P0151 Code: Understanding O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
Welcome, fellow car enthusiasts! Today, we explore a common trouble code in automotive diagnostics that can be puzzling: P0151.
If you’ve ever seen the check engine light illuminate, connected a scanner, and wondered about the meaning behind the P0151 code that has just appeared, you’ve come to the right place for answers. In this article, we’ll provide a comprehensive explanation of the P0151 code, which is defined as the O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1) code. We also cover its causes, severity, potential solutions, and estimated breakdown of repair costs.
So, let’s rev up!
P0151 Code: Quick Overview
Here is an overview of the P0151 code. Take a look!
- Definition: O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: No
- Estimated Repair Cost: $100 – $300
What Does The P0151 Code Mean?
The P0151 code indicates that the oxygen sensor Bank 2, Sensor 2 detects a voltage lower than the specified range. This sensor is typically located before the catalytic converter on the side of the engine with cylinder bank 2.
The oxygen sensor (O2/H2OS sensor) plays a crucial role in monitoring the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases. It sends voltage signals to the engine control module (ECM), providing feedback on the oxygen content. Based on this information, the ECM adjusts the fuel mixture to achieve optimal combustion and ensures the proper functioning of the emission control system.
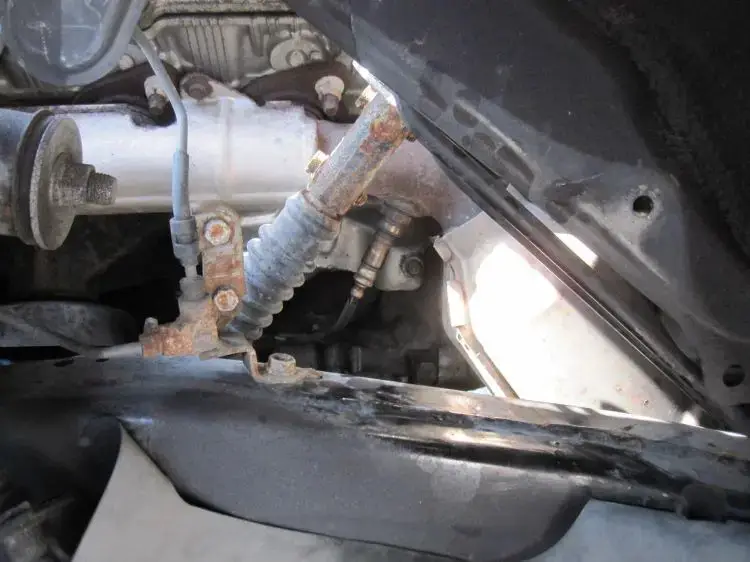

( Image credit: toyota-4runner.org)
It’s important to note that the specific definition of the P0151 code may vary depending on the vehicle manufacturer, although they generally have the same meaning. For instance, in GM vehicles, P0151 is defined as HO2S Circuit Low Voltage Bank 2 Sensor 1, whereas Ford describes this code as O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage Bank 2 Sensor 1.
Moreover, while it is commonly found in car brands like Ford (mostly F150) and Chevy, it can also occur in various other makes and models. Other O2 sensor-related codes includes P0136, P0137, and P0131.
Read more: P0136 – O2 Sensor Circuit
Is it Safe to Continue Driving With The Code P0151?
This P0151 code is typically categorized as a moderate-level issue. It can affect the engine’s fuel-air mixture and potentially decrease fuel efficiency and performance.
While the P0151 code may not cause immediate breakdown or safety concerns, it is crucial to address it promptly. Ignoring this code can lead to long-term engine damage and increased emissions. Additionally, prolonged exposure to a faulty air-fuel mixture can negatively impact other engine components, such as the catalytic converter.
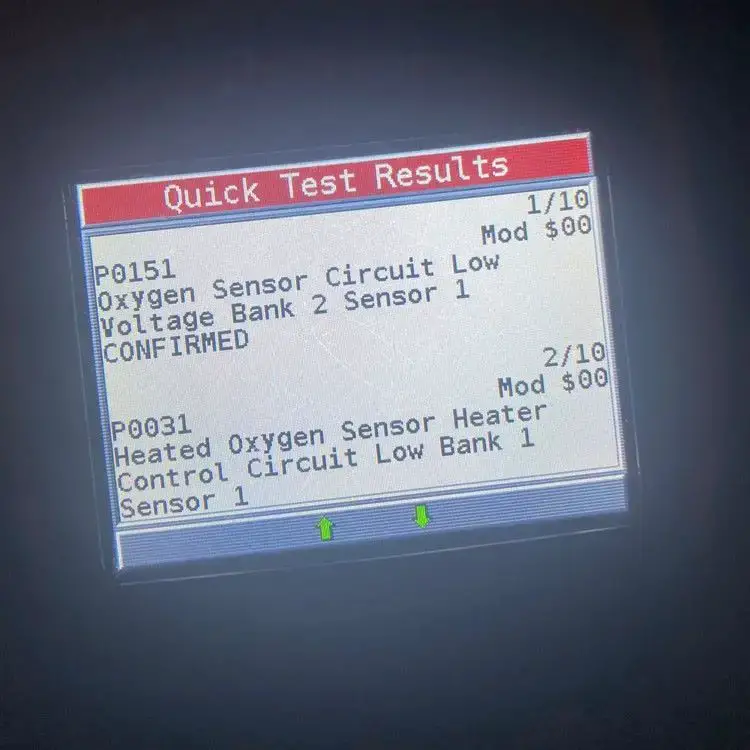
Therefore, it is advisable not to continue driving with the P0151 code present. Instead, it is recommended to have the issue diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible. By addressing the root cause and replacing faulty components, you can ensure optimal engine performance, fuel economy, and reduce the risk of further damage.
Signs Of P0151 Trouble Code
In most cases, the main symptom of the P0151 code is the Check Engine Light (CEL) illuminated on the vehicle’s dashboard, typically without any noticeable drivability issues. However, in certain instances, you may encounter additional symptoms, which can include:
- Decreased fuel efficiency
- Poor engine performance
- Rough idling or stalling
- Irregular engine surges or hesitation
- Increased emissions
Read more: P0137: O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
What Triggers the P0151 Code on Your Vehicle?
Several potential causes can trigger the P0151 code to appear:
- Faulty oxygen sensor (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
- Wiring issues, such as frayed or damaged wires
- Loose or corroded sensor connections
- Vacuum leaks in the intake manifold or exhaust system
How To Diagnose and Fix This Code
Now that we have a good understanding of the P0151 code, let’s dive into the diagnosis and repair process. In this section, we’ll cover the essential tools and parts needed, provide a step-by-step procedure, and discuss the level of DIY repair along with estimated costs.
Essential Tools and Parts
- OBD-II scanner
- Multimeter
- Oxygen sensor socket or wrench
- Wire connectors
- Electrical tape
- Replacement oxygen sensor (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
- Wiring harness (if necessary)
Step-by-Step Procedure
- Use a compatible OBD-II scanner or diagnostic tool to retrieve the trouble codes from the vehicle’s onboard computer.
- Perform a thorough visual inspection of the O2 sensor and its wiring for any signs of damage, loose connections, or corrosion. Clean/repair if necessary.
- Use a multimeter to measure the voltage output of the O2 sensor and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications. Repair if the sensor is malfunctioning.
- Inspect the exhaust system for any leaks, blockages, or damage that could affect the O2 sensor’s readings. Repair or replace any faulty components as needed.
- After performing the necessary repairs and inspections, clear codes using the OBD-II scanner and test drive.
Note: It’s recommended to consult the specific repair manual for your vehicle model for detailed instructions tailored to your car’s configuration.
DIY Repair Level and Estimated Costs
The DIY repair level for diagnosing and replacing the oxygen sensor associated with the P0151 code is moderate. While it can be done by experienced DIYers, if you’re unsure or uncomfortable with the process, it’s best to seek the assistance of a professional mechanic.
Below is a repair estimate costs table related to resolving the P0151 code:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Replacement Oxygen Sensor | $100 – $300 |
| Wiring Repair | $50 – $100 |
Please note that these estimated costs are general ranges and can vary depending on the vehicle make and model, location, and the specific parts required. It’s always recommended to consult with a trusted mechanic or service center to get accurate cost estimates tailored to your specific situation.
Read more: P0131 – O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
Final Thoughts
You’ve now gained valuable insights into the P0151 code and its implications. With this knowledge, you can confidently diagnose and address the O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1) issue. Remember, timely action is key to maintaining optimal engine performance and reducing potential long-term damage.
If you found this article helpful, don’t keep it to yourself! Share it with other car enthusiasts who may be facing similar challenges. We’d love to hear about your experiences or any additional tips and tricks you’ve discovered along the way. Feel free to leave a comment below.
Additionally, don’t forget to take a look at our OBD Code List Generator to find specific code lists, or use our OBD code lookup tool for instant reference.
Safe travels, and keep your cars running smoothly!
Reference:
- ProDemand, P0151, Replaced Oxygen Sensor (B2-S1).
- Chilton Library, DTC P0151.
- Wikipedia, Exhaust system.
