Did you know the now common On-Board Diagnostics systems were founded in the 1960s? The OBD, short for the On-Board Diagnostics system, was established to regulate vehicle emissions and facilitate the mass adoption of electronically controlled fuel injection systems.
The simple idea behind OBD functions is the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) or PCM (Powertrain Control Module). The PCM is a relatively small electronic device in a vehicle that consists of a microcontroller and a software system. This system enables the PCM to control a couple of electrical systems in the car and store important information from those systems.
The OBD serves as an interface that gives you access to the PCM data.
So, what more do you need to know about the OBD systems?

What is OBD (On-Board Diagnostics)?
On-Board Diagnostics is a vehicle system that enables external electronics to connect to the car’s computer system for diagnostic purposes. Software interfaces such as the OBD have become common since the computerization of vehicles makes it easier to identify issues using a simple tool like an OBD scan tool.
Vehicles are filled with several electronic sensors such as the Mass Air Flow Sensor (MAF), oxygen sensors, and engine speed sensors, just to mention a few. The Powertrain Control Module receives data and information from these electronic sensors to regulate and control vehicle systems.
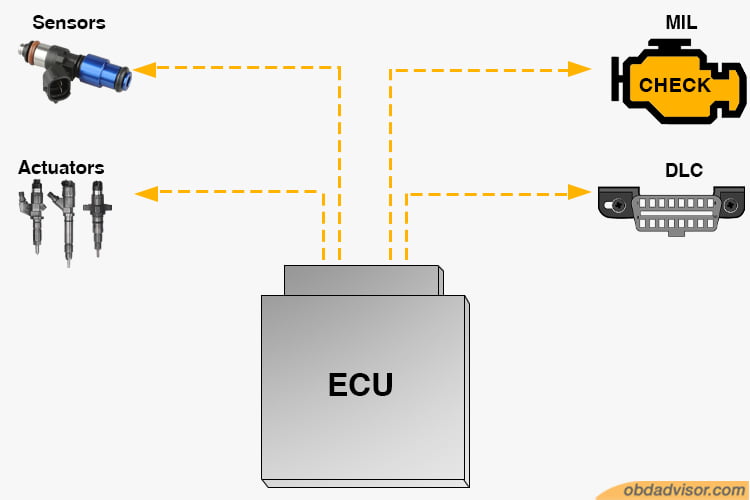
The process enables your vehicle to run at optimal performance without any manual control. Several electronic systems help the ECU perform various functions like power steering, airbag deployment, engine performance, and emissions control. The primary purpose of the system is to manage vehicle health and driving.
OBD movement timelines
The history of the Onboard diagnostics systems is a long one that is covered with multiple revisions and updates to the system. Since its foundation, the OBD system has acted as the standard protocol for most light-duty vehicles like cars, trucks, vans, and SUVs to help get vehicle diagnostic information.
For example, vehicles use engine speed sensors to control the transmission in real-time accurately. The immediate data from the sensors is used to calculate the optimal gear ratio. The Powertrain Control Module then uses this calculated data and controls the transmission to provide the best velocity and power to the wheels.
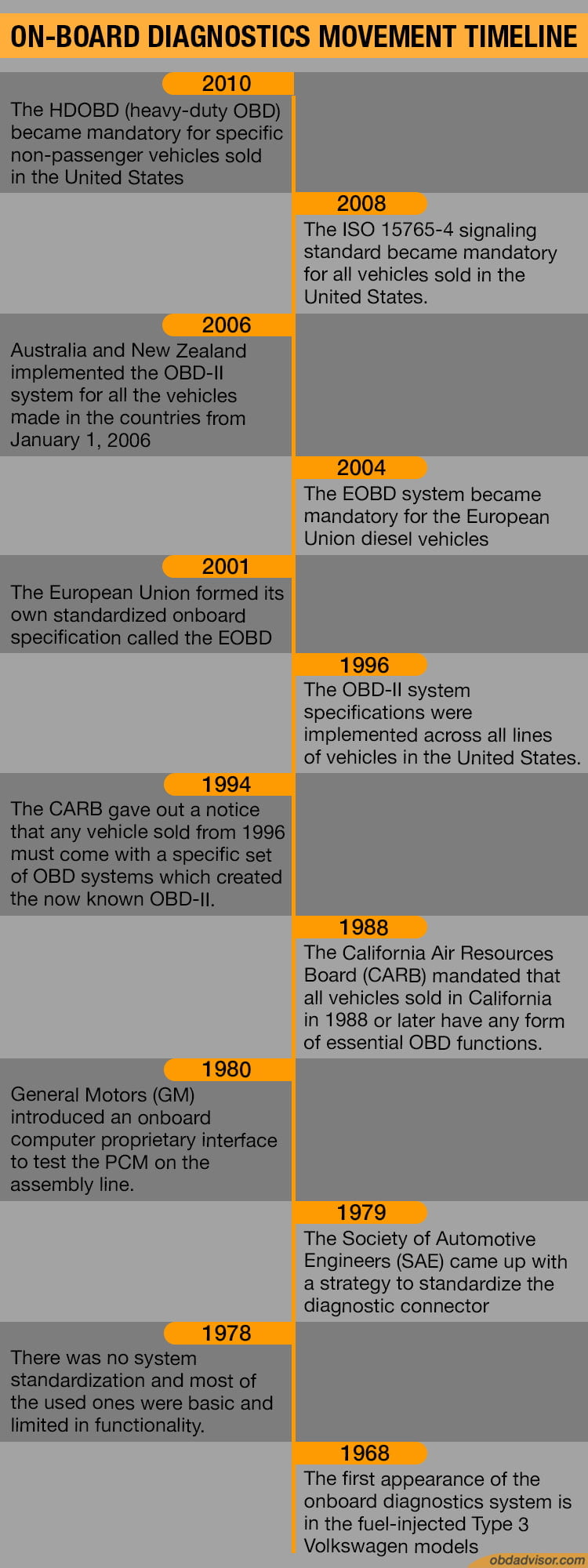
2001 – 2010:
The European Union formed their own standardized onboard specification called the EOBD in 2001. This system became mandatory for all petrol vehicles in the EU. The EOBD system became mandatory for the European Union diesel vehicles in 2004.
Australia and New Zealand implemented the OBD-II system for all the vehicles made in the countries from January 1, 2006.
In 2008, the ISO 15765-4 signaling standard became mandatory for all vehicles sold in the United States.
In 2010, the HDOBD (heavy-duty OBD) became mandatory for specific non-passenger vehicles sold in the United States.
1988- 1996:
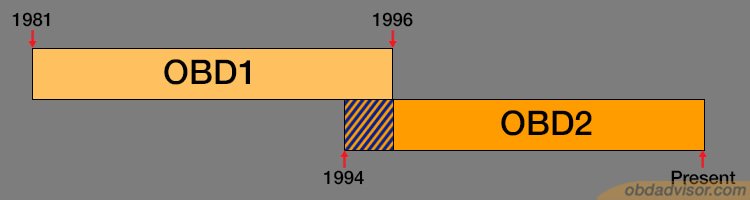
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) mandated that all vehicles sold in California in 1988 or later have any form of essential OBD functions. However, the diagnostic connector, position of the connector, and data protocol were not standardized. This was when the OBD-I standards arose, but they were not called so till the introduction of OBD-II.
It was also in 1988 that the SAE again recommended the standardization of the diagnostic connector and test signals. The California state backed up the SAE, and in 1994, the CARB gave out a notice that any vehicle sold from 1996 must come with a specific set of OBD systems which created the now known OBD-II.
The reason for this radical move was to have a state-wide emissions testing program. In 1996, the OBD-II system specifications were implemented across all lines of vehicles in the United States. According to the SAE guidelines, all the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and connectors were standardized across the board.
1979 – 1987:
In 1979, the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) came up with a strategy to standardize the diagnostic connector. They also recommended the standardization of diagnostic test signals since onboard computers were gaining popularity in many car-manufacturing companies like Volkswagen and Datsun.
In 1980, General Motors (GM) introduced an onboard computer proprietary interface to test the PCM on the assembly line. The interface was called the ALDL (Assembly Line Diagnostic Link), and it monitored very few vehicle systems. This system was never used outside the factory, and it became fully implemented in all of the United States GM factories by 1981.
1968 – 1978:
The first appearance of the onboard diagnostics system is in the fuel-injected Type 3 Volkswagen models in 1968. The system optimized the fuel injection process, which led to several companies adopting it for the same reasons. There was no system standardization by 1978, and most of the used ones were basic and limited in functionality.
OBD Standards in different areas
As you can tell, the OBD standards did not begin the same way in all the countries in the world. Different regions adopted a variation of the system even though the basic principles were similar.
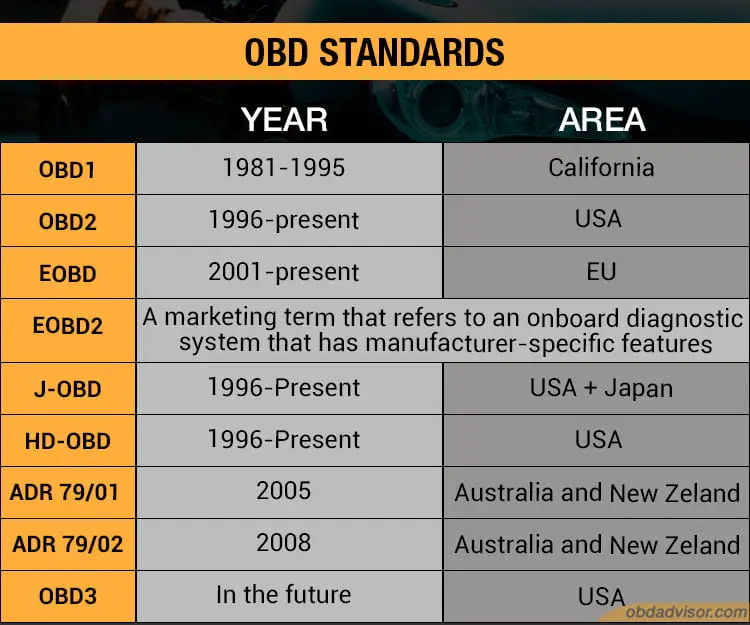
OBD1
The OBD1 was the first alteration of the now-used OBD2 system. It did not have a standardized diagnostic link connector, DLC location, Diagnostic Trouble Codes definitions, or any standard procedure for reading the vehicles’ trouble codes. Every manufacturer had its versions of these OBD1 systems and their functions.
This means that the OBD1 systems were used differently to show any vehicle faults. Most OBD1 compliant vehicles read DTCs using the blinking patterns of the CEL (Check Engine Light). This is done by connecting specific pins of the diagnostic link connector. Once they are connected, the Check Engine Light will blink to pinpoint the exact trouble code.
Other models like Honda used a series of LEDs that would light up in a given sequence to show the stored diagnostic trouble codes.
OBD2
The OBD2 system was a huge leap in the car industry since it covered all the bases when it came to onboard diagnostics. As per the regulations, the diagnostic connector was standardized in all vehicles, and so were the protocols.
Moreover, the system ensured that all candidate vehicles had a set of parameters that had to be monitored, such as the emissions. Another huge advantage of the OBD2 system is the connector which has a pin that provides power to the OBD2 scan tool so that it doesn’t have to use external power for diagnostics.
The Diagnostic Trouble Codes are standard in the OBD2 system providing a way to scan multiple vehicle models using the same OBD2 scan tool. The OBD2 system uses a 4-digit DTC format, unlike OBD1, which uses the 2-digit or 3-digit DTC format.
The 4-digit DTCs are preceded by a letter; either a P, B, C, or U. P denotes a DTC for the engine and powertrain, B denotes a DTC for the body, C for the chassis, and U represents the DTC for network systems.
EOBD
EOBD (European On-Board Diagnostics) in the European Union is comparable to the American OBD2 with a few differences. The EOBD was applied to passenger cars that fell into the M1 category, which entails cars with less than eight passenger seats and a Gross Vehicle Weight rating of 2500 kg or less.
Even though the petrol engine vehicles started EOBD standardization in 2001, new models had to implement the systems by January 1, 2000. The same went for the diesel engine vehicles, which had their new models adopt the EOBD standards as of January 1, 2003 – a year ahead of other existing models.
EOBD has a similar SAE J1962 diagnostic connector to the OBD2 system. The test signal protocols are also the same as the OBD2 system. The EOBD also uses the same 4-digit plus a letter DTC format. The format starts with a letter (P, B, C, or U) followed by the first digit, which denotes the EOBD standard, and ends with the subsystem in which the fault lies.
The first digit can be 0,1 or 2. 0 denotes the SAE OBD code (non-manufacturer specific). 1 and 2 represent the manufacturer’s own code. The last digits will indicate the subsystems like the fuel and metering systems denoted by 0 and 1. Each subsystem has its own specific digit combination to help pinpoint the fault.
EOBD2
You would think that the EOBD2 is an update to the EOBD system in the European Union, but that is not the case. The term EOBD2 is a marketing term that refers to an onboard diagnostics system that has manufacturer-specific features. These features are often advanced and aren’t part of the EOBD or the OBD standard specifications, which is to say that the E in EOBD2 stands for Enhanced.
J-OBD
J-OBD refers to onboard diagnostics that are implemented in Japanese vehicles. The J-OBD refers to a variant of the OBD2 system founded in the United States but later implemented in Japan to suit the market needs and demands. Examples of vehicles that have the J-OBD include Toyota, Honda, Daihatsu, Mitsubishi, Mazda, Nissan, Suzuki, and Subaru.
ADR 79/01 and ADR 79/02
ADR 79/01 and ADR 79/02 are Australian OBD standards with the same technical standards as the OBD2. The similarities include the same SAE J1962 diagnostic connector and the signal protocols. ADR stands for Australian Design Rules set as national standards in Australia to deal with vehicle safety, emissions, and anti-theft.
The ADR standards cover emissions, rider protections, lighting, structures, engine exhaust, braking, and other miscellaneous elements.
ADR 79/01 was specifically for Emission Control for Light Vehicles which began in 2005.
The standard applies to all M1 and M! vehicles with a Gross Vehicle Weight of 3500 or less. The cars also have to be registered from new and produced from 2006 for petrol engines and 2007 for diesel engines.
The ADR 79/02 was a supplementary standard that was added starting from 2008 to ensure tighter emission restrictions.
HD-OBD
HD – OBD (Heavy Duty OBD) refers to OBD2 standards for Heavy Duty vehicles with a gross vehicle weight of more than 14,000 pounds. The bar is applicable to diesel, petrol, alternate fuel, and hybrid engine vehicles. The standard applies to United States-based vehicles.
OBD3
OBD2 has been the standard since 1996 in many vehicles from the United States. It has remained the common standard throughout the world to date. OBD3 has not been implemented yet but talks about bringing it to California shortly, but this is all speculative.
One of the CARB’s implementations is to minimize the time delay between detecting emission malfunction by the OBD system and repairing the issue. This can be done by having roadside readers, satellites, or local station networks.
The idea is to have these stations monitor vehicles on the road, take the OBD system data, analyze it to show car faults, and then send it to a regulatory board (police or contractors). The regulatory board can then record the VIN and use it to monitor the condition of vehicles that roam the roads.
OBD port and OBD connector
OBD1 port and connector
The OBD1 port is usually located at the engine compartment near the fender by the battery. You cannot connect to the port wirelessly and will require a wired connection to be able to read the Diagnostic Trouble Codes. Moreover, the OBD1 offers limited functionalities, which means you won’t be able to identify as many errors as you can with an OBD2 port and connector.
There is only one manufacturer-specific OBD1 scanner for each vehicle. This means you cannot use a Volkswagen OBD1 scanner on a Ford OBD1 vehicle and vice versa. However, this problem can be solved by using an OBD2-to-OBD1 adapter. This adapter helps connect an OBD2 scanner to an OBD1 vehicle to read the DTCs.
Below is the OBD1 pinout on a pre-1995 GM vehicle F-body:
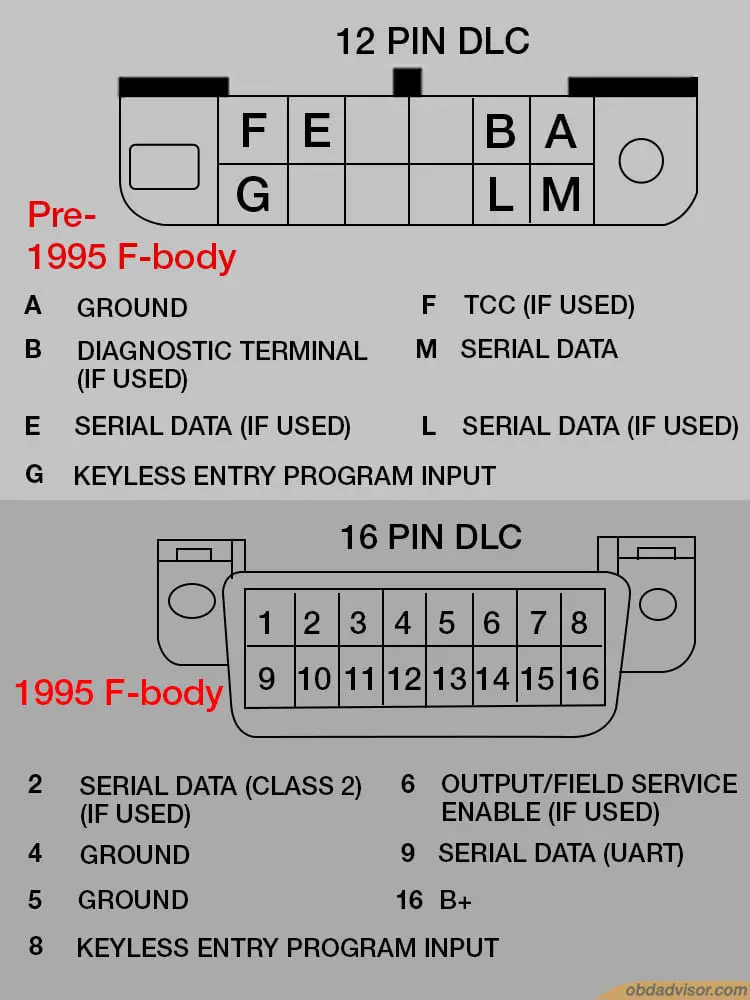
OBD2 port and connector
The beauty of the more advanced OBD2 system is that you do not have to use a wired connection like in the OBD1 system. Bluetooth-capable OBD2 scan tools connect to the onboard diagnostics wirelessly to provide a fast and seamless interface.
OBD2 port is usually found under the dashboard of your vehicle. It can also be located underneath the steering wheel. The OBD2 connector is legally required to be within 2 feet of the steering wheel regardless of the location. However, some manufacturers can get exempted so long as it is within reach of the driver.
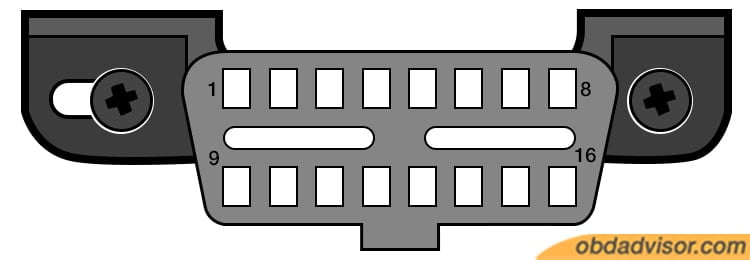
Moreover, the location of the OBD2 connector is based on what type of diagnostic link connector (DLC) it is. There are two types, namely Type A and Type B, as shown below. The difference is the connector design in the centerline: Type B has two partitions, whereas Type A has one, as seen in the images below.
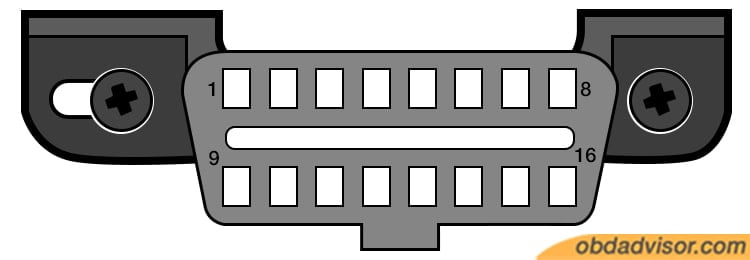
The location of the type A connector, according to SAE standards, is near the driver’s compartment, attached to the instrument panel, and easily accessible from the driver’s seat. It should also be located a1 foot beyond the car’s centerline.
The location of the Type B diagnostic link connector is in the driver or passenger compartment in a region bounded by the driver’s end of the instrument panel. It should also be located around 2.5 feet beyond a car’s centerline. It is connected to the instrument panel and is easily accessible from the driver’s seat.
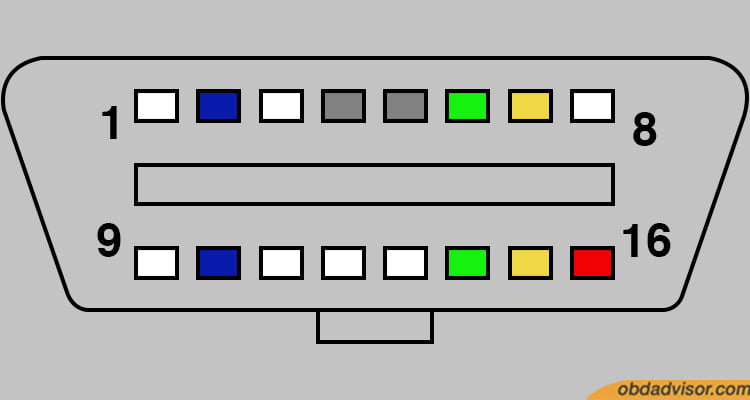
Type A and Type B diagnostic link connectors have 16 pins, as seen above. Pin numbers 1, 3, 8, 9, 11, 12, and 13 are manufacturer-specific and unnecessary for regular interfacing. These vendor-specific pins are assigned specific functions at the manufacturer’s discretion.
Pin number 2 is named the SAE J1850 Bus + and is the Bus positive pin of the protocol. The diagram below describes each pin number and its purpose:
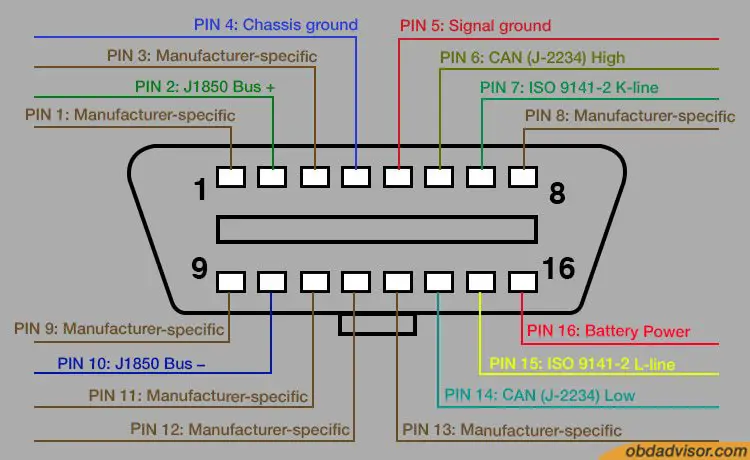
OBD2 Protocols
Were you wondering what OBD2 protocol is supported by your vehicle? Well, do not worry since it does not matter unless you plan to replace the OBD2 port. Any OBD2 standard car will use any compatible OBD2 scan tool regardless of the protocols it supports.
An OBD2 protocol defines how your vehicle can communicate through an OBD2 compliant system. You can refer to it as the accent of your car; this is why an OBD2 scan tool can communicate with several OBD2 vehicles with different protocols.
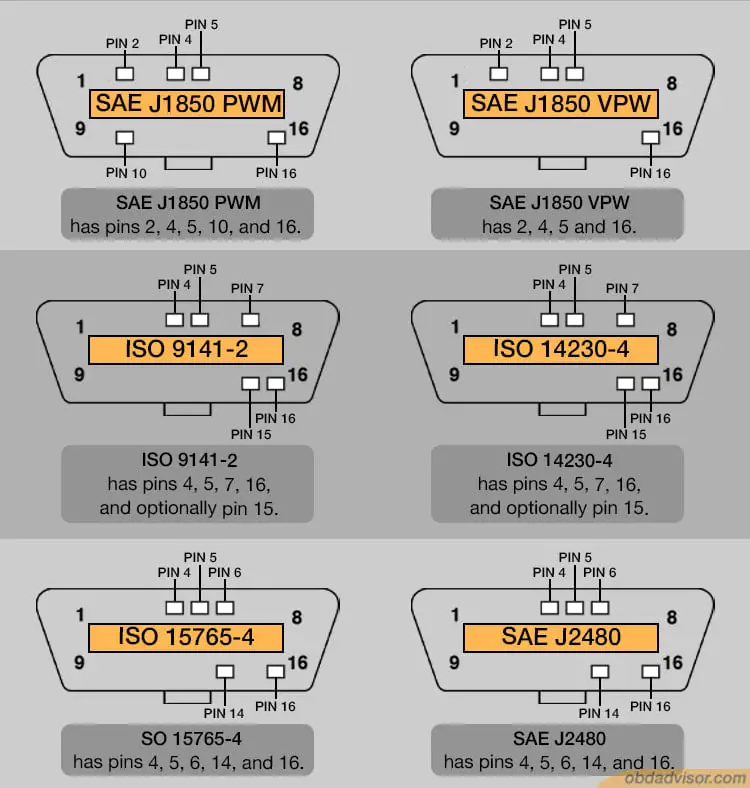
There are only five types of OBD2 protocols: SAE J1850 PWM, SAE J1850 VPW, ISO9141-2, ISO14230-4 (KWP2000), and ISO15765-4/SAE J2480. These protocols are determined by the type of present and functional pins in the diagnostic link connector. For example, newer vehicle models that use ISO14230-4 or ISO9141-2 protocols do not have pin 15, also called the L-Line.
The only pins that are essential for any of the protocols are pin 4 (Chassis Ground), pin 5 (Signal Ground), and pin 16 (Battery Positive). Below is a simplified table to show you which pins represent specific protocols.
To sum it up, the protocols are identified in the diagram below:
OBD2 Data and test modes
OBD-2 data
OBD-II standards were set to control emissions. This strategy limits the amount of data the OBD2 standards can access and manipulate. The standards are mainly from the SAE, but some come from ISO, so it is not OBD to find vehicles that can obtain more OBD2 data than others.
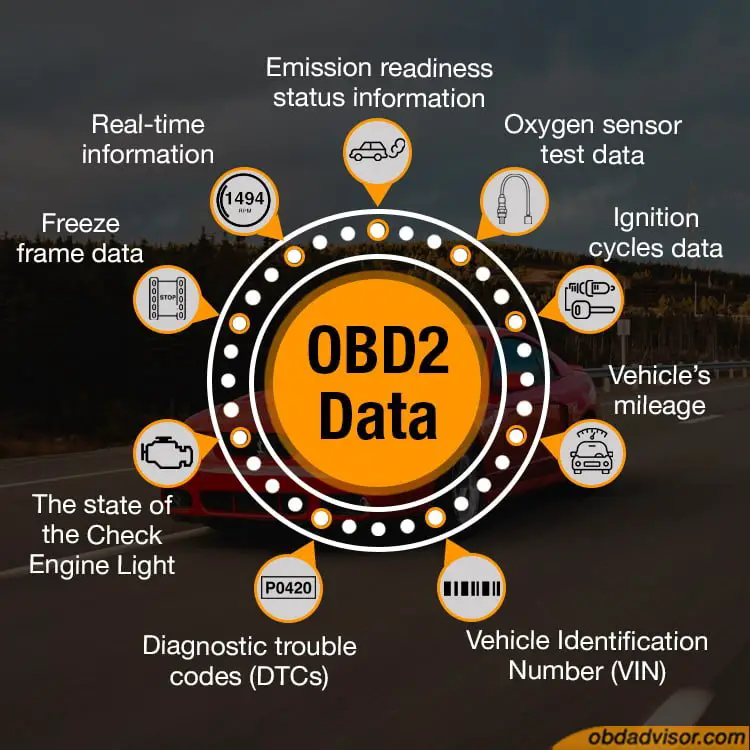
OBD2 systems can access these types of data:
- Emission readiness status information – the data helps monitor the condition of the emissions system. When an emissions issue arises, the vehicle will take note of this data and trigger the Service Engine Soon Light.
- Oxygen sensor test data – an oxygen sensor is mounted at the exhaust to monitor the amount of oxygen remaining unburnt in the exhaust system. This information is used to gauge the air and fuel mixture to see if it reduces safe emissions.
- Ignition cycles data helps monitor how air and fuel mixture is ignited in the combustion chamber to produce a driving force.
- The vehicle’s mileage since the Check Engine Light (CEL), Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) turned on.
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) – the Vin information is important data since it helps identify the vehicle’s unique features and best optimize it for safe emissions.
- Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are the fault codes that show the car owner or mechanic where an issue lies in the vehicle.
- The state of the Check Engine Light – needless to say, the state of the CEL is crucial since it is vital in identifying an issue in the car. Any damage to the CEL can lead to negligence of a serious fault.
- Freeze frame data – this is a snapshot of the data captured by an electrical sensor almost immediately after the sensor detected an issue.
- Real-time information such as speed, revolutions per minute, airflow rate, and pedal position.
OBD2 test modes
OBD2 test modes are various services that the Powertrain Control Module provides through the OBD standards. These test modes are used to access and manipulate OBD2 data like freeze frame data and diagnostic trouble codes.
Many car owners prefer the OBD2 system as a diagnostic system that can help them locate any fault in their vehicle. However, this is not the case since manufacturers tend to add additional functionalities to the OBD systems. OBD regulations only cover emissions-related components like the engine, drivetrain, and transmission.
This is where the OBD2 test modes come from. You will find specific OBD2 scan tools that can perform a lot of functions apart from these test modes; bear in mind that those are unique modes and not OBD standard features. Vehicle makers are permitted to add extra modes, and they can opt-out of a few OBD test modes if they so wish.
OBD2 test modes include:
- Request Live Data
- Request Freeze Frame data
- Request Oxygen Sensor test data
- Request VIN information
- Request stored diagnostic trouble codes
- Request pending diagnostic trouble codes
- Request permanent diagnostic trouble codes
- Reset/clear stored emissions-related data
- Request specific onboard systems test data
- Request Control of onboard systems
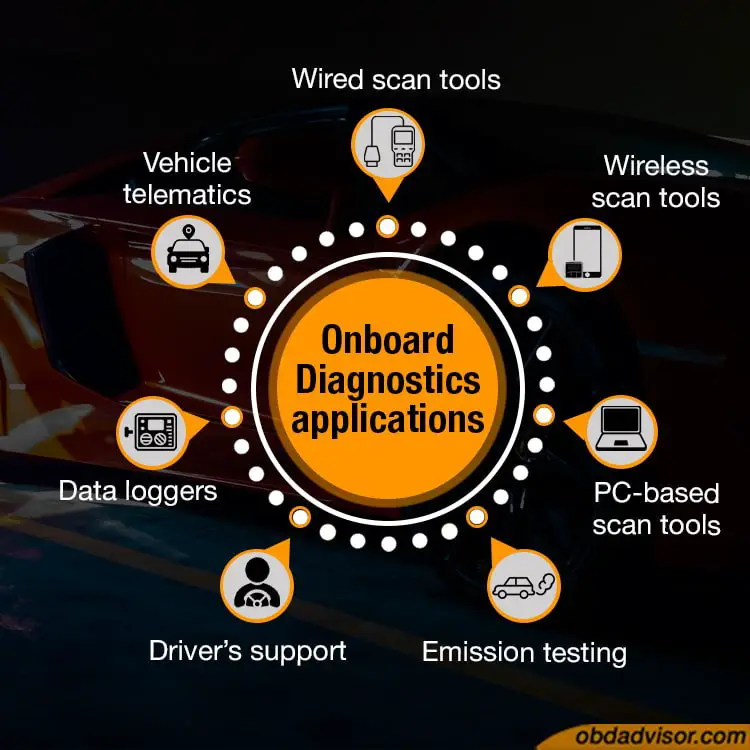
OBD applications
The adoption of OBD systems has led to the standardization of car systems and has improved vehicle emissions safety. Today, we have a lot of OBD applications that go beyond the vehicle itself. There are various manufacturers of OBD scan tools (wired, wireless, and PC-based), making it easier for anyone to diagnose a lit CEL.
OBD scan tools come in different types. They can either be wired or wireless. These scan tools can also be generic, enhanced, or factory scan tools. Generic OBD2 scanners (essentially code readers) are basic scanners that perform the bare minimum of the OBD test modes, including reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes. Upgraded versions of scan tools show code definitions.
Mechanic shops have both generic and enhanced (specialized) scan tools. Some may include OBD2 factory scanners, but these are specifically made for the OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) and often less needed. Advanced scan tools can read freeze frame data and permanent codes. Some enhanced versions take it up a notch and provide bidirectional testing and data stream.
Wired scan tools
Wired scan tools are the most popular OBD application. These tools have a scanner with a wired connection. The wired connection is connected to the diagnostic link connector in your vehicle. The wired scan tool does not use a battery since they draw power from the vehicle’s battery. However, some mechanics use an external power supply to be more cautious in a power interruption.
The most popular manufacturers of wired scan tools include Launch, Foxwell, Autophix, Innova, Autel, Bluedriver, FIXD, OBDLink, Veepeak, Actron, and Ancel.

The process of using these tools is easy:
- Take the connecting cable and attach it to the DLC on your vehicle. This link will connect the OBD2 scan tool to the onboard computer. Make sure to turn off the vehicle before connecting the scanner.
- Proceed to switch on the vehicle and wait for the scan tool to boot up. Most wired scanners will boot up automatically, but you can press the power button if it takes longer to turn on.
- Once it is on, you will be required to input some basic vehicle information like your vehicle model, engine, etc.
- The scan tool will then scan all the systems 3and provide the information on its screen. The information may include an error message or trouble codes. You can then proceed to record them or transfer them to your smartphone via Bluetooth.
- You can then turn off your car and unplug the OBD2 scan tool.
The recorded information can then be used to identify the root cause of the illuminated Check Engine Light. Vehicle manuals include some basic codes to help you locate the issue. More information can be found on the internet through the manufacturer’s website or other third-party sites.
Wireless scan tools
Wireless scan tools essentially work the same as wired scanners, but they instead connect to your vehicle via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. Wireless connection is more convenient than traditional wired connections because of flexibility and distance.
These scan tools are small adapters that you can connect to the diagnostic link connector. Once the adapter is connected, it will get power from the vehicle and turn on a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi signal. You can then connect to this signal using your smartphone or tablet.
There are smartphone applications that work with these adapters, and that is how you will be able to use the tool to scan your vehicle. The applications can either be basic or premium, with the premium one having most of the features.

Some users may prefer wired scan tools since all you need is entirely in one unit – there is no software to download (unless an update is required).
There are other high-end wireless scan tools like the $500 Autel MK808BT. This is a Bluetooth scan tool with a large touch screen display with many automotive capabilities. One may be tempted to call it a mechanic tablet since it can access the internet (even YouTube) through Wi-Fi.
The device connects to the DLC via a Bluetooth adapter that comes with the display console. Once the adapter has been powered on, you can join it to the display via Bluetooth. This device is versatile since you can look up information on the tablet as well as the internet to get a broader scope of a given issue.
PC-based scan tools
Computers can also be used as scan tools. PC-based scan tools are not only convenient but also advanced when compared to wired scan tools. To use your PC as a scan tool, you will need an OBD2 connection kit and OBD2 software.
Some of the PC-Based scanner kits are OHP FORScan, VINTscan, and OBDMONSTER ELM327 USB. A kit is a cable unit with two ends, one with a USB connector and an OBD connector.
PC Based scanners use USB adapters as well as Bluetooth adapters to connect with your PC; the examples include OBDLink MX+, OBDLink CX, OBDLink LX. So, there are not only USB adapters but also wireless ones.
It is easy to get started with PC-based scanners since all you need is to install the software on your PC and connect the kit to your PC and vehicle.

The software is rarely universal – not capable of running on Windows and Mac OS, Linux, iOS, or Android-based systems. Your choice of software will usually boil down to the operating system of your PC. Below is a list of PC-based OBD2 scanner software:
- Windows – AutoScan OBD2, Com Port Terminal, EngineCheck, ForScan, freediag, LapLogger, OBD 2007, OBD Auto Doctor, OBD2Spy, openOBD, PC Scan Tool, PCMSCAN, RealTerm, Scanclic, ScanMaster-ELM, ScanTool.net, ScanXL Pro, SynchroScan, Tera Term Pro, Terminal 1.9b, Termite, YouchScan, Toad Pro, and WinALDL.
- Mac OS X – EOBD_Facile, goSerial, Movi and Movi Pro, OBD Auto Doctor, OBD GPS Logger, LapLogger, and Storm.
- Linux – CuteCom, freediag, minicom, OBD Auto Doctor, OBD GPS Logger, OBD Logger, openOBD, Perl OBD2 Logger, picocom, pyOBD, pyOBD2, roflson.pyobd, ScanTool.net, and Serialclient.
- iOS – AutoProPlus, BT1, DashCommand, Engine Link, ezOBD, FORScan Lite, iOBD2, NOvaScan, OBD Car Doctor, and OBD Fusion.
- Android – Car Gauge Pro, Carys Scan, DashCommand, eCar PRO, EOBD Facile, ELM 327 Terminal, ELM Basic, FordSys Scan Free, Honda Database, Kwik OBD Terminal, Leaf Spy Pro, OBD Auto Doctor, OBD Car Doctor, OBD Trouble Code Lite, Piston, RaceChrono, ScanMaster for ELM327, Scanclic, ScanMyOpel Lite, Torque Lite, Torque Pro, and TouchScan.
Emission testing
Emissions tests help reduce the levels of harmful chemicals in the environment. This is a requirement in many countries and states across the world. The OBD2 emissions test is simple and straightforward.
To pass it, all you need to do is:
- Ensure your Check Engine Light is functional and your vehicle is OBD2 compliant.
- Ensure the Check Engine Light is off without intentionally ignoring it by switching it off.
- Successfully perform all the OBD2 system checks that are required by your vehicle.
Driver’s support

OBD systems are essential for passing emissions tests and for maintaining the condition of the car. The systems efficiently make sure your vehicle is in optimal condition by letting you know when there is an issue.
Moreover, the OBD system provides necessary information through the scan tools to keep you informed on properly optimizing the vehicle’s performance. You can also obtain VIN information quickly due to the OBD systems.
Data loggers
Data loggers are devices with sensors that can automatically record and monitor parameters in the vehicle’s environment over time. This is important because it helps in measuring, analyzing, and validating several environmental parameters. These parameters include temperature, RPM, speed, etc.
Data is logged in three easy steps:
- Set your OBD2 data logger with a set of OBD2 PIDS (codes used to request data from your vehicle).
- Connect the data logger to your vehicle using an OBD2 adapter and start to log.
- Once you are done logging, take out the Sd and decode the information using software alongside the data logger.
Vehicle telematics
This refers to the vehicle’s onboard communication capabilities and how it enables different applications to communicate with each other. Vehicle telematics helps in safety, navigation, security, and communication.
OBD helps collect data about the movements of your car. The captured data include speed, mileage, braking, and location.
OBD2 trouble codes
What is OBD2 code?
An OBD2 code is a diagnostic trouble code that the onboard diagnostic system in your car uses to indicate there is an issue. Your vehicle has a set of sensors and other electrical systems that will detect a problem and send the information to the onboard computer. The computer will then store a specific code to show that a particular component or system isn’t working within the acceptable limits.
Types of OBD2 codes
There are only two types of OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes: Type A and Type B. Type A is more severe and needs immediate attention than Type B OBD2 codes.
Type A:
- These codes are related to the emissions.
- The freeze frame data in this type is stored after one failed driving cycle.
- These codes will illuminate the Check Engine Light after one failed driving cycle.
Type B:
- These codes are also related to emissions.
- A pending code is set after one failed driving cycle.
- A pending code is cleared after one successful driving cycle.
- These codes will illuminate the Check Engine Light after two consecutive failed driving cycles.
- The freeze frame data in this type is stored after two consecutive failed driving cycles.
You may also find OBD codes being categorized as stored, pending, or permanent codes.
- Stored Codes – these are OBD codes that the computer has recorded and turn on the CEL to show a fault exists.
- Pending codes – these are codes that are in preparation but haven’t been stored.
- Permanent codes – these codes are similar to stored codes. However, unlike the stored codes, these ones cannot be erased with an OBD scan tool or by disconnecting the car’s battery.
The OBD codes follow a 4-digit plus letter format. The 4-digit DTCs are preceded by a letter; either a P, B, C, or U. P denotes a DTC for the powertrain, B denotes a DTC for the body, C for the chassis, and U represents the DTC for network systems. An example is P0123.
The first digit can either be a 0 for SAE (generic) codes or 1 for manufacturer-specific trouble codes. The third digit can be any number from 1 to 8, which mean:
- 1 – Fuel and Air metering (for example, MAF sensor). The generic codes include P0100 – P0199.
- 2 – Fuel and Air metering injector Circuit. Generic codes here include P0200 – P0299.
- 3 – The ignition system. The generic codes are P0300 – P0399.
- 4 – Auxiliary emissions controls. Generic codes include P0400 – P0499.
- 5 – Vehicle Speed Controls and Idle Control System. Generic codes include P0500- P0599.
- 6 – Computer Output Circuit. Generic codes include P0600 – P0699.
- 7 – Transmission. Generic codes include P0700 – P0799.
- 8 – Transmission. Generic codes include P0800 – P0899.
The fourth and fifth digits are two place trouble codes that range from 0 to 99, each denoting a specific error.
Summary
The onboard diagnostic system has changed how we operate our vehicles for decades. One may argue that it is one of the most revolutionary car components. Emissions have reduced gradually since the invention of OBD2 standards, and fixing vehicle issues has never been easier because of the scan tools.