATS antenna amplifier (if necessary)
- Wiring diagrams and service manuals (for reference)
Step-by-Step Procedure
1. Try alternate keys
If you have a spare programmed key, try using it to escape your vehicle from lock mode.
- Method 1: Insert the spare key into the ignition and turn it to the ON position for 5 seconds, then turn it back to the OFF position. Repeat this process three times.
- Method 2: If the above method doesn’t work, you can try disconnecting the vehicle’s battery for approximately 30 minutes.
After reconnecting the battery, attempt to start the car using the spare key.
2. Inspect and replace/reprogram key
Carefully examine the key for any visible damage, such as cracks, chips, or excessive wear.
- If the key shows signs of damage or wear, repair the faulty components or replace the whole key. Make sure you have the new key properly programmed.
- If the key is in good condition, it may need reprogramming. Consult a locksmith or Nissan dealership for key reprogramming services.
3. Test NATS antenna amplifier
- Locate the NATS antenna amplifier, typically near the ignition switch or the key insertion area.
- With the ignition key in the OFF position, use a test light or multimeter to check for power and ground at the NATS antenna amplifier.
- If there is no power or ground, further investigation may be required, and it is recommended to consult a professional or Nissan dealership for assistance.
4. Check NATS wiring and connections
- Inspect the wiring harness and connections related to the NATS system.
- Pay attention to any visible indications of harm, such as wires that are damaged or showing signs of wear and tear, any corrosion or rust, or connections that are not securely attached.
- Repair or replace any damaged wiring or connections as necessary.
5. Consider BCM and/or IMMU replacement
- If the P1614 code, indicating a BCM or IMMU issue, continues to appear consistently after attempting the previous steps, it may be necessary to replace the BCM and/or the IMMU.
- It is recommended to seek the assistance of a professional technician or visit a Nissan dealership for accurate diagnosis and replacement of the affected components.
Note: Consult the vehicle’s specific service manual or wiring diagrams for detailed instructions and diagrams tailored to your Nissan model.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The DIY repair level for addressing the P1610 code can range from moderate to advanced, depending on your experience and comfort level with automotive repairs. While some steps, such as escaping the lock mode, can be performed by most DIY enthusiasts, other tasks may require specialized knowledge and tools.
Below is a table outlining potential repair tasks related to the P1610 issue in a Nissan vehicle:
| Repair Task | Cost Range |
| Diagnostic fee | $50 – $150 |
| Wiring repair | $50 – $200 |
| Key replacement/reprogramming | $50 – $300 |
| NATS antenna amplifier replacement | $100 – $300 |
| BCM – IMMU replacement | $200 – $800 |
It is important to note that estimated costs may vary based on Nissan model, location, and parts availability. Consult a mechanic or Nissan dealership for accurate diagnostics and professional repairs to ensure proper NATS system functioning.
Wrapping Up
Navigating the P1610 Nissan code may seem daunting. Still, armed with the knowledge we’ve shared, you’re well-equipped to tackle this immobilizer-related challenge. Remember, timely diagnosis and repair are vital to ensuring a smooth driving experience.
If you found this article helpful, please share it with fellow Nissan owners who may benefit from it. We also encourage you to leave your comments and questions below.
Stay informed, stay empowered, and keep your Nissan running at its best. Safe travels!
Reference Sources
- Nissan & Infiniti Tech News, An Introduction to Nissan Anti-Theft Systems.
- Nissan Technical Service Bulletin, ENGINE WILL NOT START NVIS/NATS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION KEY REGISTRATION.
P1604 Toyota Code: Startability Issues And Fixes
P1604 Toyota Code: Startability Issues And Fixes
Get ready to tackle the P1604 Toyota code with our informative guide. If you’re experiencing engine starting problems, this article is your roadmap to resolution. I’ll walk you through the possible causes, step-by-step diagnosis, and effective solutions for the P1604 code.
Say goodbye to the frustration and hello to a smoothly running vehicle. Let’s dive in and address the P1604 Toyota code together.
P1604 Toyota: A Quick Overview
Here’s a summary of the P1604 for Toyota. Give it a check now!
- Definition: Startability Malfunction
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: No
- Estimated Repair Cost: $50 – $500
What Does The P1604 Mean In Toyota Vehicles?
The P1604 diagnostic trouble code (DTC) in Toyota vehicles is defined as “Startability Malfunction” and refers to engine starting trouble or long cranking times. This code is stored when the engine fails to start despite receiving the STA (Start) signal or when it takes an extended period for the engine to start. In addition, the code can be triggered if the engine speed is low or if the engine stalls shortly after starting.
Specifically, the P1604 Toyota code can be triggered if either of the following conditions is met:
- 1. The engine speed remains below 500 RPM for a specific duration while the STA signal is active.
or
- 2. The engine speed rapidly drops to 200 RPM or lower within approximately 2 seconds after the engine starts, following an initial speed of 500 RPM or higher.

(Credit: tacomaworld.com)
The P1604 code commonly occurs in various Toyota models. Some of the models that may experience this code include the Toyota Camry, Corolla, RAV4, Tundra, Camry, and Tacoma.
In some cases, the P1604 DTC may be stored due to engine starting difficulties caused by a fuel shortage. Therefore, checking the fuel level is an important initial step to ensure accurate diagnosis and avoid unnecessary troubleshooting efforts.
Read more: P1605 Toyota Code: Engine Rough Idling Solutions
How Serious Is The P1604 Toyota Code?
The severity level of the P1604 Toyota DTC is considered moderate. While this code indicates engine starting trouble or prolonged cranking times, it does not pose an immediate safety risk or cause significant damage to the vehicle. However, it is not advisable to continue driving with this code present.
When the P1604 DTC is active, the engine may experience difficulties starting, low engine speed, or stalling after starting. This can lead to inconvenience and potential breakdowns, especially in situations where the engine fails to start altogether. To avoid unexpected issues and ensure reliable vehicle operation, it is recommended to address the underlying problem causing the P1604 code immediately.
What Are The Signs Of The P1604 Toyota Code?
The following are common symptoms associated with the P1604 Toyota DTC:
- Check engine light (MIL) illuminated
- Engine fails to start
- Extended cranking time
- Low engine speed
- Engine stalls shortly after starting
- Engine misfire
What Are The Causes Of The P1604 Code In Toyota Vehicles?
The P1604 Toyota DTC can be caused by various factors, including:
- Immobilizer system malfunction
- Engine assembly issues such as excess friction or compression loss
- Faulty starter assembly
- Malfunctioning crankshaft position sensor and/or camshaft position sensor
- Malfunctioning engine coolant temperature sensor
- Issues with fuel system (fuel pump, fuel injector, etc.)
- Issues with the throttle body or pressure regulator
- Battery-related problems
- Faulty drive plate or flywheel
- Malfunctioning spark plug or ignition coil circuit
- Problems with the intake system or camshaft timing oil control valve
- Malfunctioning mass air flow meter or air-fuel ratio sensor
- Valve timing issues
- Issues with the purge VSV (Vacuum Switching Valve)
- Malfunctioning intake valve
- Problems with the Engine Control Module (ECM)
Please note that further diagnostics may be necessary to pinpoint the exact cause of the P1604 Toyota code.
Read more: Toyota OBD1/OBD2 Codes List [FREE DOWNLOAD]
How To Diagnose And Repair P1604 Toyota Code?
In this section, I’ll talk about the tools and parts you might need, walk you through a guide for diagnosing and resolving the P1604 Toyota code issue, and discuss the level of DIY repair required, along with potential cost estimates.
Though some tasks can be tackled by DIY enthusiasts, it is advisable to seek professional assistance if unsure or when dealing with more complex repairs.
Diagnostic Tools And Essential Parts
To diagnose and repair the P1604 Toyota code, you may need the following tools and parts:
- OBD-II scan tool
- Multimeter
- Fuel pressure gauge
- Spark plug wrench
- Socket set
- Replacement parts (based on diagnosis)
Step-by-Step Guide
- Use an OBD-II scan tool to retrieve and record any additional trouble codes and freeze frame data.
- Inspect the battery and electrical connections for any signs of corrosion or damage. Repair any detected problem.
- Check the fuel level and ensure the vehicle has an adequate fuel supply. Fill the tank if the fuel level is low.
- Test the fuel pressure using a fuel pressure gauge to ensure it meets manufacturer specifications. Make any modifications if needed.
- Inspect the spark plugs for wear, fouling, or damage and replace if necessary.
- Use a multimeter to test the crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sensor for proper operation. Repair or replace the parts if problems occur.
- Check the engine coolant temperature sensor for any faults or inconsistencies.
- Inspect the wiring and connections related to the starting system and repair any damaged or loose connections.
- Perform a thorough inspection of the intake system, including the throttle body and intake valve, for any obstructions or malfunctioning components. Repair or replace if necessary.
Note:
- This guide may not address all possible causes, and if the code reappears or persists, we highly recommend seeking the assistance of a skilled mechanic.
- It is important to record the freeze frame data. This data is helpful in determining the underlying cause of the code. Consult this TSB for more details.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The diagnostic procedure for the P1604 Toyota code requires intermediate-level automotive repair knowledge and experience.
While DIY enthusiasts can perform some steps, such as checking electrical connections and inspecting spark plugs, other tasks may necessitate specialized tools or expertise. We recommend consulting a professional mechanic for a comprehensive diagnosis and repair.
The estimated costs for repairing the P1604 code can vary depending on the specific cause and the necessary repairs. Here is a general cost breakdown:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Replacement of spark plugs | $40 – $100 |
| Repairing wiring/connectors | $50 – $200 |
| Replacement of sensors | $100 – $300 |
| Fuel system repairs | $100 – $500 |
| Other component repairs | Varies |
Conclusion
Resolving the P1604 Toyota code and getting your vehicle back on track is within your reach. Furthermore, with the knowledge and steps provided, you can confidently diagnose and address this issue. Don’t keep this valuable information to yourself – share it with fellow Toyota owners who may be encountering the same challenge.
Remember, if the P1604 code reappears or persists, it’s advisable to seek the expertise of a skilled mechanic for an accurate diagnosis and precise repairs.
If you have any questions or success stories, we’re here to listen. Share your experiences and insights in the comments section below. Let’s engage in a discussion and support each other!
Reference Sources
- JustAnswer, P1604 Startability Malfunction
- RepairSmith, 10 Prominent Weak Car Battery Symptoms
P1131 Ford: Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix
P1131 Ford: Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix
The OBD II code P1131 is quite common on most Ford Vehicles, including on Ford F150, Ford Ranger, Ford Taurus, Ford Explorer, Ford Expedition, Ford Mustang, and Ford Escort.

Introduction to P1131 on Ford Vehicles
The error code P1131 is displayed by getting feedback from the Lambda (or the oxygen) sensor. The Lambda sensor is responsible for detecting the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. Based on that, the PCM (Powertrain Control Module) manipulates whether the engine is running on a lean or rich fuel mixture.
A lean running condition of the engine happens when the engine runs on less fuel or too much air, ultimately resulting in the error code P1131 on Ford vehicles.
An engine running on a lean mixture, may lead to sluggish acceleration and reduced fuel economy. Thus it becomes crucial to understand the P1131 on Ford Vehicles and ways to resolve this error code.
Read more: Ford 302 vs. 351W: Which engine should I choose?
Code P1131 Ford Definition and Meaning

In simple terms, the OBD II code P1131, when displayed on your Ford Vehicle, indicates the PCM detected a malfunction. By estimating the O2 amount, the PCM assesses whether the engine is running on a rich or lean fuel mixture. A lean mixture can give rise to various problems and thus displays the code P1131.
Whereas, an optimized fuel mixture is preferred because of the following-
- Better Fuel Economy
- Better Acceleration
- Reduced tailpipe emissions
- Prolonged engine life
In contrast, an engine running on a lean mixture can give rise to many issues that can appear combinedly or separately. That is discussed in the coming sections.
Some of The Other OBD II Codes That Are Related to P1131 on Ford Vehicles are-
- P1137
- P1151
- P1157
- P0171
- P0174
Symptoms of P1131 on Ford
The most visible symptoms of the P1131 code is-
- Check Engine light ‘ON.’
- Slow Acceleration
- Poor fuel economy
- Car Unable to Start
Moreover, there are some other symptoms for the P1131 code on Ford. But, the chances of encountering them are minimal-
- Engine Stalling
- Engine Knocking
- A rise in Exhaust gas Emissions
- Engine frequently misfires
Causes of P1131 on Ford

There can be various causes for the error code P1131-
1. Fuel System Malfunctioning
Issues in the Injectors, fuel filter, pump, etc., can result in a low quantity of fuel reaching the combustion chamber. The components listed below collectively or individually can cause Fuel System Malfunctioning-
- Clogged Fuel filter: This may create a barrier to fuel passing the filter during the filtering process, thus creating a lean mixture.
- Defective Fuel Pump: A lean mixture can be formed due to the fuel pump’s inability to supply the fuel with the required optimal pressure.
- Faulty Fuel Injectors: The injectors are responsible for spraying the fuel into the combustion chamber. If they start to leak or become dirty, it may result in an interrupted fuel injection into the cylinder. The injectors with low pressure can result in the formation of a lean mixture.
2. Oxygen Sensor Inaccuracy
At times, it is possible that the sensor responsible for measuring the O2 in the cylinder malfunctions. Thus, reporting more oxygen in the mixture than the actual quantity. The amount of oxygen is proportional to the air quantity supplied. As a result, the PCM may display a lean mixture. Thus displaying the P1131 code.
3. Air Mass Flow Sensor Inaccuracy
The Air Mass Flow sensor estimates the amount of air that’s entering the cylinder. A faulty Air mass flow sensor may inaccurately assess the quantity of incoming air. Thus, as a result, the P1131 code may be displayed on the Ford vehicle.
4. Computer Malfunction
Though the chances of malfunctioning of an on-board computer are very low, however, a faulty on-board diagnostics system can inaccurately display the P1131 code.
5. Air Leaks
Innumerable hoses and gaskets are employed in an engine. These components are not built to last forever. Hence, it is possible due to incessant exposure to heat and pressure; any of these components gives rise to air leaks. Thus, air leaks can find its way into the engine, assisting in the formation of a lean mixture.
How Serious is P1131OBD II Code on Ford
Though the issues causing the P1131 code may not impact your vehicle’s functioning. However, if ignored, these can cause severe damage to other vital components in the long term.
A regular check-up or servicing might help to resolve the problems responsible for OBD II code P1131. Additionally, looking for the causes mentioned above can help fathom the issue much faster and easier.
Can You Drive with p1131?
It is not recommended to drive your Ford while the P1131 code is being displayed.
A petrol engine running on a lean mixture can cause problems like-
- Reduced Performance
- Engine Knocking (Inconsistent fuel combustion)
- Damage to Piston
A Diesel engine running on a lean mixture may not result in the same problems but still can cause-
- Low Output from engine
- Engine Stalling
However, the vehicle with the P1131 code can cause sudden jerks with lagging acceleration. Moreover, it may reduce the efficiency of the vehicle while increasing emissions.
Tools Needed to Fix any of these Issues-
How to Fix the Code P1131 on Ford?
The first and foremost thing to be done when checking for the causes of the P1131 code is to connect a car diagnostic scanner to the car’s OBD. Running a diagnostic scan can give comprehensive information on the malfunctioned system to help resolve the issue promptly.
Moreover, if running an OBD diagnostics does not helps then, follow these steps to fix the code P1131-
Step 1– Check and Replace any damaged engine air-intake hoses
Step 2– Tighten the Spark Plugs Connecting Wires
Step 3– Check and Resolve any issue with Distributor assembly, like rotor or cap
Step 4– Check any fault in the fuel supply
Step 5– Lastly, but importantly check the wiring and connection of the Oxygen Sensor.
If the issue still goes undetected, then visiting a service center might help.
Tips to Avoid p1131 in the Future
Here are a few Tips to Avoid OBD II Code P1131-
- Servicing your Ford F150/ Ford Ranger/ Ford Taurus/ Ford Explorer/ Ford Expedition/ Ford Mustang/ Ford Escort regularly
- Replacing worn off engine gaskets and hoses
- Monitoring the fuel injection pressure from the injectors
- Checking for any Engine air leaks
Frequently Asked Questions
Q) Why do lambda (oxygen) sensors fail?
- Lambda sensor is continuously exposed to the high temperature of exhaust gases. Thus heat and vibration can cause damage to the wirings and connections. Moreover, the lambda sensor can be faulty due to corrosion as well.
Q) What happens if my O2 sensor is damaged?
- A damaged O2 sensor doesn’t cause any serious problems. You can even drive with a bad O2 sensor. However, it may hamper other engine components in the long term and can even affect the overall vehicle’s performance.
Q) My Ford is driving fine, but it shows code P1131?
- This could be because of the malfunction of any of the components responsible for diagnostics, or your Ford is driving fine because the issue is still in its initial phase and can increase over time.
Read more : 9 Best Ford/Mazda OBD2/OBD1 Scan Tools for 2024
P112F BMW Explained: Symptoms, Causes, and Solutions
P112F BMW Explained: Symptoms, Causes, and Solutions
When it comes to diagnosing and resolving issues with BMW vehicles, one troublesome code that frequently arises is P112F. This fault code pertains to the “Manifold Absolute Pressure To Throttle Angle Too High Bank 1“. Understanding its symptoms, potential causes, and possible solutions is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
Let’s dive into the details and equip ourselves with the knowledge needed to address the P112F code in BMW vehicles.
P112F BMW: A Quick Overview
Look at the summary for the BMW P112F code below!
- Definition: Manifold Absolute Pressure To Throttle Angle Too High Bank 1
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: No
- Estimated Repair Cost: $50 – $500
What Does The P112F BMW Code Mean?
The P112F BMW is a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that indicates a problem with the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor. The MAP sensor is used to monitor engine load by sampling the depression in the inlet manifold. When the throttle valve is opened, the inlet manifold pressure decreases. The MAP sensor sends a signal to the Digital Motor Electronics (DME), which uses this signal to calculate the amount of fuel to inject into the engine.
When the P112F code gets triggered in a BMW, it signifies an inconsistency between the indicated intake manifold pressure and the calculated mass airflow, a value derived from the throttle-valve angle. In simpler terms, there is a discrepancy between the expected engine load and the actual measured values.

(Credit: f30.bimmerpost.com)
Here are some of the BMW models (but not limited to) usually have the P112F code: 3 Series (E90, E92, E93), 5 Series (F10, F11, N55), 7 Series (F01, F02), X3 (E83, F25), X5 (E70, F15), X6 (E71, F16).
There are a few accompanying codes that can go along with the P112F code in BMWs. These codes include: 28A0, 2D2E, P0300, P0171, P0172, etc.
How Severe Is The P1449 Code In BMW?
The P112F BMW DTC is considered a moderate severity code. This means that it can cause drivability problems, but it is not likely to cause any major damage to the engine in the short term.
However, it is still not advisable to continue driving with the P112F code. Driving with this code could eventually harm the engine. If you have the P112F code in your BMW, it is best to have it diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible. The mechanic will be able to determine the cause of the code and recommend the necessary repairs.
What Are The Signs Of The P1449 BMW Code?
Several symptoms may manifest when encountering the P112F code in a BMW vehicle. Common symptoms include:
- Check Engine Light (CEL)/Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated
- Reduced engine power or loss of acceleration
- Rough idle or stalling
- Poor fuel efficiency
- Engine misfires or hesitation
- Shaking or shuddering
What Causes The P1449 Code in BMW Vehicles?
The P112F code in BMW vehicles can have various underlying causes, including:
- Wiring or electrical connection problems
- Intake manifold leaks or vacuum hose issues
- Malfunctioning MAP sensor
- Faulty throttle valve or throttle position sensor
- DME requires updates or goes defective
How to Fix And Diagnose The P112F BMW Code?
In this section, we will discuss the essential tools and parts required for the fixes. I will also provide a step-by-step guide to diagnose and repair the P112F BMW code and the rough estimates for the main repair tasks involved.
Essential Tools And Parts
In order to effectively identify and clear the C1109 code in Nissan vehicle, you will require the subsequent tools and components:
- Diagnostic scanner
- Multimeter
- Wiring and connectors
- Throttle position sensor
- Manifold absolute pressure sensor
- Vacuum hoses
Step-by-Step Procedure
1. Retrieve fault codes
Connect a diagnostic scan tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port and retrieve any additional accompanying fault codes.
2. Inspect wiring and connectors
- Inspect the wiring harness and connectors associated with the intake pipe vacuum sensor and throttle body for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Repair if necessary
3. Check for vacuum leaks
- Check the fuel vapor lines for vacuum leaks.
- Look for cracked or disconnected hoses, loose fittings, or damaged connectors.
- Fix it if the problem is detected.
4. Test the MAP sensor and throttle position sensor
- Use the multimeter to test the MAP sensor and throttle position sensor.
- The sensor readings should be within the specified range.
- If the sensor readings are not within the specified range, then replace the faulty sensor.
5. Replace the intake manifold gasket
If the sensors are within the specified range, then replace the intake manifold gasket.
6. Clear the code and test drive
- After fixing the issues, use the OBD-II scanner to clear the BMW P112F code and other trouble codes.
- Then, take the car for a test drive to check if it’s working properly again.
Read more: BMW Fault Codes: FREE Comprehensive OBD1 And OBD2 Codes List
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
Diagnosing and repairing code P112F BMW requires intermediate to advanced automotive repair knowledge and experience. While some steps, such as fixing the wiring issue or vacuum leak repair, can be done by DIY enthusiasts, other tasks may require professional assistance.
The estimated cost of repairs can vary depending on the specific vehicle model, labor rates, and the need for replacement parts. Here is a table listing estimated costs:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Wiring repair or replacement | $100 to $300 |
| Vacuum leak detection and repair | $50 to $200 |
| MAP sensor replacement | $100 to $300 |
| Throttle position sensor replacement | $100 to $300 |
| Intake manifold gasket replacement | $200 to $500 |
It is important to note that these costs are approximate and may vary significantly based on various factors, including location and dealership or independent repair shop rates. If unsure or uncomfortable with the repair process, it is recommended to seek the assistance of a qualified mechanic or automotive professional.
Final Thoughts
Ready to tackle the P112F code in your BMW? Armed with the knowledge you’ve gained, you can confidently diagnose and resolve this issue. Don’t keep this valuable information to yourself – share it with fellow BMW enthusiasts who may be facing similar challenges.
If you have any questions or success stories, we’re here to listen in the comments section below. Keep your BMW running smoothly and stay tuned for more expert automotive guides. Drive with confidence!
If you’re interested in exploring the BMW code list or other car brand OBD2 code lists, check out our OBD2 code list generator.
Reference Sources
- Professional Auto Repair, What Is Engine Misfiring? Professional Auto Repair Blog
- Delphi Auto Parts, Making Sense of Your Sensors: MAP Sensor. Delphi Auto Parts Resource Center
P1101 Chevy Cruze – Intake Air Flow System Performance
P1101 Chevy Cruze – Intake Air Flow System Performance
One of the most common diagnostic trouble codes (DTC) Chevrolet Cruze users get is the P1101. The trouble code is expected because of the unreliable nature of the PCV (Positive Crankcase Ventilation) system that Chevrolet uses for most of its vehicles. This code and a few more will still reoccur even after replacing the whole PCV system.
There is a lot of misinformation on how this system works. Therefore, I’m going to go through a basic but clear overview of how the system works. Below is an outline of how the gas flows in a Gen 1 Chevy Cruze 1.4L Turbo PCV system.
The PCV system was created to help with the engine’s ventilation to have better efficiency and fuel economy from the engine. When the motor runs, some of the exhaust gas comes through the piston rings since there is no perfect seal, but most of it goes out through the car’s tailpipe.
The gas that comes through the piston ring enters the crankcase. This creates a positive pressure which has to be evacuated. The crankcase hosts an oil separator in the valve cover. The oil separator absorbs the oil vapor from the gas and redirects it back to the engine. The rest of the gas is directed through a chamber in the valve cover into the cylinder head and then enters the intake manifold, as shown.
There is one check valve at the entry of the intake manifold. This check valve is opened under vacuum with a PCV pressure control diaphragm to allow the gas in. The PCV pressure control diaphragm regulates the amount of vacuum produced by the intake manifold when the engine is under vacuum conditions on the crankcase (the ideal vacuum is 11-18 inches of water.)
The PCV pressure control diaphragm is shown below. A lot of people refer to it as the PCV valve or the PCV vacuum regulator diaphragm.
The PCV pressure control diaphragm is prone to failure. In most cases, this is the part you will have to fix to get rid of the P1101 code and similar ones depending on the problem’s length and severity.
Once the gas passes the first check valve, it flows through a corrugated hose that leads it into the second check valve at the turbo inlet, exiting it into the turbo inlet.
The P1101 code is mostly attributed to your PCV system’s condition, cleanliness, connections and wiring, the shape of the diaphragm, and sometimes the throttle body’s cleanliness. Various car parts will eventually develop carbon build-up and house deposits over a long period of use. This dirt may sometimes lead to the occurrence of the P1101 code.

The P1101 Definition
Definition: Intake Air Flow System Performance
In some other vehicles, the P1101 code is stored when the PCM detects a problem with the Mass Air Flow Sensor System (MAF). The PCM usually detects the problem when it runs its self-diagnostic test called the Key-On Engine Running (KOER) test. The problem is registered if the MAF voltage is lower or greater than the one set by the manufacturer.
What The P1101 Chevy Cruze Trouble Code means
The P1101 Chevy Cruze code is stored when the PCM detects a problem with the Intake Air Flow System’s performance. The problem is registered if the Intake Air Flow System’s performance is lower or greater than the one set by the manufacturer.
When you see this code, the issue lies within the realm of the Intake Air Flow System. This includes the PCV system, intake manifold, check valves, connectors, wiring, and any element associated with airflow along its vicinity.
Other codes that may be related to the P1101 code in Chevrolet Cruze vehicles (depending on the length and severity of the problem) are:
1. P0171 – Fuel Trim System Lean
2. P0106 – Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Performance
3. P0507 – Idle Air Control – RPM higher than expected
Some Of The Symptoms Associated With The P1101 Code Are:
1. Rough idling
Due to the increased idle speed (measured in RPM – Revolutions Per Minute) of the engine. Idle speed is the rotational speed an engine runs when it is idling (the vehicle isn’t moving, but the engine is still running.) This number will vary depending on the car. In Chevy Cruze vehicles, the number ranges from 600-800 rpm depending on the engine cylinders and transmission mode.
2. Reduction in fuel economy – this will be apparent with an increase in the liters per 100km you use. The lower the number of liters stated, the better the fuel economy.
3. Engine running roughly – you will probably notice this when you start experiencing some shaking and bouncing sensation in the car, followed by odd sounds and irregular RPM.
4. Smoke from the tailpipe – smoke out of the tailpipe is associated with several causes such as oil leakage and condensation. The smoke may appear white or blue.
5. Hissing noise in the engine bay – this will imply that there may be a leak in the engine bay (punctured hose/broken connections) or a ruptured PCV pressure control diaphragm.
Causes Of The P1101 Trouble Code In Chevy Cruze Vehicles:
1. Broken or blocked PCV system hose – The blocked hose may cause the oil to be pushed up into the combustion chamber, causing the oil to burn inside the engine and out the exhaust pipe.
2. Check valves may be blocked/clogged. Pressure change in the PCV system or dirt accumulation in the check valves will prevent efficient gas flow. The result will be a low fuel economy due to the gas and oil mixture difference.
3. Air leakage before and after the Intake Air Flow System. This may be leakage along the corrugated hose connecting the turbo and the intake manifold.
4. The PCV pressure control diaphragm may have busted/ruptured. A faulty PCV pressure control diaphragm will affect the pressure difference in the PCV system resulting in a hissing sound.
5. Air filters may be blocked. Dirty air filters may prevent sensors from getting correct readings, therefore, resulting in reading errors.
How Serious Is The P1101 Code On Chevy Cruze?
The P1101 code is mostly not an indicator of a significant problem in your Chevy Cruze. However, it would cause internal problems in your engine if left unchecked for a prolonged period. Also, depending on the severity of the problem, it will result in rough driving, terrible fuel consumption, and power loss.
Moreover, the repair cost for the problem is relatively cheap at around $50 -$60 (applies when you are replacing the PCV regulator system by yourself – which is most of the time).
As a rule of thumb, always make sure you take every warning sign seriously, especially when you don’t know the problem. Early diagnosis and fixes will save you a lot of money down the road and maybe your life too.
Also, make sure to always do regular maintenance on your Chevrolet Cruze. Just because the check engine light isn’t on, it doesn’t mean that your car is running optimally.
How To Diagnose And Fix The P1101 Code Quickly On Any Chevy Cruze
Before you pop the hood and take a look inside, you will need an OBD-II scanner.
These are the step-by-step procedures you should follow:
1. Use the OBD-II scanner to detect all the trouble codes stored in the car system.
2. Remove the PCV system cosmetic cover. Start the engine and let it run while the car is idle. Place a finger on the opening of the PCV pressure control diaphragm if you notice a hissing sound from it. If the hissing sound stops, you may have found your problem. If that is the case, all you have to do is replace the entire PCV cover since the diaphragm is fixed to it. However, it is advisable to keep diagnosing more problems to see if there is a more significant underlying issue, i.e., faulty PCV check valves.
3. Turn the engine off and locate the corrugated hose connected to the PCV check valve on the intake manifold. The hose is brittle; it may break if not carefully handled. Disconnect the hose from the base. Use a torch to look inside the pathway from which the hose has been disconnected.
4. You may notice an orange or pink like a nipple at the back of the pathway. That is the check valve. If it is not visible, use cotton swabs and rubbing alcohol to clean the region. Check again. If the check valve is not visible, this may be the problem that you were looking for. A replacement part (for the entire intake manifold from a certified seller) and further analysis from a certified mechanic may be required.
5. The next step is to check the PCV hose connected to the two check valves. Without disconnecting the other side, blow air into the hose; it should blow freely. The next step is to suck air back from the hose, after which it should block the airflow. It will need to be replaced if it doesn’t do any of the above. A hissing sound will be present if the hose is leaking while the engine is running.
6. Fix the leaks, if any, and re-run the scanner test to see whether the code is still there. If you followed all of these procedures, your problem should be fixed.
7. If the replacement unit doesn’t fix the problem, you will have to test the PCM to determine if it is terrible. A lousy PCM will have to be replaced, but this would require a qualified professional’s extensive work.
Tips To Help You Avoid Getting The P1101 Code In The Future
1. Regular cleaning and maintenance. Most car troubles can be fixed by a regular cleaning habit and a short, frequent visit to the mechanic.
2. Check for vacuum leaks regularly.
Read more: P1345 Chevy: Crankshaft position- camshaft position correlation
Frequently Asked Questions
How to replace the intake manifold?
The process is simple and straight forward. Please read this article to learn how to do it.
Can I fix the P1101 trouble code by cleaning the PCV?
Sometimes, yes. Carbon build-up and depositions tend to clog pathways and restrict airflow. A regular cleaning schedule and maintenance check may help fix the problem. However, you should make sure to check for any underlying issues even if the problem disappears.
How long can I drive my Chevy Cruze with the P1101 code?
From a statistic standpoint, you would have to reach 50000 – 70000 miles before replacing any of these parts. However, this will depend on the car model, year of make, and usage.
Is fixing the problem worth it? Should I get a better car instead?
You may be tempted to get rid of your vehicle mainly because the problem is likely to occur time and time again. However, the cost of repairing the car is more economical than what you will get by selling it. The critical parts of the vehicle are quite reliable, hence, worth the keep.
Should I buy any generic replacement parts?
No. As mentioned earlier, even the most certified replacement parts will eventually fail. It is advisable to get the most reliable one of them all for a longer life span, in which case you will need the ones from General Motors themselves.
Read More: Bad MAP Sensor Symptoms and How To Troubleshoot
B1352 Ford Code: Ignition Troubles Unveiled And Resolved
You’re out and about in your Ford, enjoying the ride, when suddenly, the Check Engine Light springs to life on your dashboard. That’s when you reach for your trusty OBD scanner, revealing the culprit: the B1352 Ford code.
Don’t worry, though – in this article, we’ll decode this secret language and help you understand what the B1352 code is all about. Whether you’re a curious driver or a DIY enthusiast, get ready to unravel the mystery behind your car’s messages and learn how to tackle the B1352 code.
B1352 Ford: A Quick Overview
Below is a summary of the B1352 Ford Code. Check it out!
- Definition: Ignition Key-In Circuit Failure
- Severity: Low
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $20 – $250
What Does The B1352 Code Mean On Ford?
When you see fault code B1352, it means the car’s control module (BCM) noticed a problem with the ignition key circuit. This happens when you put in the key, and one of the critical wires isn’t working as it should. You might like to know, this often affects the wires that provide power to the door chimes through the ignition switch.
(Credit: Powerstroke.org)
Please note that the B1352 fault code is specific to certain manufacturers, appearing exclusively in Ford and Jaguar vehicles. This code doesn’t apply to all types of cars, so it’s limited to these particular brands.
Additionally, it’s essential to be aware of similar fault codes that might be recorded and could assist in identifying the issue. Codes such as B2961 and B2965 are among the codes to look for. These codes can provide further insights into the problem at hand.
How Severe Is The B1352 Ford Code?
B1352 fault code is typically a minor issue. Sometimes, the vehicle runs fine with the code, but it might also lead to a no-start condition. If the engine doesn’t crank, fixing the code quickly is best to get the vehicle running. Otherwise, addressing the problem whenever possible is a good idea to prevent potential complications.
What Are The Signs Of The B1352 Code On Ford Vehicles?
The symptoms of the B1352 Ford code may include the following:
- Check Engine Light on
- Engine cranking but not starting
- Car not starting at all
Read more: P1131 Ford: Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix
What Causes The B1352 Ford Code?
The B1352 Ford code can be caused by the following:
- Defective door chime component
- Wiring or connection issues
- Malfunctioning ignition switch
- Bad PCM or BCM (rarely)
How To Diagnose And Fix The B1352 Ford Code
When faced with the B1352 Ford code, addressing the issue promptly is crucial for maintaining the functionality of your vehicle’s ignition system and security features. The following parts will show you essential stuff for your fixing process as well as a step-by-step guide to address the problem.
Essential Tools And Parts
- Replacement door chime component
- Wiring harness or connectors
- Ignition switch assembly
- Replacement keys (if required)
- Replacement PCM or BCM
- Obd-II scanner
- Multimeter
- Trim removal tools
- Socket and wrench set
Step-by-step Procedure
Step 1: Inspect the door chime component
Check for any signs of damage or malfunction in the door chime system. If necessary, replace the faulty component to ensure proper functionality.
Step 2: Check wiring and connections
Carefully inspect the wiring and connections related to the ignition key circuit, including those associated with the door-open switches and the ignition switch. Repair or replace any damaged wires or connectors.
Step 3: Examine the ignition switch
Inspect the ignition switch for any signs of wear, damage, or irregular operation. If the switch is problematic, consider replacing it to restore proper functionality.
Step 4: Diagnose the PCM and BCM
The PCM and BCM are integral to the vehicle’s operation and security systems. If other solutions do not resolve the issue, a comprehensive diagnostic scan of these modules may be necessary. Seek professional help to diagnose and address any potential problems with these modules.
Step 5: Clear the trouble codes
After identifying and resolving the underlying issues, it’s essential to clear the B1352 trouble code from the vehicle’s memory. This can typically be done using a diagnostic tool or by disconnecting the vehicle’s battery for a short period. Clearing the code ensures that the issue has been successfully addressed.
Read more: Complete List Of Ford OBD2 Codes for FREE Download
Estimated Costs For B1352 Code In Ford Vehicles
The cost of replacement parts for addressing the B1352 Ford code can vary based on factors such as the specific vehicle model, brand, and parts availability. If you are not confident in fixing the problem yourself, just find a skilled Ford mechanic to do it for you flawlessly.
Here’s a rough estimate of the cost for the components that might be involved in fixing the issue:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Door chime component replacement | $20 to $50 |
| Ignition switch assembly replacement | $50 – $150 |
| Key replacement | $50 – $250 |
| PCM or BCM replacement/repair | $200- $1000 |
B1352 Ford Infographic
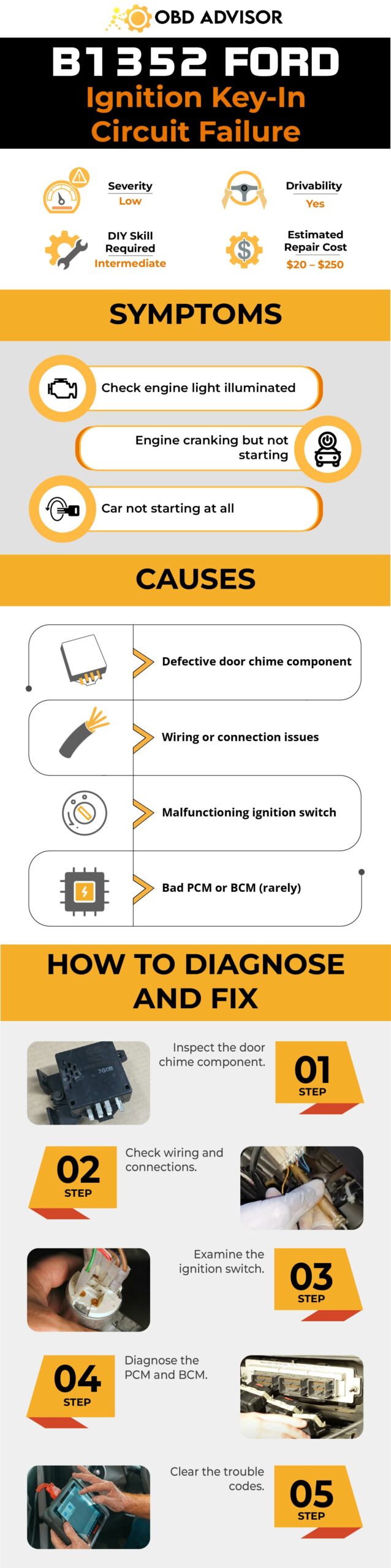
Final Thoughts
In the world of modern vehicle diagnostics, understanding and addressing specific trouble codes like the B1352 Ford code is crucial. By recognizing its significance and potential causes, you’re better equipped to navigate the path toward effective solutions.
If this article has been helpful, consider sharing it with fellow car enthusiasts. Feel free to leave your comments below, sharing your experiences or questions related to the B1352 code. Safe driving and smooth troubleshooting!
References Sources
TroubleCodes.net, B1352 OBD Trouble Code.
P1326 KIA Code: What KIA Drivers Need to Know
P1326 KIA Code: What KIA Drivers Need to Know
For KIA vehicle owners, encountering an unfamiliar error code like P1326 can be a source of confusion. Fear not, I’m going to shed light on its significance and implications.
In this article, I’ll break down what this code means, why it pops up, and what you can do about it. From understanding its potential impact on your vehicle’s performance to learning about effective solutions and preventive measures, I’ve got you covered.
Whether you’re a hands-on car enthusiast or a concerned KIA owner, we provide you with the insights needed to address the P1326 code with confidence.
Let’s dive in!
P1326 KIA: A Quick Overview
Go through the P1326 KIA code summary outlined below!
- Definition: Knock Sensor Detection System
- Severity: High
- DIY Skill Level: Advance
- Continue To Drive?: No
- Estimated Repair Cost: $100 – $400
What Does The P1326 KIA Code Mean?
The P1326 error code is associated with the Knock Sensor Detection System (KSDS) in certain Kia models. This code serves as an early warning system, detecting vibrations that indicate potential excessive wear in the connecting rod bearings of the engine.
When this code appears, the vehicle is placed in Limp Home Mode, which limits acceleration and restricts engine RPMs to approximately 1800-2000 RPM. The purpose of Limp Home Mode is to minimize further damage to the engine and prevent potential engine failure. Prompt action is crucial to address the underlying problem and avoid severe consequences.

(Credit: kia-forums.com)
The code P1326 is commonly set in many different KIA models, such as Optima, Sorento, Soul, Sportage, etc. According to Technical Service Bulletin (TSB) PI1803W/X, Kia dealers are instructed to perform specific procedures for certain models (2011-2014 Kia Optima, 2011-2013 Kia Sportage, 2012-2014 Kia Sorento) affected by the P1326 error code. Even if your Kia model is not listed or no longer under warranty, it is still recommended to take your car to a Kia dealer for a check-up and seek their advice.
How Severe Is The P1326 Code In KIA?
The P1326 error code in KIA vehicles has a high severity level. In theory, when a car experiences the P1326 error code, it may go into limp mode, where it is still technically driveable.
However, it is advisable not to continue driving your car in this state. Limp mode is a safety feature that limits the vehicle’s performance to prevent further damage. It is strongly advised to avoid driving the vehicle in limp mode and instead seek professional assistance to diagnose and address the problem promptly.
What Are The Signs Of The P1326 KIA Code?
The P1326 error code in KIA vehicles is accompanied by a range of noticeable symptoms:
- Check Engine Light (CEL) blinking
- Reduced engine power or acceleration
- Rough idling
- Engine stalling or difficulty starting
- Limp mode activated
- Knocking sound
What Causes The P1326 Code in KIA Vehicles?
Various underlying causes can trigger the P1326 error code in KIA vehicles. Some common causes for this code are:
- Faulty knock sensor
- Wiring issues
- Excessive wear in connecting rod bearings
- Engine mechanical failures (seized engine or rod knock)
- Faulty ECM (Need to update or replace)
Keep in mind that these are possible reasons, and it’s crucial to go through a detailed diagnostic procedure to pinpoint the actual issue in your specific vehicle accurately.
Read more: P1777 Nissan Code: A Practical Repair Guide
What To Do When Encountering The P1326 In Your KIA?
When encountering the P1326 error code in a KIA vehicle, it is important to take appropriate actions to address the issue effectively. In most cases, this code’s presence indicates a potential problem with the engine, which typically requires professional inspection and may involve updating or replacing the engine. Therefore, it is crucial not to drive the vehicle and immediately take it to a KIA dealer for a thorough inspection.
Attempting to clear the code yourself is not recommended, as the dealer will need to see the CEL blinking to accept addressing the issue. According to a post by Joel Strawn on Optimaforums.com, he shared his experience as follows: “I recently encountered this code and cleared it to drive home. However, when I contacted the dealer, they informed me that they would not take any action unless the MIL was flashing and the previous code was stored in the ECU. Eventually, I managed to get the light to come back on, and now they have agreed to honor the warranty for my 2016 Sorento, despite it having 113,000 miles on it. Now, I will wait and see how long it takes for the repairs to be completed.“
Why Choosing The KIA Dealer Over DIY?
It is important to understand that the faulty engine associated with the P1326 code is not something you can handle on your own. Take your car to a KIA dealer to assess if an engine update or replacement is necessary. They have the expertise and technical knowledge to diagnose the problem accurately and recommend the appropriate course of action.
KIA services are known for their excellent customer support and satisfaction. In most cases, car owners have reported receiving a new engine, albeit with additional fees for minor components or services. Therefore, it is reassuring to rely on KIA services to address the issue effectively.
If it turns out that the engine isn’t causing the issue, it might be due to problems with sensors or wiring. In this case, you’re in luck, as fixing these sensors or wiring issues usually costs around $100 to $400. This is much more affordable than having to replace the whole engine, which could cost a lot more.
Final Thoughts
So, there you have it—a glimpse of the P1326 error code in KIA vehicles. Armed with this insight, you have a better understanding of this trouble code and draw up a plan to get your KIA back on track properly.
If this article is helpful, don’t hold back—share your thoughts with fellow car enthusiasts and KIA owners. Keep the conversation going by leaving a comment below.
Here’s to smoother rides and empowered driving experiences ahead!
If you have any other codes you want to learn about, check out our OBD2 Code Lookup Tool! Get fast answers for those trouble codes. Try it now for smoother drives and peace of mind.
Reference Sources
- Technical Service Bulletin, ENGINE REPLACEMENT INSTRUCTIONS FOR DTC P1326 (PI1803W/X)
- Carotech Automotive, Can a Seized Engine Be Fixed?
- MotorTrend, What Is Rod Knock?
P1260 Ford Code: Vehicle Theft Detection?
P1260 Ford Code: Vehicle Theft Detection?
Attention, Ford owners! If you’re encountering the P1260 code on your vehicle, you’ve come to the right place.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the P1260 Ford code. From its meaning and severity to symptoms, causes, and repair solutions, we’ve got you covered.
So, let’s get started!
P1260 Ford: A Brief Summary
Here’s a quick summary of the P1260 in Ford vehicles to provide you with essential information!
- Definition: Theft Detected, Vehicle Immobilized
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $100 – $500
What Is The P1260 Error In Ford Vehicles?
The P1260 code in Ford vehicles is related to the Passive Anti-Theft System (PATS). It indicates a “theft condition,” which occurs when the PATS detects either an incorrect signal or no signal at all from the chipped key. The purpose of the PATS is to prevent the unauthorized starting of the engine by immobilizing it when an incorrect key is used.
Several components are involved in triggering this code. When you insert the chipped key into the ignition, it transmits a unique code to the PATS transceiver module. This code is then sent to the instrument cluster (IC), which verifies its authenticity. If the key is determined to be valid, a signal is sent to the powertrain control module (PCM), allowing the engine to start.
However, if the IC receives an incorrect or no signal from the chipped key, the P1260 code is triggered, and the engine is disabled, preventing it from starting. It’s important to note that this code can also occur if a new instrument panel cluster (IPC), IC, or PCM is installed without proper programming, even if the vehicle is not equipped with PATS.

(Image credit: Explorer Forum)
The P1260 code is commonly found in various Ford models such as the F150, Mustang, Focus, Escape, Expedition, Explorer, and Fusion. If you experience a theft condition in your Ford vehicle equipped with PATS, this code may appear. It serves as an indicator to investigate the PATS system for any other related diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that may provide additional information about the issue.
How Serious Is The P1260 Ford Code?
The P1260 code in a Ford vehicle carries a moderate severity level. While you can still drive with this code present, it’s best to keep it to a minimum and address the issue promptly.
Sometimes the engine may engage after a short time, allowing you to continue your journey. However, there is a chance that the engine may not start at all.
So, it’s important to take action as soon as you can to restore the normal functioning of the vehicle’s anti-theft system and ensure reliable engine startup. By dealing with the code promptly, you can avoid potential inconveniences and unexpected situations on the road.
Signs Of The P1260 Ford Code
When the P1260 code is present in a Ford vehicle, it can cause several noticeable symptoms.
- Engine startup failure
- Engine immobilization
- Anti-theft light illuminated
Read more: Ford Dashboard Symbols and Meaning
Understanding Why The P1260 Ford Code Occurs
The P1260 code in Ford vehicles can be triggered by various underlying causes.
- Use of an incorrect key
- Malfunctioning key chip (transponder)
- Previous theft condition
- Issues with the wiring integrity between the transceiver and PATS module
- Malfunctioning transceiver module
- Internal concerns with the PATS or PCM module
- Incorrect programming of the PCM, IC, or IPC
Read more: Complete List Of Ford OBD2 Codes for FREE Download
Steps To Diagnose And Resolve The P1260 Ford Code
This section starts with a quick solution for the P1260 error code. Then, we’ll cover the tools, step-by-step troubleshooting, DIY repair level, and estimated costs. Let’s get started!
Quick Solution: Driving Cycle Clearing Method
Start the engine and drive the vehicle for two “driving cycles.” A driving cycle consists of starting the engine, driving the vehicle for at least 15 minutes, and then shutting it down. Repeat this process once more, completing a total of two driving cycles.
After completing the two driving cycles, start the engine for the third time. If the issue is successfully resolved, the P1260 code should clear itself.
If the quick solution does not resolve the issue, you can proceed with the following detailed steps.
Essential Tools And Parts
To diagnose and repair the P1260 code, you will need the following tools and parts:
- OBD-II scanner
- Basic hand tools: Screwdrivers, pliers, etc.
- Multimeter
- Replacement parts: Key, wiring harness, transceiver module, etc.
Your Step-by-Step Guide
- Retrieve codes using a compatible diagnostic tool. Connect the tool to the OBD-II port and access the PATS module to get the codes indicating PATS-related problems.
- Analyze retrieved codes and troubleshoot PATS issues. Review the codes obtained from the PATS module and use them to identify specific PATS-related problems. Perform necessary troubleshooting steps, such as checking wiring connections, inspecting components, or replacing faulty parts, based on the analysis of the codes.
- Ensure proper key usage. Verify the correct key and try a second key, if available, to rule out a faulty key.
- Reset the P1260 code after resolving PATS issues. Keep the key in the “on” position for about two minutes or until the theft light stops flashing. Attempt to start the vehicle and check if the system resets.
- Check the steering column shroud for tampering. Inspect for damage and ensure the transceiver module behind the shroud is securely in place.
- Look for aftermarket remote start systems. If present, have them inspected or removed by a professional, as they can interfere with the PATS system.
- Ensure proper programming if a new PCM was installed. Reprogram keys to synchronize with the new PCM if needed. Seek assistance from a locksmith or professional experienced in PATS reprogramming.
- If the issue persists, visit a dealer or shop with a compatible scanner to perform advanced diagnostics and troubleshooting on the PATS system.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
When it comes to repairing the P1260 code related to the PATS system, the level of DIY repair can vary depending on the specific cause and the individual’s expertise. It is essential to assess your own skills and comfort level with automotive repairs before attempting to fix PATS-related issues on your own. If you are unsure or have limited experience, it is recommended to seek assistance from an expert or mechanic who specializes in automotive security systems.
Here is a breakdown of estimated costs for some of the main repair tasks associated with the P1260 code and the PATS system. Please note that these costs are approximate and can vary based on factors such as location and specific vehicle requirements.
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Wiring Harness Repair | $30 to $200 or more |
| Key Replacement | $50 to $300 |
| PATS Module Replacement | $100 to $200 |
It’s important to consider these costs as a general guideline and be aware that actual expenses may differ. Before making any decisions, it’s advisable to research local prices and consult with professionals or authorized service centers for accurate estimates tailored to your specific situation.
P1260 Ford Infographic
Wrapping Up
Dealing with the P1260 Ford code can be a bit tricky, but we’re here to help you out. If you follow our instructions and have the right tools and parts, you have a good chance of fixing the issue.
However, it’s important to remember that if you’re unsure or lack experience, seeking professional assistance is always a wise decision. Don’t hesitate to reach out to an expert or mechanic for accurate diagnosis and guidance.
If you found this information helpful, feel free to share it with others who may benefit, and don’t forget to leave your comments and questions below. Safe travels!
Reference Sources
- Sportsmobile Forum,How to clear P1260 error – Theft Detected – Engine Disabled.
- Trouble Codes, P1260 – Theft Detected Vehicle Immobilized.
- JustAnswer, P1260 – Theft Detected, Vehicle Immobilized – Is There a Fix?.
- Fixya, Code P1260, what does it mean and how to fix it.
- Craig D, 2021, 2012 Ford Fusion – MotoLogic.
- McGill University, 2007 PCED On Board Diagnostics – SECTION 4: Powertrain.
P1605 Toyota Code: Engine Rough Idling Solutions
P1605 Toyota Code: Engine Rough Idling Solutions
Welcome to our informative guide on P1605 Toyota, a diagnostic trouble code that can affect the performance and reliability of your Toyota vehicle.
If you’ve encountered this code, it’s important not to panic. In this article, we’ll explore P1605 Toyota in-depth, covering its meaning, severity, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and repair steps.
As a seasoned mechanic with years of experience, I aim to share my expertise and help you navigate through this issue effectively.
So, let’s dive in and solve the P1605 Toyota together.
P1605 Toyota: A Quick Overview
Here’s a quick overview of the P1605 for Toyota. Check it out!
- Definition: Engine Rough Idling
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Advanced
- Continue To Drive?: No
- Estimated Repair Cost: $200 – $500
Understanding The Meaning Of P1605 Toyota – Engine Rough Idling
The P1605 diagnostic trouble code is triggered when the engine speed of a Toyota vehicle drops below the set speed. Specifically, this code is stored when, after 5 seconds or more elapse following engine startup, the engine speed decreases to 400 rpm or less, as detected by the vehicle’s onboard computer (ECM) using a one-trip detection logic.
To fully comprehend the implications of P1605 Toyota, it’s essential to understand the systems and components involved. This code is typically associated with the engine control and SFI (Sequential Fuel Injection) systems. These systems work together to regulate the engine’s performance, fuel injection timing, and various other parameters to ensure smooth operation.
When the engine speed drops below the set speed, it indicates an irregularity in the engine’s idle control or a potential malfunction within the components linked to idle stability.
Commonly affected models include the Corolla (especially years 2012 and 2015), Highlander, Tundra, Camry (especially years 2012, 2013, and 2014), RAV4, Tacoma, Vitz, Hilux, Land Cruiser, Prado, 4Runner, Belta, Yaris, and Land Cruiser.
It’s worth noting that the P1605 code is often associated with related codes, such as P1603 and P1604, which further aid in diagnosing the underlying issue.
Read more: Complete Toyota OBD1/OBD2 Codes List [FREE DOWNLOAD]
Special Note About P1605 Toyota Code
In some specific Toyota models, the P1605 code can refer to a Knock Control CPU malfunction, indicating a problem with the engine’s knock control system. However, it’s important to note that this article specifically focuses on the P1605 code pertaining to Engine Rough Idling. The information provided here is intended for diagnosing and resolving engine rough idling issues associated with the P1605 code.
If your Toyota model is affected by the Knock Control CPU malfunction, it is recommended to consult a professional mechanic or authorized Toyota service center for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate resolution, which may involve checking the Engine Control Module (ECM) for faults or malfunctions and repairing or replacing it if necessary.
How Serious Is The P1605 Toyota Code?
When it comes to the severity of the P1605 Toyota code, it is generally considered to have a moderate level of severity. While it may not pose an immediate safety risk, it is crucial not to ignore or neglect this code.
Driving with the P1605 code present can lead to various issues, including rough idling, decreased engine performance, and potential stalling. These symptoms can impact the overall drivability and reliability of your Toyota vehicle.
To ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your vehicle, it is advisable to address the P1605 code promptly. Continuing to drive without addressing the underlying cause can potentially lead to further damage to engine components or other related systems.
Read more: Toyota Dashboard Symbols and Meanings (FULL list, Free Download)
Common Symptoms Of P1605 Toyota
The P1605 Toyota code can manifest in various symptoms, indicating an issue with the engine speed or idle control. Common symptoms include:
- Check engine light illuminated
- Rough idle
- Slow acceleration
- Engine vibration leading to engine shutdown
- Engine shutdown without vibration
- Engine starts with accelerator pedal depressed
- Rough idling after engine startup

(Image credit: Toyota Owners Club Forum)
Exploring The Causes Of P1605 Toyota
The P1605 Toyota code can have various underlying causes that trigger the engine speed drop. To help you easily follow the list, the causes are categorized as follows:
| System/Component | Causes |
| Intake System | Air leak in the intake system |
| Emission Control System | Brake booster assembly |
| Purge VSV | |
| Sensor and Sensor Circuit | Power supply circuit |
| Engine coolant temperature sensor | |
| Mass air flow meter subassembly | |
| Fuel System | Fuel pump control circuit |
| Fuel pump | |
| Fuel line | |
| PCV valve and hose | |
| Engine Control System | Ignition system |
| Camshaft timing oil control valve assembly | |
| Knock control sensor | |
| Other Systems and Components | Wire harness or connector |
| Thermostat | |
| Park/Neutral Position switch assembly | |
| Air Conditioning system | |
| Electrical load signal system | |
| Power Steering system | |
| Charging system | |
| Automatic Transaxle system | |
| Immobilizer system | |
| ECM |
How To Accurately Diagnose And Repair P1605 Toyota Code?
In this section, we will cover the essential tools and parts required, provide a step-by-step procedure for diagnosing and fixing the code, and discuss the DIY repair level and estimated costs.
Diagnostic Tools And Essential Parts
To diagnose and repair the P1605 Toyota code, you may need the following tools and parts:
- Diagnostic scanner
- Multimeter
- Vacuum gauge
- Smoke machine
- Intake gaskets
- Sensor replacement parts
- Ignition components
- Fuel system components
Step-by-Step Guide
Diagnosing and fixing the P1605 Toyota code involves two cases based on the engine speed decrease. Follow the steps below for each case:
Case 1: Engine Speed Decreased Slowly
Step 1: Inspect ignition system
Inspect the ignition system components, including spark plugs, power supply circuit, and ignition coil assembly. Look for any faults or malfunctions. Repair or replace if required.
Step 2: Perform air fuel ratio check
- Inspect the intake system for air leaks. Check the connections and brake booster assembly. Repair any leaks found.
- Test the air-fuel ratio related sensors, such as the mass air flow meter, air-fuel ratio sensor, thermostat sensor, and engine coolant temperature sensor. Repair or replace any malfunctioning sensors indicating richness or leanness beyond normal limits.
- Verify the fuel supply system, including the fuel pump control circuit, purge VSV system, fuel lines, and ECM. Repair or replace any damaged components.
If the vehicle still exhibits abnormal behavior, proceed to the next steps.
Step 3: Check intake air volume
- Check the intake air volume to ensure it is sufficient. Inspect the air passage for obstructions and excessive valve overlap in the camshaft timing oil control valve assembly. Repair or replace faulty components if necessary.
- Clean the intake manifold and throttle body if required.
- Check the vacuum system for leaks and repair any detected issues.
Step 4: Verify ignition timing
Verify that the ignition timing is operating properly. Adjust it if necessary to ensure correct timing.
Case 2: Engine Speed Decreased Rapidly
Step 1: Check electrical system
- Inspect the ignition and injection system for any electrical system malfunctions.
- Look for signs of power interruption or temporary power cuts.
- Examine the power supply circuit to the fuel injector and ignition coil assemblies.
- Repair or replace any faulty components in the electrical system.
Step 2: Verify external load
- Examine external components that may be causing an increased load on the engine, such as the power steering or air conditioning system.
- Note any malfunctions or abnormalities in these external parts.
Step 3: Address external part malfunctions
If any external part malfunctions are identified, repair or replace the faulty components. Ensure proper functioning of external systems that can impact engine load.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The repair procedure for the P1605 Toyota code is classified as advanced. It involves checking and inspecting multiple components within the engine system, requiring a good understanding of engine systems, diagnostic tools, and troubleshooting techniques.
If you are unsure or uncomfortable with the procedure, it is highly recommended to seek assistance from an experienced mechanic or automotive professional who can accurately diagnose and resolve the issue.
Estimated costs for main repair tasks are as follows:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Wiring repairs | $50 – $150 |
| Vacuum system leak repair | $50 – $150 |
| Air-fuel ratio sensor replacement | $50 – $200 |
| Mass air flow meter replacement | $100 – $300 |
| Thermostat sensor replacement | $50 – $150 |
| Engine coolant temperature sensor replacement | $50 – $150 |
| Ignition component replacement | $100 – $300 |
| Fuel system component replacement | $100 – $500 |
Remember, these are estimated costs and can vary based on various factors such as location, vehicle model, and labor rates. It is advisable to consult with a professional for accurate cost estimates.
P1605 Toyota Infographic
Wrapping Up
Before we wrap up our discussion on the P1605 Toyota code, let’s take a moment to applaud your commitment to understanding, diagnosing, and fixing the issue. It’s no easy task, but with the right tools, knowledge, and a dash of persistence, you’re well on your way to getting your Toyota back in top shape.
Remember to approach the process step-by-step, examining the air-fuel ratio, intake system, sensors, ignition components, and fuel system. If you ever feel stuck or unsure, don’t hesitate to ask a trusted mechanic for help.
Keep up the great work, and we’re here to support you every step of the way! Share your thoughts or questions below – we’d love to hear from you.
Reference Sources
MotoLogic, 2014 Toyota RAV4 P1603, P1605 Repair Manual
P1614 Nissan Code: Causes And Solutions Of NATS Issues
P1614 Nissan Code: Causes And Solutions Of NATS Issues
Hello, fellow Nissan enthusiasts! Are you stumped by the P1614 code?
It can be a real head-scratcher but don’t worry – as an experienced mechanic and lover of all things Nissan, I’m here to help.
In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the P1614 Nissan code and what it means for your vehicle. We’ll cover everything from the symptoms to the solutions, so grab a cup of coffee and let’s dive in!
P1614 Nissan: A Quick Overview
Below is a summary of the P1614 Nissan code. Check it out!
- Definition: Chain of IMMU-KEY
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: No
- Estimated Repair Cost: $100 – $500
What Does The P1614 Code Mean On Nissan?
The P1614 trouble code on Nissan vehicles is a signal of a communication issue between the key and the engine immobilizer in the Nissan Anti-Theft System (NATS). Specifically, this code indicates a chain of IMMU-KEY errors, as explained by Nissan in a technical document used for advanced diagnostics that “IMMU cannot receive key ID & Dongle unit is malfunctioning (IF FITTED).“

The NATS or Nissan Vehicle Immobilizer System (NVIS) is an integrated anti-theft system designed to prevent the unauthorized starting of the engine. This system works through the cooperation between the key, engine control module (ECM), and immobilizer control unit (IMMU). The IMMU is responsible for validating the key and sending a signal to the ECM to allow the engine to start. If the IMMU detects an issue with the key or the signal, it will set the P1614 code. Other codes related to the Nissan anti-theft system, such as P1610 (Lock Mode), P1615 (Difference of Key), and P1612 (Chain of ECM-IMMU), can also be triggered alongside the P1614 code.
Is the P1614 Nissan Code Serious?
The P1614 code in Nissan vehicles is a moderately severe issue that should be addressed as soon as possible. While it may not have immediate consequences, neglecting the issue could lead to potential problems down the line.
Regarding driving with the P1614 code, it is not recommended. This is because the code is often related to the vehicle’s immobilizer system, which could prevent the car from starting or operating properly. Attempting to drive the vehicle with this code active could cause further damage, resulting in costly repairs.
What Are The Warning Signs of the P1614 Nissan Code?
Here are some warning signs that you may encounter if the P1614 code is triggered:
- Car starting issues such as engine cranking but not starting, engine starting, and then stalling. This is because the immobilizer system is preventing the engine from starting without a properly registered key.
- Immobilizer warning lights
- Illuminated check engine light
What Causes the P1614 Nissan Code?
There are several possible causes of the P1614 code on Nissan vehicles:
- Damaged, not programmed, improperly registered NATS ignition key
- Dead or low battery in the key fob
- Failed NATS (especially NATS antenna)
- Faulty IMMU or BCM
- Faulty ECM (in rare cases)
How To Diagnose and Fix The P1614 Nissan Code?
If your Nissan is displaying the P1614 code, it’s crucial to address the issue promptly to ensure the proper functioning of your vehicle’s immobilizer system. Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to diagnose and fix the problem, as below. Let’s explore!
Tip: If you see the P1614 error code along with the P1610 code, it’s important to escape from the lock mode. So how to do it? First, turn the key to the “ON” position and wait for the security light to turn off. Then, turn the key to the “OFF” position. Next, repeat this process for a total of three cycles.
Essential Tools and Parts
- Diagnostic scanner
- Car key programmer
- Nissan key fob battery
- Key fob transponder chip
- NATS antenna
Step-by-step Procedure
Step 1: Use a diagnostic scanner to retrieve any trouble codes that may be present. This can help identify any related issues that may be contributing to the P1614 code.
Step 2: Check that you are using the correct key for your Nissan. Make sure it is not damaged or worn out. Sometimes you might find a damaged transponder chip inside the key. If you have a spare key, try using it to determine if the error code still appears.
Note: I always recommend testing the key using a car key programmer/tester to be sure. Sometimes, I’ve found that a faulty ignition switch coil can cause the engine not to start and trigger the P1614 code. In these cases, the key test tool may detect the issue. If the ignition switch coil is found to be faulty, I replace it and test again to see if the problem is resolved.
Step 3: Check the condition of the key fob’s battery. If it’s weak or dead, communication issues between the key and the IMMU might occur. Replace the battery if necessary.
Step 4: Reset the immobilizer system by disconnecting the battery for several minutes, then reconnecting it.
Step 5: Inspect the NATS antenna operation. Replace it if necessary by following the steps in the service manual.
Step 6: If the above steps do not resolve the issue, reprogramming the key to the vehicle’s IMMU system may be necessary. To ensure proper reprogramming, it’s best to seek the help of a qualified automotive locksmith or a Nissan dealership as they have the necessary expertise and equipment.
Step 7: If the issue still persists, there may be a problem with the IMMU system itself. As dealing with this system is a complex task, it is advisable to leave it to your nearest Nissan dealership or a certified mechanic with experience in Nissan vehicles. If the issue is determined to be with the BCM, it may need to be reprogrammed.
Estimated Repair Costs for P1614 Code in Nissan Vehicles
While DIYers can do some of the steps outlined above with some automotive experience, it’s important to recognize when a repair is beyond your skill level and seek assistance from a qualified professional. In particular, tasks such as replacing the NATS antenna or reprogramming the key or BCM require specialized equipment and knowledge and can be costly if done incorrectly.
The estimated repair costs for these steps can vary widely, as shown in the table below. It’s important to be prepared for some variation in repair costs, depending on the specific task and where you have it done.
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Key fob battery replacement | $5-$20 |
| NATS antenna replacement | $200-$500 |
| Key reprogramming | $50-$150 |
| BCM reprogramming | $200-$500 |
P1614 Nissan Infographic
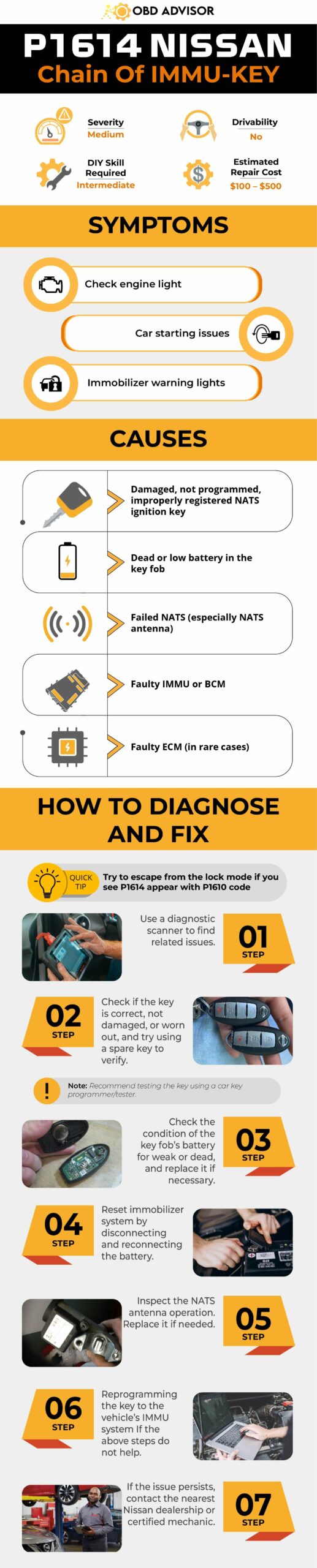
Final Thoughts
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the P1614 Nissan code. Remember, working with the immobilizer system can be complex. Therefore, if you’re not confident in automotive repairs, it’s always best to seek assistance from a professional to avoid causing further damage. Additionally, always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and safety protocols when working on your vehicle.
If you have any questions or comments, feel free to leave them below. And if you found this article helpful, please share it with your fellow Nissan enthusiasts. Safe driving!
References Sources
- Nissan Manual for Advanced Diagnostics
- Nissan North America (2005), Technical Service Bulletin: Campaign – ECM reprogramming for engine misfire diagnostic trouble codes (DTC P0300-P0306).
P1399 Honda – Random Cylinder Misfire Detected
P1399 Honda – Random Cylinder Misfire Detected
Introduction To P1399 Honda OBD2
P1399 is a manufacturer-specific code, not a generic one. You will find it in any Honda vehicles – including Honda Accord, Honda CRV, Honda Odyssey, Honda Civic, etc. It shows up whenever there is a random misfire in the engine.
Just locate the vehicle’s OBD2 system to begin the diagnostic process, and you will readily detect this error code.
There are possible steps to follow to correct this issue. Check the provided step-by-step guide in this post for a better understanding.

Code P1399 Honda Definition And Meaning (Technical Description)
P1399 Honda Definition:
Random Cylinder Misfire Detected
Meaning of P1399 on Honda cars
P1399 signifies a random cylinder misfire in your Honda. You are likely to see it if your car’s crankshaft fluctuates in speed. This OBD2 code can easily be picked up by a Crankshaft Positioning (CKP) sensor. The CKP sensor then passes the error to the Engine Control Module (ECM) from where the issue is confirmed.
Symptoms Of P1399 On Honda
A vehicle experiencing engine misfire most often gives you one or more warning signs. Some of these signs could be visible; others are only felt. As a result, you need to be keen enough to spot all these telltale signs before the issue worsens. The symptoms of P1399 are:
- Check Engine light turns on (This is also known as a malfunction indicator lamp)
- A hard start experience
- Engine hesitation issues
- Lack or loss of engine power
Causes Of P1399 On Honda
There are two leading causes of the P1399 Honda error code. These include a:
- Valve clearance not in the normal range
- Clogged exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) Passages
How Serious Is The P1399 Code For Your Honda?
Under any circumstance, never try to continue driving. This advice is especially true if you still don’t know the cause or extent of the damage. Otherwise, the issue might be worsened, making it more costly to repair. Correct the problem as soon as you spot the first symptom. It will save you from all unwanted stress and disappointment.
How To Diagnose And Fix The Code P1399 On Your Honda?
Tools Needed
You need two crucial tools for the process. First is an OBD2 scanner, which will help you know if you are experiencing P1399. Second is a multimeter to test the vehicle’s electrical components.
Procedure To Diagnose And Fix the Code
Step 1: Prepare Your Tools:
Gather your OBD2 scanner and multimeter to ensure that they work well.
Step 2: Retrieve The Error Codes:
Use your OBD2 scanner to retrieve the codes causing your engine to misfire. Most often, you will find P1399 alongside codes like P0301, P0302, P0303, and P0300. Don’t be surprised since all these are misfiring codes. Always try solving these other codes to see if the situation becomes any different.
Step 3: Scan Electrical Components:
Cylinder misfire is, at times, attributed to computer or wiring problems. Use your multimeter to see if the vehicle’s electrical components are in a good state. Correct any fault you find. Otherwise, move to the next step.
Step 4: Check Ignition Coils:
Test your ignition coils to see if one or more are causing the misfire. Do this by unplugging one at a time while the engine is left on idle. Keenly observe the sound produced by the engine when you unplug each. A faulty coil won’t make any changes in engine sound when unplugged. Pull it out to see if it is cracked or damaged in any way. You’ll have to replace or adjust all faulty coils.
Step 5: Check Oxygen Sensors:
A bad oxygen sensor always throws off the fuel-combustion system. It causes an imbalance in fuel to air ratio. It also allows too much fuel into the engine, reducing the vehicle’s gas mileage, which causes the engine to misfire, one of the probable causes of P1399 in Honda vehicles. Check to see if it is in a good state. You must check and correct any faults found.
Step 6: Check Your Valve Clearance:
A blocked or clogged valve clearance can cause the error. At times, the valves become too tight or too loose, making them close and open irregularly. Make the necessary adjustments to ensure enough space for valve expansion when the valves heat up. Tighten or loosen then a bit.
Step 7: Check Your Exhaust Gas Recirculation:
Is your EGR clogged? If yes, then this could be the cause or one of the causes of the P1399 error. Unclog it for a smooth flow of exhaust gasses within the system.
If these solutions fail, then you will have to go deeper into your engine. You might have to look at components like the vehicle’s piston rings and valves. Seek professional advice if the issue is unresolved. It might be more in-depth and more technical than you think. Consider hiring a qualified automotive technician in such situations to make the work more comfortable since they have the right tools and expertise for such challenging tasks.
Tips To Avoid P1399 In The Future
The best solution is to service the vehicle frequently. You can do this on your own or hire a professional technician to ensure that the engine is always operating at optimum levels. Form a habit of continuously checking and replacing faulty parts such as ignition coils and spark plugs. Keep checking your clearance valves to ensure that they are not too tight or loose. Adjust each of them as is required. You should also ensure that your EGR passage remains unclogged. Kindly note that you must adjust the valves every 50,000 miles. All in all, be keen while driving your vehicle. Try not to dismiss warning signs such as when the Check Engine light turns on.
Read More: 8 Best OBD2 Scanners for Honda 2024 [Comparison & Review]
C1109 Nissan Code: ABS Voltage Trouble Exposed
C1109 Nissan Code: ABS Voltage Trouble Exposed
You’ve come across the C1109 code in your Nissan? Don’t you worry! Prepare to gain insights, solutions, and expert guidance for addressing this unique situation.
In this article, we’ll explore the intricacies of the C1109 code, diving into its effects on your vehicle’s performance. From understanding symptoms to conducting diagnostics, we’ll walk you through each stage, keeping you informed and empowered throughout the process.
C1109 Nissan Code: A Quick Overview
Take a look at the summary of the Nissan C1109 code provided below!
- Definition: Battery Voltage [Abnormal]
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: No
- Estimated Repair Cost: $50 – $300
What Does The C1109 Nissan Code Mean?
The C1109 code in Nissan vehicles points to an issue labeled as “Battery Voltage [Abnormal]” within the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) actuator and electric unit control (ECU) unit. This alert activates when the voltage being delivered to the ABS system goes outside the standard operational range. Specifically, it triggers when the voltage drops below 10 volts (indicating low ignition voltage) or rises above 16 volts (indicating high ignition voltage).

(Credit: altimaforums.net)
The ABS system in a vehicle is a crucial safety feature that prevents wheel lock-up during heavy braking, enhancing control and stability. The C1109 code alerts the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system that there is an issue with the battery voltage affecting the ABS control unit. This can lead to compromised performance of the ABS system and potentially impact the vehicle’s braking performance.
The C1109 code can be found in various Nissan models when battery voltage irregularities occur. Some of the Nissan models that are known to experience the C1109 code include Altima, Maxima, Sentra, Rogue, Murano, 370Z, etc.
How Severe Is The C1109 Code On Nissan?
The C1109 code’s severity in Nissan vehicles can vary from moderate to potentially hazardous. Continuing to drive with the C1109 code illuminated could jeopardize braking performance and compromise vehicle stability. It’s strongly advised to avoid driving with this code active.
Get professional inspection and repair are recommended to ensure the ABS functions correctly, maintaining optimal control and safety while driving.
What Are The Signs Of The C1109 Code On Nissan Vehicles?
When the C1109 code surfaces in Nissan vehicles, it comes accompanied by noticeable symptoms that can’t be ignored. Being focused on the signs is crucial for timely diagnosis and resolution. Some of the common symptoms associated with the C1109 code include:
- Illuminated ABS warning light
- Unusual brake pedal feel (sponginess or increased resistance)
- Decreased effectiveness of the ABS system during braking
- Irregularities in vehicle stability during abrupt stops
Read more: P1715 Nissan Code Solved: Tips For Dealing With Transmission Issues
What Are The Causes Of The C1109 Nissan Code?
The underlying triggers behind the C1109 code in Nissan vehicles can be attributed to various components and systems within the vehicle. Understanding these potential causes is key to effectively addressing the issue:
- Faulty harnesses or connectors in the ABS system
- Malfunctioning ABS actuator and ECU
- Blown fuse
- Defective ignition power supply system
- Battery-related issues
How To Diagnose And Fix The C1109 Code On Nissan?
When dealing with the C1109 code, a systematic diagnosis and repair approach can effectively address the issue. Below is a comprehensive breakdown of the process, including essential tools and parts, a detailed step-by-step guide, and a DIY repair assessment:
Essential Tools And Parts
In order to effectively identify and rectify the C1109 code in Nissan vehicle, you will require the subsequent tools and components:
- OBD-II scanner
- Digital multimeter
- Wiring and connectors
- Basic hand tools
- Replacement ABS unit (if required)
- Wiring diagrams
Step-by-Step Procedure
- Code retrieval and initial check
- Use the OBD-II scanner to retrieve the C1109 code and associated freeze frame data.
- Inspect the ABS warning light for illumination.
- Check if there are any noticeable issues with braking performance.
- Visual inspection
- Examine the wiring harnesses and connectors connected to the ABS unit for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Pay special attention to any visible wear on the wiring insulation.
- Replace or repair if necessary.
- Battery voltage test
- With the vehicle’s engine running, use the multimeter to measure the battery voltage.
- Check for voltage fluctuations during engine operation, noting any irregularities.
- Inspect the battery for indications of loose terminals, insufficient voltage, or other anomalies.
- If any components fail, proceed to repair or substitute them accordingly.
- ABS actuator and control unit test
- Disconnect the ABS unit’s electrical connector.
- Use the multimeter to check the resistance and continuity of the connector pins, comparing the readings with manufacturer specifications.
- If the ABS unit or control unit is faulty, consider replacing it with a new or tested one.
- Clearing the code and test drive
- Once repairs are made, use the OBD-II scanner to clear the C1109 code and any associated trouble codes.
- Take the vehicle for a test drive to verify that the ABS system operates correctly and that the code does not return.
Note:
- Ensure proper safety measures are taken, such as disconnecting the vehicle’s battery before working on electrical components.
- Refer to the vehicle’s repair manual and wiring diagrams for accurate information.
Read more: P1217 Nissan Code: Engine Cooling Insights
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
This procedure demands intermediate mechanical skills. While simple tasks like inspecting connectors are feasible for DIY enthusiasts, handling complex electrical components may require professional assistance. Prioritize accuracy and safety. If uncertain, consult a mechanic for a thorough diagnosis and repair.
Take a look at the estimated cost table we have provided for various necessary tasks.
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Wiring and Connector Repair | $50 – $150 |
| Replacement ABS unit (if required) | $200 – $500 |
This is just a rough estimate. Remember, costs can vary based on factors like location and specific tools chosen. Always gather accurate pricing information before proceeding with repairs.
C1109 Nissan Infographic

Final Thoughts
Having explored this comprehensive article on the C1109 Nissan code, you now have a good insight into this code’s symptoms, causes, and repair procedures. This newfound knowledge empowers you to enhance your vehicle’s performance with confidence.
Share this newfound knowledge with fellow Nissan enthusiasts and join the conversation with your comments and questions below.
Safe drive!
Reference Sources
- NiRogue, Nissan Rogue Service Manual.
- ALLDATAdiy, 2009 Nissan-Datsun Altima V6-3.5L.
P17F1 Nissan Code: Diagnosing And Fixing Nissan CVT Judder
P17F1 Nissan Code: Diagnosing And Fixing Nissan CVT Judder
You’ve encountered the P17F1 code in your Nissan? And you’ve been wondering if there would be any danger behind this trouble code? Don’t fret – I’ll make it clear.
In this article, we delve into the meaning, causes, symptoms, severity level, solutions, and estimated costs related to the P17F1 code in a Nissan. Whether you’re a car owner or a seasoned mechanic, understanding this code is essential for maintaining optimal vehicle performance.
I’ll shed light on the P17F1 Nissan code and empower you to execute some fixes with the CVT issues. As a result, you can get your Nissan buddy back on track.
Give it a check now!
P17F1 Nissan: A Quick Overview
Take a look at the summary for the P17F1 code provided below!
- Definition: CVT Judder
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: No
- Estimated Repair Cost: $100 – $500
What Does The P17F1 Code Mean In Nissan Vehicles?
The P17F1 code is a manufacturer-specific diagnostic trouble code (DTC). When this code is logged in Nissan models, it is defined as “CVT Judder”. The code indicates a problem with the continuously variable transmission (CVT) belt slip, leading to juddering or vibration during acceleration or while driving. Proper diagnosis and repair are necessary to address this issue and restore optimal CVT performance.
Let’s have some background information about CVT first. CVT, or Continuously Variable Transmission, is a type of automatic transmission commonly found in Nissan vehicles. Unlike traditional transmissions, CVTs don’t have fixed gears but instead use pulleys and a belt or chain to provide a continuous range of gear ratios. This results in smooth acceleration and improved fuel efficiency.
(Image credit: Best Car Fixes Youtube channel)
It is essential to note that the P17F1 code may be accompanied by other related codes, which can provide further insight into the issue. It is recommended to check for accompanying codes such as P17F0 and P17F2.
The P17F1 code can be found in various Nissan models, including Altima, Maxima Murano, Pathfinder, Rogue, Sentra, etc.
How Severe Is The P17F1 Code In Nissan?
The severity level of the P17F1 code in Nissan vehicles can be classified as medium. The P17F1 code can affect the driving experience by making the car shake or vibrate. While the code may not cause immediate safety hazards or leave you stranded on the road, it is important to address the issue promptly.
Please note that driving with transmission problems can be dangerous and potentially cause further damage to the vehicle. It is strongly advised not to continue driving with the P17F1 code present. Ignoring or neglecting CVT transmission issues can lead to drivability problems, sudden loss of power, or even complete transmission failure, which could result in a breakdown or unsafe driving conditions.
To ensure your safety and prevent further damage, it is recommended to stop driving the vehicle and have it inspected by a qualified mechanic or towed to a repair facility for proper diagnosis and repair.
What Are The Signs Of The P17F1 Code?
The P17F1 code for Nissan can lead to a range of possible issues. If you have this code, you might observe any combination of the following symptoms:
- Illuminated Check Engine Light (MIL)
- Vibrations or shaking during acceleration
- Juddering sensation while driving
- Reduced power or sluggish acceleration
- Transmission slipping or hesitation
What Causes The P17F1 Code in Nissan Vehicles?
The P17F1 code in Nissan vehicles can stem from a variety of factors. Some common causes for this code to appear are:
- Worn or damaged CVT belt
- Improper CVT fluid level or condition
- Faulty CVT pulleys or pulley bearings
- Issues with CVT control module (rarely) or sensors
Remember that these are potential causes and an in-depth diagnostic process is essential to identify the underlying problem in your particular vehicle accurately.
Read more: P1777 Nissan Code: A Practical Repair Guide
How To Diagnose And Fix The P17F1 Code In Your Nissan?
Diagnosing and repairing the P17F1 code in Nissan vehicles requires specific tools, parts, and a systematic approach. Here’s a breakdown of the essential tools and parts, followed by a step-by-step procedure to address the code.
Essential Tools And Parts
To diagnose and repair the P17F1 Nissan code, it is advisable to gather the following tools and parts:
- OBD-II scanner or diagnostic tool
- CVT fluid level gauge
- CVT fluid (if required)
- Replacement CVT belt or pulley (if necessary)
- Basic hand tools (sockets, wrenches, etc.)
Step-by-Step Procedure
1. Code retrieval
Use an OBD-II scanner or diagnostic tool to retrieve and document any additional codes present in the vehicle’s onboard computer system.
2. CVT fluid inspection and adjustment
- Use a CVT fluid level gauge to check the fluid level against the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Ensure the fluid is clean and free from contaminants.
- If the CVT fluid level is low or the fluid condition is poor, perform a CVT fluid change or top-up as necessary.
- Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the correct type and quantity of CVT fluid to use.
3. Belt, pulley inspection and replacement
- Visually examine the CVT belt and pulleys for any visible damage or signs of wear. Check for fraying, cracks, or excessive wear on the belt.
- If the CVT belt is worn, damaged, or nearing the recommended replacement interval, replace it with a new belt following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Ensure proper installation and tensioning of the belt.
- Inspect the pulleys for proper alignment and smooth operation.
4. CVT control module and sensor testing
- Test and troubleshoot the CVT control module and related sensors if the issue persists.
- Use appropriate diagnostic procedures outlined in the vehicle’s service manual to identify and rectify any problems.
- This stage requires advanced skills. It’s advisable to find a skilled mechanic to execute this.
5. Clear codes and road test
- Clear the stored codes using the OBD-II scanner or diagnostic tool.
- Perform a road test to verify if the P17F1 code has been successfully resolved.
- Monitor for any abnormal symptoms or indications of recurring issues.
Note: It is essential to consult the specific service manual for your Nissan model for detailed instructions and specifications.
Read more: C1109 Nissan Code: ABS Voltage Trouble Exposed
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
Diagnosing the P17F1 code can be performed by DIY enthusiasts with moderate automotive repair experience. However, it is advisable to seek expert assistance if unsure, considering the complexity of CVT systems.
The estimated costs for repairing the P17F1 code can vary depending on the specific issue and required parts. Here is a breakdown of the general costs:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| CVT fluid change | $100-$200 |
| CVT belt replacement | $300-$800 |
| CVT replacement (rarely) | $3,000 – $6,000 |
These are rough estimates, and actual costs may vary depending on factors such as the vehicle model, location, and labor rates. It is advisable to consult a qualified mechanic or service center for an accurate diagnosis and cost estimation.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding the P17F1 code is crucial for maintaining vehicle health and performance. It’s vital to address the code promptly, as its severity level can lead to drivability issues.
Consultation with a professional mechanic is recommended to diagnose and resolve the problem accurately. While estimated costs may vary, the investment in timely repairs outweighs potential long-term expenses.
To learn more about P17F1 and share your insights, feel free to comment below and share this article with fellow enthusiasts. Your engagement helps build a knowledgeable community of car owners.
Discover quick answers for OBD2 codes! Visit our lookup tool for instant insights into your Nissan’s health.
Reference Sources
- Technical Service Bulletin: Transmission Shift Actuator Plate/PRNDL Switch [PDF file]
- Car and Driver, What Is a CVT Transmission?
- Boulder Nissan Blog, The Importance of Changing Your CVT Fluid
P1464 Ford Code: A Guide To Handling AC System Issues
P1464 Ford Code: A Guide To Handling AC System Issues
You’re driving your Ford when suddenly, the check engine light switches on. Wondering what’s up, then decide to run some tests. By using a scan tool, you perform the Key On Engine Off (KOEO) and Key On Engine Running (KOER) tests, which check the engine’s parts. Looking at the results show that the AC voltage isn’t normal. This is what triggers the P1464 code to be set.
In this article, we will explain what the P1464 code means, what are its symptoms and causes, and how to fix it.
Let’s get started!
P1464 Ford: A Quick Overview
Below is a summary of the P1464 Ford code. Check it out.
- Definition: Air Conditioning Demand Out Of Self Test Range
- Severity: Low
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $10 – $150
What Does The P1464 Code Mean On Ford?
The P1464 code on Ford is possibly set when the A/C or defroster is activated while performing the Key On Engine Off (KOEO) or Key On Engine Running (KOER) self-test. Besides, there is one more case for the P1464 is when the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) detects a high ACCS input during the self-test process.
In case you want to know more about self-test processes. Here is the answer – KOEO and KOER are self-tests that can be performed with a scan tool to check the sensors and actuators of the engine. KOEO, which means the test is done when the ignition switch is turned to the ON position and the engine is stopped. KOER, which means the test is done when the engine is running at normal operating temperature. These tests can help diagnose problems and report trouble codes.

(Image credit: mavericktruckclub.com)
How Serious Is The P1464 Ford Code?
The P1464 DTC code’s severity is generally low, and it typically doesn’t impact immediate driveability or safety in Ford vehicles. While it relates to the AC system‘s self-test process, it doesn’t affect critical vehicle functions.
So can you are able to continue to drive with this code? The answer is YES. However, addressing the issue promptly is advised to prevent potential long-term AC problems and maintain optimal comfort.
What Are The Symptoms Of P1464 Code On Your Ford?
Identifying the P1464 code’s presence can be crucial in addressing potential AC system issues. Here are the key symptoms associated with this DTC:
- Check engine light illuminated
- Bad AC performance
Read more: Complete List Of Ford OBD2 Codes for FREE Download
What Are The P1464 Ford Code’s Potential Causes?
Let’s explore the common causes behind this P1464 Ford code:
- A/C or defrost on during self-test
- A/CCS circuit short to voltage
- Faulty A/C demand switch
- Damaged Wide Open Throttle A/C Cutoff (WAC) relay
Note: If the A/C or defrost functions were active during the self-test, it’s recommended to deactivate them and then repeat the self-test process.
How To Diagnose And Fix The P1464 Ford Code?
In this section, I will guide you through the process of addressing the issue, along with detailing the necessary tools and parts required for the task.
Essential Tools And Parts
To address the P1464 DTC code in your Ford vehicle’s AC system, you might need the following tools and parts:
Fixing Nissan P1464: Step-by-step Procedure
Resolving the P1464 DTC code in your Ford vehicle involves a systematic approach to identifying and addressing the underlying issue. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to fix this code:
Step 1: Turn off A/C and defrost
If the air conditioning (A/C) or defrost functions were active during the self-test when the code was triggered, start by turning them off.
Step 2: Rerun the self-test
After disabling the A/C and defrost, rerun the self-test procedure. This can sometimes reset the system and clear the code if it was triggered due to temporary conditions.
Step 3: Inspect wiring and connectors
Inspect the wiring and connectors associated with both the A/C demand switch and the A/C control module, searching for indications of damage, corrosion, or connections that have become loose.
Step 4: Test the A/C demand switch
Using specialized equipment, test the A/C demand switch’s readings to ensure they are within the expected range. Replace the sensor if it’s providing inaccurate readings.
Step 5: Check WAC Relay Harness
Examine the wiring harness of the WAC relay for any signs of damage. Repair or replace the harness as needed.
Step 6: Clear the Code
After making necessary repairs, use an OBD-II scanner to clear the P1464 code from the vehicle’s memory. This step will also reset the check engine light.
Step 7: Test Drive
Take your vehicle for a test drive to ensure the code doesn’t reappear and that the A/C system is operating smoothly.
Read more: P1131 Ford: Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix
Estimated Cost For Fixing P1464 On Ford Vehicles
If you’re not confident in your DIY skills or if the tasks involved seem challenging, it’s important to consider seeking the expertise of a professional mechanic. Complex automotive systems require precision and experience to diagnose and fix effectively. Attempting tasks beyond your comfort level could lead to further issues or safety concerns. Your safety and the optimal functioning of your vehicle are paramount, so if in doubt, don’t hesitate to consult a skilled professional who can handle the task with confidence.
Here’s a general breakdown of estimated costs for the outlined repairs. Please note that these figures are rough estimates and the actual expenses may fluctuate based on a range of factors.
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost |
| Wiring and Connectors Repair | $50 to $100 |
| A/C Demand Switch Replacement | $20 to $100 |
| Throttle A/C Cutoff Relay Fixing | $10 to $50 |
P1464 Ford Infographic

Conclusion
With the insights provided in this article, tackling the P1464 DTC in your Ford vehicle’s AC system becomes more manageable. Though the severity is typically low, taking action promptly is advised to prevent potential future issues. Whether you’re a confident DIYer or prefer professional assistance, the outlined steps offer a path to restoring your AC system’s optimal function.
If you found this article useful, consider sharing it with others who might benefit. Feel free to leave your comments below; your experiences and feedback are valuable. Together, we can ensure comfortable and hassle-free journeys in our Ford vehicles.
Reference Sources
- 2005 Ford Pickup F150 P1464 – PRODEMAND
- HOW DO AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEMS WORK IN A CAR? – Universal Technical Institute
P1701 Nissan Code: Get It Fixed With Ease Like Never Before
P1701 Nissan Code: Get It Fixed With Ease Like Never Before
Hey there! Stumbled upon the P1701 Nissan code, huh? If you find yourself scratching your head trying to decipher its meaning, you’re in the right place.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dig deep into the meaning of the P1701 Nissan code, its severity, causes, and the telltale symptoms to watch out for.
But that’s not all – I’ll also provide you with expert tips on diagnosing the issue and fixing it easily.
So, grab your toolbox, and let’s get started!
P1701 Nissan: A Quick Overview
Below is a summary of the P1701 Nissan Code. Check it out!
- Definition: Transmission Control Module (Power Supply)
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes
- Estimated Repair Cost: $75-$200
What Does The P1701 Code Mean On Nissan?
According to the manufacturer’s manual, the P1701 Nissan code is often triggered when the power supply to the transmission control module (TCM) is deliberately shut off. In simpler terms, this code is like a secret message from your vehicle, telling you there’s a hiccup in the power supply to the TCM.
Think of the TCM as the brain of your transmission system, responsible for things like gear shifting and controlling solenoids. Here’s the deal: The TCM relies on a steady and reliable power supply to work its magic.
But sometimes, things go awry. The P1701 code pops up when there’s an interruption or disconnection in the power supply to the TCM. This can happen when you mess with the battery, remove it, or if there’s a pesky wiring issue in the TCM circuit.
Note: Friendly reminder! Sometimes, the P1701 code doesn’t indicate a real problem. When you intentionally cut off the power supply to the TCM, this message might appear on the screen.
To tell the difference between intentional power interruptions and actual malfunctions, consider the situation in which the code appears. If it shows up without you intentionally cutting off the power supply, it’s likely pointing to a genuine malfunction that needs your attention.
Additionally, it’s worth noting that the P1701 code most commonly appears in the following Nissan models: Altima, Maxima, Murano (2005, 2007), Rogue (2008, 2009, 2011, 2013), Sentra, Altima (2008, 2009, 2011, 2012), Nissan Juke, Sentra (2008, 2010, 2011, 2012), and X-Trail. This code is frequently associated with the P0826 code.
The Severity Of P1701: Is Your Nissan In Danger?
The severity level of the P1701 code can be considered medium. While it doesn’t indicate an immediate danger to your Nissan, it shouldn’t be ignored.
You can continue to drive with the code present, but it is recommended for the short term only. It’s important to address the issue as soon as possible to prevent potential transmission problems.
Listen To Your Car: Recognizing Symptoms Of P1701
Common symptoms associated with the P1701 Nissan code include:
- Illuminated check engine light (CEL) or service engine soon (SES) warning light
- Battery light on
- Transmission-related issues, such as rough shifting, slipping, or hesitation
Read more: 4 Most common transmission control module symptoms
Solving The Puzzle: Common Causes Of P1701 Nissan Code
Based on my experience dealing with Nissan vehicles, the P1701 code is often caused by harness or connector issues.
Picture this: open or shorted circuits in the battery or ignition switch or a glitch in the TCM circuit. Those pesky wires! Sometimes they get damaged—frayed or broken, you know. And loose or corroded connectors? They can mess with the electrical connections, triggering the P1701 code.
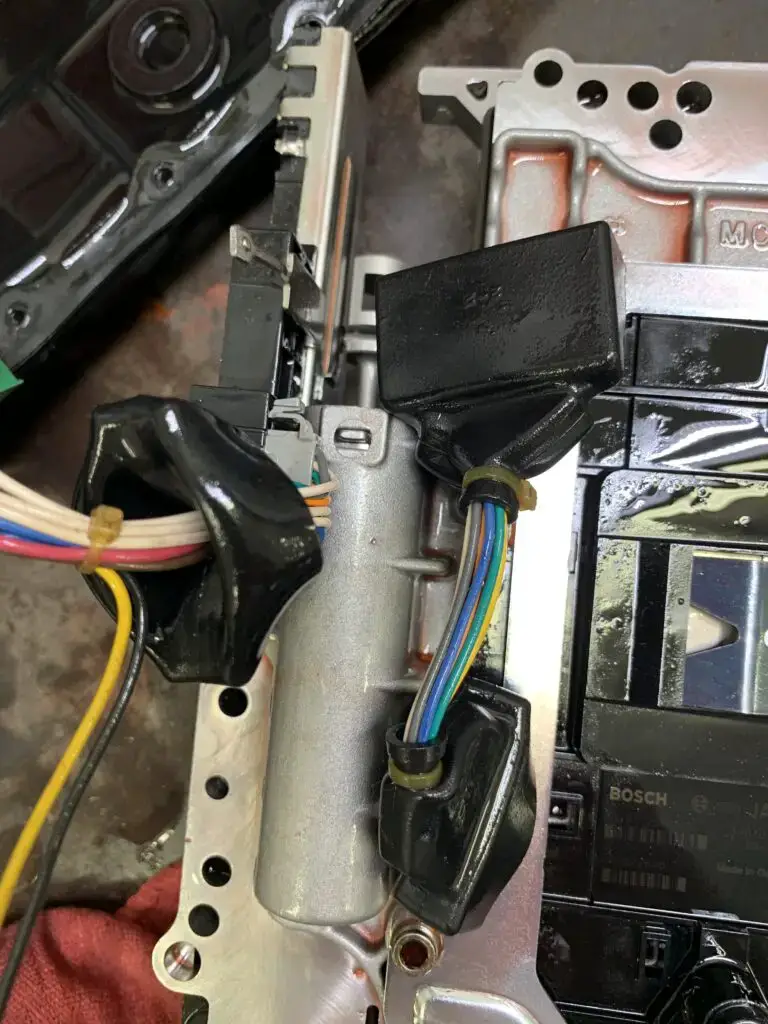

(Image credit: JustAnswer)
In rare cases, I’ve also seen instances where the TCM itself can go wrong, leading to this code. However, harness and connector issues tend to be more common culprits.
Read more: 6 Easy Ways To Find What Transmission You Have [with Transmission Lookup Tool]
Fixing P1701: Step-by-Step Repair And Diagnosis
Now that we’ve uncovered the common causes behind the P1701 Nissan code, it’s time to roll up our sleeves and dive into the world of repairs.
An effective way to tackle the P1701 code is by examining the harnesses and connectors associated with the battery, ignition switch, and TCM. Look for damage, loose connections, or corrosion.
Let’s dive into the nitty-gritty details with our step-by-step procedure below.
Essential Tools And Parts
- Wire connectors
- Nissan ignition switch
- Multimeter
- Inspection mirror
- Electrical tape
- Pullers
- Screwdriver
- Electrical cleaner
Step-by-step Procedure
Step 1: Use a multimeter to verify the TCM power source. Check the voltage at specific terminals of the TCM harness connector.
Step 2: Inspect the TCM ground circuit. Check the continuity between specific terminals of the TCM harness connector and ground.
Step 3: Confirm the TCM power circuit by measuring the voltage at specific terminals of the TCM harness connector.
Step 4: Examine the harnesses between the TCM and IPDM E/R, as well as between the TCM and the battery, ensuring continuity between specific terminals. If any damaged or faulty components are found, repair or replace them accordingly.
Step 5: Check the continuity between specific terminals of the TCM harness connector and ground. Then, inspect and replace faulty components, such as fuses or the ignition switch, as needed.
Step 6: Detect malfunctioning items by inspecting the TCM connector pin terminals for damage or loose connections with the harness connector. Repair or replace any faulty or damaged components/parts found during this inspection.
Please note that specific Nissan models may have additional information or variations related to this code. To ensure accuracy, refer to your vehicle’s service manual and consult relevant Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). Those documents might have specific directions on checking fuses, battery voltage, terminal locations, and other relevant details.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs For Fixing P1701 Code In Nissan Vehicles
The above procedure requires an intermediate level of automotive repair knowledge and experience. It involves performing various electrical tests, checking harnesses, and potentially replacing damaged components. If you have experience in automotive diagnostics and repair, you can confidently tackle this repair.
However, if you are unsure or lack experience, seeking professional assistance’s always a good idea. This approach can help you avoid unnecessary expenses resulting from inaccurate diagnoses or improper repairs.
To give you a general idea of the estimated repair costs for the P1701 code in Nissan vehicles, here’s a breakdown of the main repair tasks and their associated costs:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Diagnostic Fee | $80 – $150 |
| Wiring Harness Repair/Replacement | $200 – $500 |
| Fuse Replacement | $10 – $50 |
| Ignition Switch Replacement | $100 – $300 |
| TCM Replacement | $400 – $700 |
| Professional Labor (per hour) | $80 – $150 |
Please keep in mind that these are rough estimates, and the actual costs can vary depending on factors such as your specific Nissan model, labor rates in your area, and the extent of the repair required.
It’s always recommended to consult with local repair shops or dealerships to get more accurate and tailored cost estimates for your specific situation.
P1701 Nissan Infographic

Final Thoughts
In a nutshell, promptly addressing the P1701 Nissan code is crucial to avoid potential transmission troubles.
Get to grips with its meaning, symptoms, and causes to make savvy decisions about the repairs needed. Remember to arm yourself with the right tools, follow the steps carefully, and don’t hesitate to seek pro help if required.
Never underestimate the importance of nipping that P1701 code in the bud to keep your Nissan purring like a well-oiled machine.
Got any questions or tales to share?
Drop a comment or pass on this article to fellow gearheads who might find it handy.
Let’s keep the conversation rolling and lend a hand on our automotive adventures!
Reference Sources
- Nialtima, P1701 Transmission Control Module (Power Supply)
- JustAnswer, Code P1701: No Symptoms or Transmission Issues
- 2CarPros, Transmission Codes
P1715 Nissan Code Solved: Tips For Dealing With Transmission Issues
P1715 Nissan Code Solved: Tips For Dealing With Transmission Issues
Welcome, fellow Nissan owners and avid mechanics!
Today, we’re here to uncover the secrets of a common trouble code that might have left you scratching your head: P1715 Nissan.
If you’ve encountered this code during a scan or noticed unusual behavior in your Nissan vehicle, fear not!
In this blog post, we’ll explore P1715: its meaning, severity, symptoms, causes, as well as diagnosis and repair process. Gain a clear understanding of this code and learn how to address it in your Nissan vehicle.
Let’s dive in!
P1715 Nissan: A Quick Overview
Here’s a quick overview of the P1715 code for Nissan. Check it out!
- Definition: Input Speed Sensor (Primary Speed Sensor/TCM Output)
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Advanced
- Continue To Drive?: Yes (at a safe speed)
- Estimated Repair Cost: $100 – $500
Understanding The P1715 Code In Nissan Vehicles
The P1715 code is a diagnostic trouble code commonly encountered in Nissan vehicles. It relates to issues of the input speed sensor and its circuit, which are crucial components of the transmission system. Let’s explore what this code means and how it can be triggered.
In Nissan vehicles, the input speed sensor monitors how fast the transmission’s input shaft rotates. It provides essential information to the transmission control module (TCM) about the transmission’s input speed. This data helps the TCM make decisions regarding gear shifting, torque converter lock-up, and overall transmission performance.
(Credit: nirogue.com)
When the input speed sensor circuit malfunctions or fails to provide accurate data, it triggers the P1715 code. It’s worth noting that the P1715 code is commonly found in Nissan models including the Nissan Rogue, Sentra, Altima, Murano, Pathfinder, and Versa.
Additionally, the P1715 code is often associated with other codes like P1778, which indicates critical CVT failure, and P0776, which relates to pressure control solenoid performance. It’s important to address the P1715 code promptly to prevent further damage to the transmission system.
Oh No! How Serious Is The P1715 Code?
The P1715 code has a moderate severity level. While it’s not considered a critical issue that requires immediate action, it shouldn’t be ignored either. Driving with the P1715 code present may lead to irregular shifting, decreased fuel efficiency, and potential transmission issues.
Always prioritize safety and drive at a safe speed. It’s highly recommended to address the code as soon as possible to prevent further damage to the transmission system.
Even though you can still drive with the code, you should have a qualified mechanic inspect your vehicle at your earliest convenience. They will diagnose the underlying cause and perform the necessary repairs to ensure your car continues to perform well and stays reliable for the long haul.
Remember, timely attention to the P1715 code can help avoid more severe transmission problems down the road.
Read more: P1701 Nissan Code: Transmission Control Module (Power Supply)
Common Symptoms Of The P1715 Code
When the P1715 code is triggered in a Nissan vehicle, it can manifest through various symptoms, including:
- Illuminated Check Engine Light
- Irregular shifting or hesitation during gear changes
- Harsh or delayed engagement when shifting gears
- Decreased fuel efficiency
- Transmission slipping or jerking
If the P1715 code is accompanied by the P0776 code, you may also experience the following:
- Hesitation and/or reduced power
If the P1715 code is together with the P1778 code, you may observe the following:
- Check Engine Light, AWD light, and ABS light all coming on
- Codes being triggered only when the transmission is cold and disappearing when warm
Causes Of The P1715 Code In Nissan Vehicles
The P1715 code in Nissan vehicles can be caused by several factors, such as:
- Open or shorted CAN communication line
- Open or shorted input speed sensor circuit
- Faulty input speed sensor
- TCM malfunction
Let’s Get Technical: Diagnose & Resolve P1715 Nissan Code
When dealing with the P1715 code in Nissan vehicles, the main solution typically involves the following steps:
Diagnostic Tools And Essential Parts
- OBD-II scanner
- Mechanical CVT repair tools
- Replacement input speed sensor (if necessary)
- TCM reprogramming or replacement tools (if necessary)
Step-by-Step Guide To Repairing The P1715 Nissan Code
- Use an OBD-II scanner or code reader to retrieve and note any additional codes present in the system.
- Inspect the wiring and connectors related to the input speed sensor circuit for any damage, loose connections, or corrosion.
- Test the input speed sensor using a multimeter to ensure it is functioning properly.
- If the sensor is faulty, replace it with a new one, ensuring proper alignment and positioning.
- Perform mechanical CVT repair if needed, addressing any internal issues or failures. This may involve:
- Replacing the CVT belt or chain if worn or damaged
- Repairing or replacing pulleys or cones if they are faulty
- Repairing or replacing the valve body if it is damaged
- Replacing faulty bearings within the CVT
- If the P1715 code persists, consider reprogramming or replacing the TCM to ensure proper communication and functionality.
Notes: It is crucial to follow manufacturer guidelines and consult service manuals for specific procedures and specifications during CVT repair and TCM replacement.
DIY Repair Level And Estimated Costs
The diagnostics and repairs for the P1715 code, particularly mechanical CVT repair, and TCM replacement, often require advanced automotive knowledge and specialized tools. You should consult with an experienced mechanic or authorized dealership for these repairs.
Costs for repairing the P1715 Nissan code can vary significantly depending on the extent of the issue, the specific vehicle model, and labor rates. It is advisable to consult with a professional for an accurate cost estimate. Below is a breakdown:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Wiring and Connectors Repair/Replacement | $100 – $500 |
| Input Speed Sensor Replacement | $100 – $300 |
| Mechanical CVT Repair | $500 – $1500 |
| TCM Reprogramming | $100 – $300 |
| TCM Replacement | $300 – $800 |
P1715 Nissan Infographic

Final Thoughts
In a nutshell, fixing the P1715 Nissan code requires a careful approach and targeted repairs. But don’t worry! You don’t have to face it alone.
Reach out to a skilled mechanic or authorized dealership who can guide you through the process with expertise and a friendly smile.
If you found this information helpful, why not spread the love?
Share it with your friends and family who might be dealing with the same issue.
And hey, we’re all ears for your thoughts and experiences too! Drop us a comment below, and let’s keep the conversation rolling.
Reference Sources
- Nissan North America, 2018, Technical Service Bulletin AT18-009.
- Nissan Rogue, Service Manual: P1715 input speed sensor.
- Nissan Sentra, Service Manual: P1715 input speed sensor.
- Nissan Altima, Service Manual: P1715 input speed sensor.
- JustAnswer, Code P1715 Question – Answered by Nissan Mechanic Ron.
