P0120: Throttle Position Sensor/Switch (TPS) A Circuit Malfunction
Is your scanner showing P0120?
No worries. We'll show you what it means and how to deal with it.
P0120: Throttle Position Sensor/Switch (TPS) A Circuit Malfunction
OVERVIEWWhat Does The P0120 Code Mean?
The TPS (Throttle Position Sensor) is a potentiometer that is mounted to the throttle body. It detects the throttle blade angle. As the throttle blade moves, the TPS sends a signal to the PCM (Powertrain Control Module). Usually a three wire sensor: A 5 volt reference from the PCM to the TPS, a ground from the PCM to the TPS, and a signal return from the TPS to the PCM.
The TPS sends the throttle position information back to the PCM on this signal wire. When the throttle is closed the signal is near .45 volts. At WOT (Wide Open Throttle) the TPS signal voltage will approach a full 5 volts. When the PCM sees a voltage that is outside of normal operating range, P0120 will set.
NOTE: The PCM knows that any large change in throttle position means a corresponding change in manifold pressure (MAP). On some models the PCM will monitor MAP and TPS operation for comparison.
Meaning that if the PCM sees a large percentage change in throttle position, it expects to see a corresponding change in manifold pressure and vice versa. If it doesn’t see this comparative change, P0120 may set. This doesn’t apply to all models.
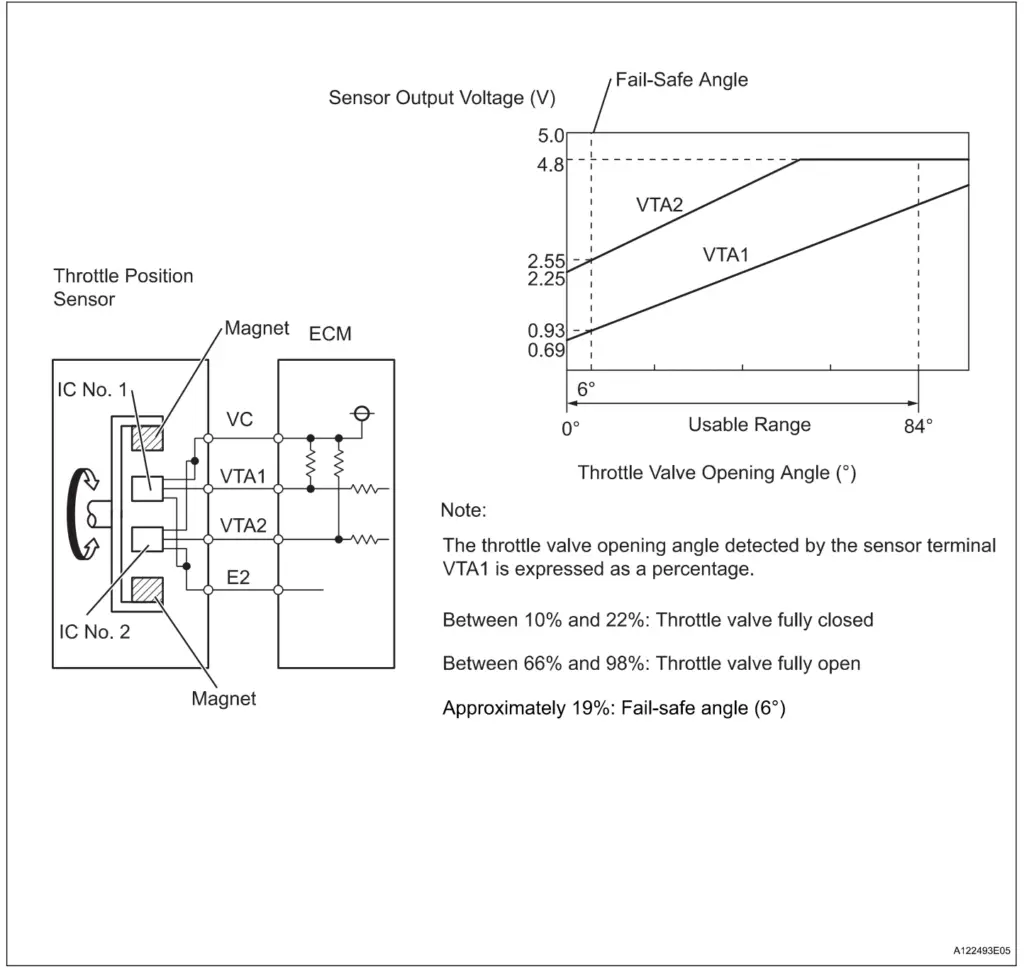
P0120 wiring diagram
What Are The Symptoms Of The P0120 Code?
Potential symptoms include:
- MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp) illumination
- Misfiring at idle or at highway speed
- Poor idle quality
- Possibly won’t idle
- Possibly starts and stalls
What Are The Potential Causes Of The P0120 Code?
Potential causes of the P0120 code include:
- Sticking throttle return spring
- MAP or TPS connector corrosion
- Misrouted harness causing chafing
- Bad TPS
- Bad PCM
How Can You Fix The P0120 Code?
If you have access to a scan tool, with KOEO (Key on engine off) observe the TPS voltage. With throttle closed, voltage should be about .45 volts. It should gradually sweep upwards to approximately 4.5 to 5 volts as you depress the throttle. Sometimes only a scope can capture an intermittent glitch in the TPS signal voltage. If you notice a glitch in the TPS sweep voltage, replace the TPS.
NOTE: Some TPS sensors require fine adjustment. If you aren’t comfortable with using a DVOM (Digital Volt Ohm meter) to adjust the new TPS, then it’s best to take the vehicle to a shop. If the voltage is not .45 volts (+or- .3 volts or so) with the throttle closed or if the reading is “stuck” then unplug the TPS connector. With KOEO check for 5 volts reference voltage present at the connector and a good ground.
You can check the signal circuit for continuity by jumping a fused wire between the ground circuit of the TPS connector and the signal circuit. If the TPS reading on the scan tool now reads zero, then replace the TPS. However if that doesn’t change the reading to zero, then check for an open or a short on the signal wire and if none is found, suspect a bad PCM. If manipulating the TPS wiring harness causes any change in idle, then suspect bad TPS.
Other TPS sensor and circuit related DTCs: P0121, P0122, P0123, P0124
Recommended Parts
Below are some recommended auto parts to help you address the trouble code affecting your vehicle and get it running smoothly again:
Note: During the purchasing process, please check carefully whether the part you want to buy fits your car!